Difference between revisions of "AY Honors/Fungi/Rust infection"
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | '''Rusts''' are [[fungi]] of the order '''Uredinales'''. Many of these species are plant [ | + | '''Rusts''' are [[fungi]] of the order '''Uredinales'''. Many of these species are plant [[parasites]]. Some are superficially similar to the [[smut (fungus)|smuts]], although their relation to each other is not clear. The taxonomy of Urediniomycota, as a whole, is in a state of flux. |
| + | |||
| + | Many of the rusts have two or more hosts ([[heteroecious]]) and up to five spore stages. However they most commonly reproduce via [[asexual]] [[spore]] production. Their spores are airborne and can travel great distances. They mostly cause [[foliar]] infections. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The group received its common name from the fact that some species have a reddish [[spore]] stage, which resembles the corrosion process known as [[rust]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Infection Process== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Rust occurs on many species of plant, but in most cases any one species of rust can only infect one species of plant. The following describes the infection process of asexual spores. A picture summarizing the process can be found in the gallery below. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Spore Attachment=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | When a rust [[conidia]] spore lands on a plant surface it needs to attach to it, or it would simply be washed off. First, weak, [[hydrophobic]] interactions are formed between the spore and the [[cutin]] of the plant cell surface. Then unknown signals cause the production of hydrophobic mucilaginous macromolecules called adhesins. These will stick the spore irreversibly to the plant surface.<ref>Osherov, N. and G.S. May, The molecular mechanisms of conidial germination. FEMS Microbiol. Lett, 2001. 199(2): p. 153–160.</ref> Once attached, the spore will germinate. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Germ Tube Elongation=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Rust fungi penetrate the plant by using the natural opening of the [[stomata]], but first the growing [[germ tube]] must locate it. Rust fungi have evolved to more efficiently locate stomata by the use of [[thigmotropism]]. The germ tube grows in a random manner until it reaches a ridge between [[epidermal cell]]s. At this point it will start to grow [[perpendicular]] to the ridge, greatly increasing its chances of locating a stomata.<ref>Dickinson, M. Molecular Plant Pathology. 2003.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Appresorium Formation=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The stomata is the site of [[appresorium]] formation, a structure that functions to both firmly anchor the fungus and aid in penetration.<ref>Deising, H.B., S. Werner, and M. Wernitz, The role of fungal appressoria in plant infection. Microbes Infect, 2000. 2(13): p. 1631-41.</ref> In the rust fungi appresorial formation is controlled by a process of [[thigmodifferentiation]]. Appresoria are formed when the germ tube detects ridges that match the dimensions of the stomatal lips of its [[Host (biology)|host]] species. | ||
| + | |||
| + | It has been proposed that this process is mediated by a mechanosensitive [[calcium]] [[ion]] channel that is located at the germ tube tip. This ion channel would transduce the stretching of the [[cell membrane]] caused by changes in [[leaf]] [[topography]] into [[ion flux]]es that lead to changes in [[gene]] expression and appresorium formation.<ref>Zhou, X.L., et al., A mechanosensitive channel in whole cells and in membrane patches of the fungus Uromyces. Science, 1991. 253(5026): p. 1415.</ref>. This theory is supported by experiments that show that applying Ca<sup>2+</sup> externally to the germ tube causes [[differentiation]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | From the appresoria an infection peg growns down into the plant and between the [[mesophyll]] cells. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===The Haustoria=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Rust fungi are [[biotroph]]s, meaning they gain their nutrients from living cells. This requires a specialised entension of the fungi into a living plant cell called a [[haustoria]]. This develops from a haustorial mother cell. The plant cell membrane invaginates around the main haustorial body and the space between the two membranes becomes known as the extra-haustorial matrix. An [[iron]] and [[phosphorus]] rich neck band bridges the plant and fungal membranes and acts as a seal preventing the escape of [[nutrient]]s into the plant [[apoplast]]. The haustoria contains [[amino acid]] and [[hexose]] [[sugar]] transporters and H<sup>+</sup>-ATPases for the [[active transport]] of nutrients from the plant cell.<ref>Voegele, R.T. and K. Mendgen, Rust haustoria: nutrient uptake and beyond. New Phytologist, 2003. 159(1): p. 93-100.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The rust fungi will then continue to grow and invade the plant until it is ready for [[sporulation]]. | ||
==Gallery== | ==Gallery== | ||
| Line 51: | Line 81: | ||
[[eo:Rustofungoj]] | [[eo:Rustofungoj]] | ||
[[fr:Rouille (maladie)]] | [[fr:Rouille (maladie)]] | ||
| + | [[ja:サビキン目]] | ||
[[nl:Roesten]] | [[nl:Roesten]] | ||
Revision as of 21:06, 22 October 2007
- This article is about the fungus. For the corrosion process, see rust.
Rusts are fungi of the order Uredinales. Many of these species are plant parasites. Some are superficially similar to the smuts, although their relation to each other is not clear. The taxonomy of Urediniomycota, as a whole, is in a state of flux.
Many of the rusts have two or more hosts (heteroecious) and up to five spore stages. However they most commonly reproduce via asexual spore production. Their spores are airborne and can travel great distances. They mostly cause foliar infections.
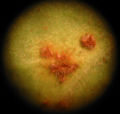
The group received its common name from the fact that some species have a reddish spore stage, which resembles the corrosion process known as rust.
Infection Process
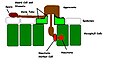
Rust occurs on many species of plant, but in most cases any one species of rust can only infect one species of plant. The following describes the infection process of asexual spores. A picture summarizing the process can be found in the gallery below.
Spore Attachment
When a rust conidia spore lands on a plant surface it needs to attach to it, or it would simply be washed off. First, weak, hydrophobic interactions are formed between the spore and the cutin of the plant cell surface. Then unknown signals cause the production of hydrophobic mucilaginous macromolecules called adhesins. These will stick the spore irreversibly to the plant surface.& Once attached, the spore will germinate.
Germ Tube Elongation
Rust fungi penetrate the plant by using the natural opening of the stomata, but first the growing germ tube must locate it. Rust fungi have evolved to more efficiently locate stomata by the use of thigmotropism. The germ tube grows in a random manner until it reaches a ridge between epidermal cells. At this point it will start to grow perpendicular to the ridge, greatly increasing its chances of locating a stomata.&
Appresorium Formation
The stomata is the site of appresorium formation, a structure that functions to both firmly anchor the fungus and aid in penetration.& In the rust fungi appresorial formation is controlled by a process of thigmodifferentiation. Appresoria are formed when the germ tube detects ridges that match the dimensions of the stomatal lips of its host species.
It has been proposed that this process is mediated by a mechanosensitive calcium ion channel that is located at the germ tube tip. This ion channel would transduce the stretching of the cell membrane caused by changes in leaf topography into ion fluxes that lead to changes in gene expression and appresorium formation.&. This theory is supported by experiments that show that applying Ca2+ externally to the germ tube causes differentiation.
From the appresoria an infection peg growns down into the plant and between the mesophyll cells.
The Haustoria
Rust fungi are biotrophs, meaning they gain their nutrients from living cells. This requires a specialised entension of the fungi into a living plant cell called a haustoria. This develops from a haustorial mother cell. The plant cell membrane invaginates around the main haustorial body and the space between the two membranes becomes known as the extra-haustorial matrix. An iron and phosphorus rich neck band bridges the plant and fungal membranes and acts as a seal preventing the escape of nutrients into the plant apoplast. The haustoria contains amino acid and hexose sugar transporters and H+-ATPases for the active transport of nutrients from the plant cell.&
The rust fungi will then continue to grow and invade the plant until it is ready for sporulation.
Gallery
See also
- soybean rust
- Wheat leaf rust
- Robigus
- Groundsel, a species susceptible to rust
External links
- A New Strain Of Wheat Could Avert Rust Fungus Catastrophe
- Images of some rusts
- Rust Fungi from Deacon, J: "Fungal Biology", Blackwell Publishing, 2005
References
- ↑ Osherov, N. and G.S. May, The molecular mechanisms of conidial germination. FEMS Microbiol. Lett, 2001. 199(2): p. 153–160.
- ↑ Dickinson, M. Molecular Plant Pathology. 2003.
- ↑ Deising, H.B., S. Werner, and M. Wernitz, The role of fungal appressoria in plant infection. Microbes Infect, 2000. 2(13): p. 1631-41.
- ↑ Zhou, X.L., et al., A mechanosensitive channel in whole cells and in membrane patches of the fungus Uromyces. Science, 1991. 253(5026): p. 1415.
- ↑ Voegele, R.T. and K. Mendgen, Rust haustoria: nutrient uptake and beyond. New Phytologist, 2003. 159(1): p. 93-100.
da:Rustsvampe de:Rostpilze es:Urediniomycetes eo:Rustofungoj fr:Rouille (maladie) ja:サビキン目 nl:Roesten