Difference between revisions of "AY Honors/Drumming & Percussion/Answer Key"
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
There have been many attempts to formalize a standard list of [[snare drum]] rudiments. The [[National Association of Rudimental Drummers]] (NARD), an organization established to promote rudimental drumming, put forward a list of 13 "essential" rudiments, and later a second set of thirteen to form the original 26. Finally, the [[Percussive Arts Society]] (PAS) reorganized the first 26 and added another 14 to form the current 40 International Drum Rudiments. | There have been many attempts to formalize a standard list of [[snare drum]] rudiments. The [[National Association of Rudimental Drummers]] (NARD), an organization established to promote rudimental drumming, put forward a list of 13 "essential" rudiments, and later a second set of thirteen to form the original 26. Finally, the [[Percussive Arts Society]] (PAS) reorganized the first 26 and added another 14 to form the current 40 International Drum Rudiments. | ||
| − | The first written rudiment goes back to the year 1610 in Basel, Swizerland<ref>http://www.pfyffersyte.ch/files/repertoire/hit2005_PundT.php</ref>. Anyhow the candle of rudimental drumming is said to be France because in the 17th / 18th century professional drummers became part of the life guard of the kings. It was perfectionized during Napoleon I. The marsh [[Le Rigodon]] is one of the cornerstones that laid the foundation for modern rudimental drumming. <ref>http://www.tamboursde89.com/revue/88.pdf</ref> <ref>http://www.pfyffersyte.ch/files/repertoire/hit2005_PundT.php</ref> [encyclopedia Brockhaus] | + | The first written rudiment goes back to the year 1610 in Basel, Swizerland<ref>http://www.pfyffersyte.ch/files/repertoire/hit2005_PundT.php</ref>. Anyhow the candle of rudimental drumming is said to be France because in the 17th / 18th century professional drummers became part of the life guard of the kings. It was perfectionized during Napoleon I. The marsh [[Le Rigodon]] and his different interpretations in the 18th century is one of the cornerstones that laid the foundation for modern rudimental drumming (among others the "two level"-playing). <ref>http://www.tamboursde89.com/revue/88.pdf</ref> <ref>http://www.pfyffersyte.ch/files/repertoire/hit2005_PundT.php</ref> [encyclopedia Brockhaus] |
The "buzzer-drums", later called "tambours" (French) came originally from Turkey to Europe during the crusades. Later other drums came with the Turkish wars in the 17th century. (encyclopedia Brockhaus) | The "buzzer-drums", later called "tambours" (French) came originally from Turkey to Europe during the crusades. Later other drums came with the Turkish wars in the 17th century. (encyclopedia Brockhaus) | ||
Revision as of 17:53, 15 November 2008
Template:Otheruses Template:Redirect A rudiment is one of a set of basic patterns used in rudimental drumming. These patterns form the basic building blocks or "vocabulary" of drumming, and can be combined in a great variety of ways to create drumming music.
There have been many attempts to formalize a standard list of snare drum rudiments. The National Association of Rudimental Drummers (NARD), an organization established to promote rudimental drumming, put forward a list of 13 "essential" rudiments, and later a second set of thirteen to form the original 26. Finally, the Percussive Arts Society (PAS) reorganized the first 26 and added another 14 to form the current 40 International Drum Rudiments.
The first written rudiment goes back to the year 1610 in Basel, Swizerland&. Anyhow the candle of rudimental drumming is said to be France because in the 17th / 18th century professional drummers became part of the life guard of the kings. It was perfectionized during Napoleon I. The marsh Le Rigodon and his different interpretations in the 18th century is one of the cornerstones that laid the foundation for modern rudimental drumming (among others the "two level"-playing). & & [encyclopedia Brockhaus]
The "buzzer-drums", later called "tambours" (French) came originally from Turkey to Europe during the crusades. Later other drums came with the Turkish wars in the 17th century. (encyclopedia Brockhaus)
40 P.A.S. International Drum Rudiments
Single stroke rudiments
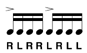
The single-stroke roll consists of alternating sticking (i.e., RLRL, etc.) of indeterminate speed and length.
| Name | Notation | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Single Stroke Roll | Evenly-spaced notes played with alternating sticking. Though usually played fast, even half notes with alternating sticking would be considered a single stroke roll. | |
| Single Stroke Four | 
|
Four notes played with alternating sticking, usually as a triplet followed by a strong beat (as in the picture) or as three grace notes before a downbeat (like a ruff). |
| Single Stroke Seven | 
|
Seven notes played with alternating sticking, usually as sextuplet followed by a strong beat. |
Multiple bounce roll rudiments
Double-stroke rudiments
The double-stroke roll is a rudiment consisting of alternating diddles (i.e., RR, LL, etc) of indeterminate speed and length. There are 10 official variants of the double-stroke roll (see below).& The double-stroke roll is often played in the open, closed, open format; starting very slowly, gradually accelerating to maximum speed, then gradually slowing down again.
| Name | Notation | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Double Stroke Open Roll | Like the single-stroke roll, usually played fast, but even when played slowly, alternating diddles are considered a double stroke roll. Played so each individual note can be heard distinctly. | |
| Five Stroke Roll | 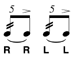
|
Two diddles followed by an accented note. |
| Six Stroke Roll | 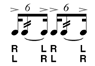
|
Unlike most other double stroke rudiments, the six stroke roll begins with an accented single note. Then it is followed by the diddles and another accented note. |
| Seven Stroke Roll | 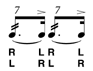
|
Three diddles followed by an accented note. |
| Nine Stroke Roll | 
|
Four diddles followed by an accented note. |
| Ten Stroke Roll | 
|
Four diddles followed by two accented notes. |
| Eleven Stroke Roll | 
|
Five diddles followed by an accented note. |
| Thirteen Stroke Roll | 
|
Six diddles followed by an accented note. |
| Fifteen Stroke Roll | 
|
Seven diddles followed by an accented note. |
| Seventeen Stroke Roll | 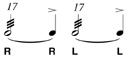
|
Eight diddles followed by an accented note. |
Diddle rudiments
In percussion, the paradiddle is a rudiment consisting of a four-note pattern of the form RLRR or LRLL.& When multiple paradiddles are played in succession, the first note always alternates between right and left. There are also several official variations of paradiddle rudiments. Paradiddles are often used to switch hands while playing steady notes. For example, if steadily playing sixteenth notes, with right hand lead (RLRL, etc), then wanting to end on a drum to the left of the current drum, he may stick it as follows: RLRL RLRL RLRL RLRR L with the final left tap on the ending drum.
Flam rudiments
A flam is a rudiment consisting of a quiet "grace" note on one hand followed by a louder "primary" stroke on the opposite hand. The two notes are played almost simultaneously, and are intended to sound like a single, 'broader' note.&
| Name | Notation | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Flam | A single primary note note preceded by a grace note which is played with the opposite hand. The temporal distance between the grace note and the primary note can vary depending on the style and context of the piece being played. | |
| Flam Accent | 
|
Alternating groups of three notes of the form [Flam - tap - tap]. |
| Flam Tap | 
|
Alternating diddles with flams on the first note of each. |
| Flamacue | 
|
A group of four notes and an ending downbeat, where the first note and the down beat are flammed, and the second note is accented. |
| Flam Paradiddle | 
|
A paradiddle with a flam on the first note.& |
| Single Flammed Mill | 
|
An inverted paradiddle (RRLR, LLRL) with a flam on the first note of each diddle. |
| Flam Paradiddle-diddle | 
|
Alternating paradiddle-diddles with flams on the first note of each. |
| Pataflafla | 
|
A four-note pattern with flams on the first and last notes.& |
| Swiss Army Triplet | 
|
A right hand flam followed by a right tap and a left tap, or (using a left hand lead) a left hand flam followed by a left tap and a right tap. && It is often used in the place of a flam accent, since repeated flam accents will have three taps on the same hand in a row, where repeated swiss army triplets only involve two taps on the same hand. |
| Inverted Flam Tap | 
|
Alternating diddles (offset by one sixteenth note) with a flam on the second note of each diddle. |
| Flam Drag | 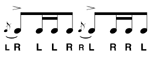
|
Alternating groups of three notes of the form [flam - drag - tap]. |
Drag rudiments
| Name | Notation | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Drag | A drag consists of two consecutive notes played by the same hand (either RR or LL). This is similar to the diddle, except that by convention diddles are played the same speed as the context in which they are placed, where drags are played at twice the speed as the context in which they are placed. For example, if a sixteenth note passage is being played then any drags in that passage would by definition be thirty-second notes, where diddles would be sixteenth notes. Drags can also be played as grace notes. When played as grace notes on timpani, the grace notes are alternated (rlR, lrL). &
Continuously playing alternating drags (or diddles) results in a double-stroke roll. A similar rudiment is the ruff, which is a note with three grace notes, but they are usually alternated & | |
| Single Drag Tap | 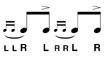
|
A single drag tap is two alternating notes where the first note has drag grace notes and the second is accented. |
| Double Drag Tap | 
|
A double drag tap is a single drag tap with another grace note drag before it. |
| Lesson 25 | 
|
A lesson 25 is three alternating notes where the first note has drag grace notes and the third is accented. |
| Single Dragadiddle | 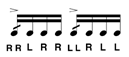
|
A single dragadiddle is a paradiddle where the first note is a drag. |
| Drag Paradiddle #1 | 
|
The first drag paradiddle is an accented note followed by a paradiddle with drag grace notes on the first note. |
| Drag Paradiddle #2 | 
|
The second drag paradiddle is two accented notes followed by a paradiddle with drag grace notes on the second accented note and the first note of the paradiddle. |
| Single Ratamacue | 
|
A single ratamacue consists of four notes where the first note has drag grace notes and the fourth is accented. & |
| Double Ratamacue | 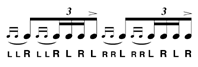
|
A double ratamacue consists of a single ratamacue with a drag before it. |
| Triple Ratamacue | 
|
A triple ratamacue consists of a single ratamacue with two drags before it. |
Historical organization
Thirteen "essential" rudiments
- The Long Roll
- The Five Stroke Roll
- The Seven Stroke Roll
- The Flam
- The Flam Accent
- The Flam Paradiddle
- The Flamacue
- The Ruff
- The Single Drag
- The Double Drag
- The Double Paradiddle
- The Single Ratamacue
- The Triple Ratamacue
Second thirteen rudiments
- The Single Stroke Roll
- The Nine Stroke Roll
- The Ten Stroke Roll
- The Eleven Stroke Roll
- The Thirteen Stroke Roll
- The Fifteen Stroke Roll
- The Flam Tap
- The Single Paradiddle
- The Drag Paradiddle #1
- The Drag Paradiddle #2
- The Flam Paradiddle-diddle
- The Lesson 25
- The Double Ratamacue
Last fourteen rudiments
More recently, the Percussive Arts Society added 14 more rudiments to extend the list to the current 40 International Drum Rudiments. Note that the ordering was completely changed during this last re-organization, so these numbers won't match those above.
- The Single Stroke Four
- The Single Stroke Seven
- The Multiple Bounce Roll
- The Triple Stroke Roll
- The Six Stroke Roll
- The Seventeen Stroke Roll
- The Triple Paradiddle
- The Single Paradiddle-Diddle
- The Single Flammed Mill
- The Pataflafla
- The Swiss Army Triplet
- The Inverted Flam Tap
- The Flam Drag
- The Single Dragadiddle
| Publishing year | Name | Author |
|---|---|---|
| 1812 | A New, Useful, and Complete System of Drum Beating | Charles Ashworth |
| 1815 | The Art of Beating the Drum | Samuel Potter |
| 1861 | The Drummers' and Fifers' Guide | Bruce Emmett |
| 1869 | Strube's Drum and Fife Instructor | Gardiner A. Strube |
| 1886 | The Trumpet and Drum | John Philip Sousa |
| 1935 | Stick Control | George Lawrence Stone |
| 1942 | Modern Interpretation of Snare Drum Rudiments | Buddy Rich |
| 1945 | The All-American Drummer | Charley Wilcoxon |
| 1959 | 14 Modern Contest Solos For Snare Drum | John S. Pratt |
| 1979 | The Technique and Mechanics of Rudimental Snare Drumming | Ken Mazur |
| 1992 | The Drummer's Rudimental Reference Book | John Wooton |
| 2004 | The Beat of a Different Drummer | Dominick Cuccia |
Notable contributors
- Charley Wilcoxon: instructor, author, and teacher
- J. Burns Moore: instructor, author, and teacher
- George Lawrence Stone: instructor, author, and teacher
- Earl Sturtze: instructor, author, and teacher
- Les Parks: instructor and arranger, Sons of Liberty Fife and Drum Corps, Hawthorne Cabaleros, Garfield Cadets
- John S. Pratt: instructor, author, and teacher
- Fred Sanford: instructor and arranger, Santa Clara Vanguard Drum and Bugle Corps
- Ralph Hardimon: instructor and arranger, Santa Clara Vanguard Drum and Bugle Corps
- Tom Float: instructor and arranger, Blue Devils Drum and Bugle Corps
- Marty Hurley: instructor and arranger, Phantom Regiment Drum and Bugle Corps during the 1970's and early '80s
- Paul Rennick: instructor and arranger, Phantom Regiment Drum and Bugle Corps
- Scott Johnson: instructor and arranger, Blue Devils Drum and Bugle Corps
- James Campbell: instructor and arranger, The Cavaliers Drum and Bugle Corps
- Bret Kuhn: instructor and arranger, The Cavaliers Drum and Bugle Corps
- Dennis DeLucia: instructor and arranger, Bridgemen Drum and Bugle Corps
- Thom Hannum: instructor and arranger, Cadets Drum and Bugle Corps
- Charley Poole, Jr. instructor and arranger, 27th Lancers Drum and Bugle Corps
Hybrid rudiments
Over the years, many other rudimental patterns have been informally identified and given creative names, although most of these are based upon the original 40. They are commonly known as "hybrid rudiments" or "hybrids," and are especially common in drumlines and drum corps. A few notable examples are the herta, which is a drag played with alternating sticking, and the cheese, a diddle with a grace note.
References
- ↑ http://www.pfyffersyte.ch/files/repertoire/hit2005_PundT.php
- ↑ http://www.tamboursde89.com/revue/88.pdf
- ↑ http://www.pfyffersyte.ch/files/repertoire/hit2005_PundT.php
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 "International Drum Rudiments" Page of the Percussive Arts Society (PAS) Accessed 1/23/2008.
- ↑ Swiss Army Triplet Example on VicFirth.com Accessed 8/11/2007.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Nasatir, Cary. "Too Many Rudiments?". Conn-Selmer Keynotes. http://www.keynotesmagazine.com/article.php?uid=120. Retrieved 2008.
External links
- DrumRudiments.com- All 40 Drum Rudiments with Video examples.
- The Percussive Arts Society International Drum Rudiments
- RudimentalDrumming.com
Template:Percussion Template:Rudimental Percussion
de:Rudiment (Schlagzeug) it:Rudimento nl:Rudiments ja:ルーディメンツ fi:Rudimentit