|
|
| (42 intermediate revisions by 9 users not shown) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| − | {{otheruses}} | + | {{Bird id |
| − | {{Taxobox
| |
| − | | color = pink
| |
| | | name = Golden Eagle | | | name = Golden Eagle |
| − | | status = LC | + | | latin_name = Aquila chrysaetos |
| − | | image = GoldenEagle1.jpg | + | | level = 4 |
| − | | image_width = 250px | + | | image_1 = GoldenEagle-Nova.jpg |
| − | | regnum = [[Animal]]ia | + | | caption_1 = Golden Eagle |
| − | | phylum = [[Chordate|Chordata]] | + | | image_2 = |
| − | | classis = [[Bird|Aves]] | + | | caption_2 = Adult Golden Eagle in flight |
| − | | ordo = [[Falconiformes]] | + | | image_3 = Golden eagle.jpg |
| − | | familia = [[Accipitridae]]
| + | | caption_3 = Adult and juvenile |
| − | | genus = ''[[Aquila (genus)|Aquila]]''
| + | | range_map = Aquila_chrysaetos_dis(Aiger).png |
| − | | species = '''''A. chrysaetos'''''
| |
| − | | binomial = ''Aquila chrysaetos''
| |
| − | | binomial_authority = [[Carolus Linnaeus|Linnaeus]], [[1758]] | |
| − | | range_map = Aquila_chrysaetos_dis(Aiger).PNG | |
| − | | range_map_width = 250px
| |
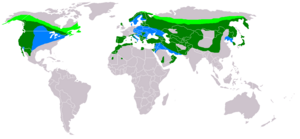
| | | range_map_caption = World distribution of the golden eagle<br>Light green = Nesting area <br> Blue = Wintering area <br> Dark green = All year distribution | | | range_map_caption = World distribution of the golden eagle<br>Light green = Nesting area <br> Blue = Wintering area <br> Dark green = All year distribution |
| − | }}
| + | | description = The '''Golden Eagle''' (''Aquila chrysaetos'') is one of the best known birds of prey in the Northern Hemisphere. |
| − | The '''Golden Eagle''' (''Aquila chrysaetos'') is one of the best known [[bird of prey|birds of prey]] in the Northern Hemisphere. Like all [[eagle]]s, it belongs to the family [[Accipitridae]]. | |
| | | | |
| − | There are six [[subspecies]] of Golden Eagle that differ slightly in size and [[plumage]]. They can be found in different parts of the world:
| + | A pair of Golden Eagles remains together for life. They build several eyries within their territory and use them alternately for several years. The nest consists of heavy tree branches, upholstered with grass. |
| | | | |
| − | * ''A. c. chrysaetos'': [[Eurasia]] except [[Iberian peninsula]], east to western [[Siberia]].
| + | Old eyries may be {{units|2 meters|6.6 ft}} in diameter and {{units|1 meter|3.3 ft}} in height, as the eagles enlarge their nests every year. If the eyrie is situated on a tree, supporting tree branches may break because of the weight of the nest. |
| − | * ''A. c. canadensis'': [[North America]].
| |
| − | * ''A. c. homeryi'': [[Iberian peninsula]] and [[North Africa]], east to [[Turkey]] and [[Iran]].
| |
| − | * ''A. c. japonica'': [[Japan]] and [[Korea]].
| |
| − | * ''A. c. daphanea'': From southern [[Kazakhstan]] east to [[Manchuria]] and south-west [[China]] including northern [[India]] and [[Pakistan]].
| |
| − | * ''A. c. kamtschatica'': Eastern Siberia, from the [[Altay Mountains|Altay]] to the [[Kamchatka Peninsula]].
| |
| − | Golden Eagles are renowned for their striking appearance and combining power with agility in flight.
| |
| − | | |
| − | ==Distribution==
| |
| − | [[Image:GoldenEagle2.jpg|thumb|left|Adult in flight]]
| |
| − | At one time, the Golden Eagle lived in temperate [[Europe]], North [[Asia]], [[North America]], North [[Africa]] and [[Japan]]. In most areas this bird is now a mountain-dweller, but in former centuries it also bred in the plains and the forests. In recent years it has started to breed in lowland areas again ([[Sweden]], [[Denmark]]).
| |
| − | | |
| − | There was a great decline in [[Central Europe]], and the Golden Eagle is now restricted to the higher central Appennine regions of Italy (the regional capital of [[Abruzzo]] is named after the Latin/Italian word for eagle, [[L'Aquila]]), and the [[Alps]]. In [[Britain]], there are about 420 pairs left in the [[Scottish highlands]], and between [[1969]] and [[2004]] they bred in the English [[Lake District]]. In [[North America]] the situation is not as dramatic, but there has still been a noticeable decline.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Efforts are being made to re-introduce the species in [[Glenveagh National Park]], [[County Donegal]], [[Ireland]], where they had been extinct since the early 20th Century. Forty-six birds have been released into the wild from 2001 to 2006, with at least three known female fatalities since then. It is intended to release a total of sixty birds, to ensure a viable population.
| |
| − | | |
| − | == Reproduction ==
| |
| − | [[Image:GoldenEagle3.jpg|thumb|right|Swooping down to land]]
| |
| − | | |
| − | A pair of Golden Eagles remains together for life. They build several [[eyrie]]s within their territory and use them alternately for several years. The nest consists of heavy tree branches, upholstered with grass.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Old eyries may be 2 metres (6.6 ft) in diameter and 1 metre (3.3 ft) in height, as the eagles enlarge their nests every year. If the eyrie is situated on a tree, supporting tree branches may break because of the weight of the nest. | |
| | | | |
| | The female lays two eggs between January and May (depending on the area). After 45 days the young hatch. They are entirely white and are fed for fifty days before they are able to make their first flight attempts and eat on their own. In most cases only the older chick, which takes most of the food, survives, while the younger one dies without leaving the eyrie. | | The female lays two eggs between January and May (depending on the area). After 45 days the young hatch. They are entirely white and are fed for fifty days before they are able to make their first flight attempts and eat on their own. In most cases only the older chick, which takes most of the food, survives, while the younger one dies without leaving the eyrie. |
| | | | |
| − | == Physical characteristics ==
| + | Adult Golden Eagles have an average length of {{units|75-85 cm|30-34"}}, a wingspan of {{units|150-210 cm|59-83"}}, and a weight of {{units|3-5 kg|7-11 lb}}. As in all birds of prey, the females are generally slightly larger than the males. |
| − | | |
| − | Adult Golden Eagles have an average length of 75-85 cm (30-34"), a wingspan of 150-210 cm (59-83"), and a weight of 3-5 kg (7-11 lb). As in all birds of prey, the females are generally slightly larger than the males. The largest golden eagle on record measured 41 inches (103cm) in length and weighed in an excess of 9kg (20.245lb). It was a female found in Spain. She also held the record for the tallest Golden eagle, standing 66 cm (26 inches){{Fact|date=February 2007}}. The largest North American Golden Eagle was captured for research in Grand Teton National Park in 2006, with a weight of 8.4kg (18.5lb){{Fact|date=February 2007}}. She was caught by researchers Bryan Bedrosian and Tom Rogers working for Beringia South in Kelly, WY. She was determined to be healthy and released. | |
| − | | |
| − | The plumage colours range from black-brown to dark brown, with a striking golden-buff crown and nape, which give the bird its name. The juveniles resemble the adults, but have a duller more mottled appearance. Also they have a white-banded tail and a white patch at the carpal joint, that gradually disappear with every [[moult]] until full adult plumage is reached in the fifth year.
| |
| − | | |
| − | == Hunting ==
| |
| − | | |
| − | Golden Eagles often have a division of labour while hunting: one partner drives the prey to its waiting partner. They have very good eyesight and can spot prey from a long distance. The talons are used for killing and carrying the prey, the beak is used only for eating. The talons of a Golden Eagle are thought to be more powerful than the hand and arm strength of any human being. Their prey includes [[marmot]]s, [[hare]]s and [[mouse|mice]], and sometimes [[bird]]s, [[marten]]s, [[fox]]es and young [[deer]]. Large [[mammal]]s like [[chamois]] or deer can only be taken if they are wounded or as sick. During winter months when prey is scarce, Golden Eagles scavenge on carrion to supplement their diet.
| |
| − | | |
| − | In [[Central Asia]], Golden Eagles sometimes are trained for [[falconry]]: in [[Kazakhstan]] there are still hunters using these eagles in order to catch deer and antelopes; in [[Kyrgyzstan]] hunters will use them to hunt [[foxes]] [http://www.avmv20.dsl.pipex.com/Photo%20Album/Kyrgyzstan/Ishpays%20eagle.htm]; and in [[Mongolia]] they are traditionally trained to hunt [[wolves]]. Some of the animals that Golden Eagles have been trained to kill can weigh 45 kg (100 lb){{Fact|date=February 2007}}.
| |
| − | | |
| − | ==Heraldry==
| |
| − | {{main|Eagle (heraldry)}}
| |
| − | The Golden Eagle is featured in the national coat of arms of [[Coat of arms of Mexico|Mexico]], [[Coat of arms of Germany|Germany]], [[Coat of arms of Egypt|Egypt]] [[Gallery of sovereign state coats of arms|many other countries]]
| |
| − | | |
| − | ==Gallery==
| |
| − | <gallery>
| |
| − | Image:GoldenEagle-Nova.jpg |American subspecies
| |
| − | Image:Hunting with Golden Eagles .jpg|Illustration of a Burkut of Eastern Turkestan (1870s)
| |
| − | Image:Steinadler Aquila chrysaetos.jpg|Golden eagle in a zoo, Germany
| |
| − | Image:Audubon GoldenEagle.jpg|[[John James Audubon|Audubon's]] illustration
| |
| − | </gallery>
| |
| − | | |
| − | ==References==<!-- Auk64:287 -->
| |
| − | <div class="references-small"><references/>
| |
| − | * {{IUCN2006|assessors=BirdLife International|year=2004|id=49452|title=Aquila chrysaetos|downloaded=12 May 2006}} Database entry includes justification for why this species is of least concern
| |
| − | * Cramp, S. and Simmons, KEL(eds) (1980) ''The Birds of the Western Palearctic'' Vol. II, Oxford University Press, ISBN 0-19-854099-x
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Average Identification tips
| |
| − | Length: 32 inches
| |
| − | Wingspan: 78 inches
| |
| − | Identification: A very large, big, winged broad tail hawk.
| |
| − | Lifespan:30 years
| |
| − | Short, dark, hooked beak, and a yellow cere (membranous covering of the base of the upper mandible of a bird).
| |
| − | Adult identification
| |
| − | Golden feathers on the back of the head
| |
| − | Plumage almost entirely brown.
| |
| − | Pale brown tail
| |
| − | Golden band on upper wing.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Young adult
| |
| − | About the same thing as a grown adult, but whiter wings. And whiter body
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Young kid
| |
| − | Almost entirely dark brown
| |
| − | White patches of fur
| |
| − | White tail
| |
| − | | |
| − | The Golden Eagle parent does care for its young. It usually has 2 eggs.
| |
| − | The baby is taught to fly and flies off at about 4 years of age.
| |
| − | The baby finds another young golden eagle -of the other gender- and stays with it for mostly the rest of their life.
| |
| − | Sometimes the young eagle will find an eagle with the same gender and will stay with them. And when they want to have eggs or have another life they find one with a different gender.
| |
| − | The Golden eagles like to Eat many foods. This includes groundhogs, marmots, foxes, skunk, cats, rabbits, grouse, ground, squirrels, crows, tortoise, snakes, meadowlarks, and pheasants.
| |
| − | How they get them is very easy to them. All they have to do is sneak up on their prey, and quickly dive down at about 30 miles per hour, which is easy for them.
| |
| − | It’s hunting territories extend up to 162 square feet.
| |
| − | It has strong feet with curved claws, so it makes it easy to kill the prey.
| |
| − | It soars over pray for a long time and dives down and kills prey on the ground.
| |
| − | Also they are day hunters
| |
| − | | |
| − | The Golden Eagles live in large nests in tall trees, mountains, tundras, grasslands and deserts in the east of North America.
| |
| − | They live in remote (opened) areas.
| |
| − | They usually die in the winter.
| |
| − | Some golden eagles live in their nest all year. Others may move around mostly because of the lack of food in the winter. They don’t need to move long distances because of their excellent hunting abilities.
| |
| − | | |
| − | The golden eagle is a vertebrate
| |
| − | Most birds are vertebrates.
| |
| − | Without a back bone the Golden eagle would not be able to do some of their special talents
| |
| − | | |
| − | The golden eagle has fur and feathers both dark brown.
| |
| − | Sometimes on it’s legs it is sort of red.
| |
| − | The golden eagle is named the golden eagle because on the back of it’s neck and many other small areas it is slightly gold.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | The golden Eagle has eggs.
| |
| − | It mostly lays two eggs.
| |
| − | Most birds lay eggs. Barely any birds have live birth so it’s very rare to find a bird with live birth
| |
| − | If they don’t lay 2 eggs they lay 1 or 3. they barely ever lay more than 3
| |
| − | A chick is only 3 ounces when it is born
| |
| − | | |
| − | Eagles are Warm blooded.
| |
| − | So are the rest of the birds.
| |
| − | Only Reptiles, insects and are cold blooded.
| |
| − | The golden Eagle’s body temperature is 112 degrees F.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Did you know A golden eagle’s wings are more powerful than an airplanes (Warning: just because it’s more powerful don’t have 100 people ride on it! )
| |
| − | Bald eagles and golden eagles have about the same characteristics.
| |
| − | Golden eagles are one of the best flyers in the world.
| |
| − | The golden eagle is about the size of a hawk!
| |
| − | They are uncommon now because people used kill them because they thought that they caused too much animal losses but then people found out that they where wrong and they stopped killing them.
| |
| − | Their nests are 8-10 feet across and 2-3 deep!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
| |
| − | It’s scientific name is the Aquila Chrysaetos which comes from the Latin word Aquila which means eagle in Englesh.
| |
| − | It’s lifespan is about 30 years
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | ==External links==
| |
| − | {{commons|Aquila chrysaetos}}
| |
| − | {{wikispecies|Aquila chrysaetos}}
| |
| − | *[http://www.birds.cornell.edu/AllAboutBirds/BirdGuide/Golden_Eagle.html Cornell Lab of Ornithology - Species Account]
| |
| − | *[http://www.sdakotabirds.com/species/golden_eagle_info.htm Golden Eagle Information and Photos]
| |
| − | *[http://www.mbr-pwrc.usgs.gov/id/framlst/i3490id.html Golden Eagle InfoCenter]
| |
| − | *ARKive - [http://www.arkive.org/species/ARK/birds/Aquila_chrysaetos/ images and movies of the golden eagle ''(Aquila chrysaetos)'']
| |
| − | *[http://www.animallaw.info/articles/ar22hstclq771.htm Access to Eagles and Eagle Parts: Environmental Protection v. Native American Free Exercise of Religion]
| |
| − | *[http://www.mongoliaphoto.com/index-81.html Photos Hunting with Golden Eagles]
| |
| − | *[http://www.rspb.org.uk/birds/guide/g/goldeneagle/index.asp RSPB A to Z of UK Birds]
| |
| − | *[http://www.aquilalp.net AQUILALP.NET - Monitoring Golden Eagles in the Eastern Alps]
| |
| − | *[http://www.pauldfrost.co.uk/goldeneagle.html Golden Eagle (Aquila chrysaetos) at www.pauldfrost.co.uk/]
| |
| − | *[http://www.natural-research.org Current Research on Golden Eagles]
| |
| − | *[http://www.birdwatching-bliss.com/bird-pictures.html Picture of Golden Eagle chick in nest]
| |
| − | *[http://www.tarsiger.com/index.php?p=pics&sp=find&lang=eng&order=nro,paiva%20DESC&species=11330 Picture sequence of Golden Eagle attaching fox]
| |
| | | | |
| − | [[Category:Aquila]]
| + | The plumage colors range from black-brown to dark brown, with a striking golden-buff crown and nape, which give the bird its name. The juveniles resemble the adults, but have a duller more mottled appearance. Also they have a white-banded tail and a white patch at the carpal joint, that gradually disappear with every moult until full adult plumage is reached in the fifth year. |
| − | [[Category:Birds of the United States]]
| |
| − | [[Category:Eagles]]
| |
| − | [[Category:Fauna of the Alps]]
| |
| − | [[Category:Fauna of Ireland]]
| |
| − | [[Category:Fauna of Norway]]
| |
| − | [[Category:Fauna of Scotland]]
| |
| − | [[Category:Fauna of Italy]]
| |
| − | [[Category:Fauna of Kazakhstan]]
| |
| − | [[Category:Fauna of Pakistan]]
| |
| − | [[Category:African raptors]]
| |
| | | | |
| − | [[ar:نسر ذهبي]]
| + | Golden Eagles often have a division of labor while hunting: one partner drives the prey to its waiting partner. They have very good eyesight and can spot prey from a long distance. The talons are used for killing and carrying the prey, the beak is used only for eating. The talons of a Golden Eagle are thought to be more powerful than the hand and arm strength of any human being. |
| − | [[bg:Скален орел]]
| + | }}<noinclude>[[Category:Adventist Youth Honors Answer Book/Transcluded Modules|{{FULLCHAPTERNAME}}]]</noinclude> |
| − | [[cs:Orel skalní]]
| |
| − | [[da:Kongeørn]]
| |
| − | [[de:Steinadler]]
| |
| − | [[et:Kaljukotkas]]
| |
| − | [[es:Aquila chrysaetos]]
| |
| − | [[eo:Reĝa aglo]]
| |
| − | [[fr:Aigle royal]]
| |
| − | [[fy:Keningsearn]]
| |
| − | [[gl:Aguia real]]
| |
| − | [[it:Aquila chrysaetos]]
| |
| − | [[he:עיט זהוב]]
| |
| − | [[la:Aquila chrysaetos]]
| |
| − | [[lt:Kilnusis erelis]]
| |
| − | [[lmo:Aquila Nègra]]
| |
| − | [[nl:Steenarend]]
| |
| − | [[ja:イヌワシ]]
| |
| − | [[no:Kongeørn]]
| |
| − | [[nn:Kongeørn]]
| |
| − | [[pl:Orzeł przedni]]
| |
| − | [[pt:Águia-real]]
| |
| − | [[ru:Беркут]]
| |
| − | [[sk:Orol skalný]]
| |
| − | [[sl:Planinski orel]]
| |
| − | [[fi:Maakotka]]
| |
| − | [[sv:Kungsörn]]
| |
| − | [[ta:பொன்னாங் கழுகு]]
| |
| − | [[tr:Kaya kartalı]] | |