Difference between revisions of "AY Honors/Forestry/Answer Key"
| (5 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
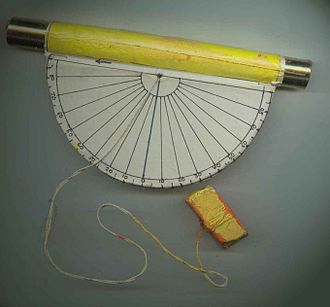
[[Image:Stanley_compass_1.jpg|thumb|right|200px|Compass with inclinometer]] | [[Image:Stanley_compass_1.jpg|thumb|right|200px|Compass with inclinometer]] | ||
An '''inclinometer''' or '''clinometer''' is an instrument for measuring angles of [[slope]] (or [[tilt]]), [[elevation]] or [[inclination]] of an object with respect to gravity. It is also known as a ''tilt meter'', ''tilt indicator'', ''slope alert'', ''slope gauge'', ''gradient meter'', ''gradiometer'', ''level gauge'', ''level meter'', ''declinometer'', and ''pitch & roll indicator''. | An '''inclinometer''' or '''clinometer''' is an instrument for measuring angles of [[slope]] (or [[tilt]]), [[elevation]] or [[inclination]] of an object with respect to gravity. It is also known as a ''tilt meter'', ''tilt indicator'', ''slope alert'', ''slope gauge'', ''gradient meter'', ''gradiometer'', ''level gauge'', ''level meter'', ''declinometer'', and ''pitch & roll indicator''. | ||
| − | Clinometers measure both inclines (positive slopes, as seen by an observer looking upwards) and declines (negative slopes, as seen by an observer looking | + | Clinometers measure both inclines (positive slopes, as seen by an observer looking upwards) and declines (negative slopes, as seen by an observer looking downward). |
==History== | ==History== | ||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
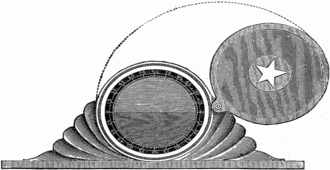
Early inclinometers include examples such as Well's inclinometer, the essential parts of which are a flat side, or base, on which it stands, and a hollow disk just half filled with some heavy liquid. The glass face of the disk is surrounded by a graduated scale that marks the angle at which the surface of the liquid stands, with reference to the flat base. The line 0.——0. being parallel to the base, when the liquid stands on that line, the flat side is horizontal; the line 90.——90. being perpendicular to the base, when the liquid stands on that line, the flat side is perpendicular or plumb. Intervening angles are marked, and, by the aid of simple conversion tables, the instrument indicates the rate of fall per set distance of horizontal measurement, and set distance of the sloping line. | Early inclinometers include examples such as Well's inclinometer, the essential parts of which are a flat side, or base, on which it stands, and a hollow disk just half filled with some heavy liquid. The glass face of the disk is surrounded by a graduated scale that marks the angle at which the surface of the liquid stands, with reference to the flat base. The line 0.——0. being parallel to the base, when the liquid stands on that line, the flat side is horizontal; the line 90.——90. being perpendicular to the base, when the liquid stands on that line, the flat side is perpendicular or plumb. Intervening angles are marked, and, by the aid of simple conversion tables, the instrument indicates the rate of fall per set distance of horizontal measurement, and set distance of the sloping line. | ||
| − | The earliest electronic inclinometers used a weight, an extension, and a [[potentiometer]]. Early in the 1900's (circa 1917) precision curved glass tubes filled with a damping liquid and steel ball were introduced to provide accurate visual angle indication. Common sensor technologies for electronic tilt sensors and inclinometers are [[accelerometer]], [[Liquid Capacitive Basics |liquid capacitive]], electrolytic, gas bubble in liquid, and pendulum. | + | The earliest electronic inclinometers used a weight, an extension, and a [[potentiometer]]. Early in the 1900's ([[circa]] 1917) precision curved glass tubes filled with a damping liquid and steel ball were introduced to provide accurate visual angle indication. Common sensor technologies for electronic tilt sensors and inclinometers are [[accelerometer]], [[Liquid Capacitive Basics |liquid capacitive]], electrolytic, gas bubble in liquid, and pendulum. [[MEMS]] (Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems) technology is becoming the new standard due to their tiny size and low cost. |
==Accuracy== | ==Accuracy== | ||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
Common sensor technologies for tilt sensors and inclinometers are accelerometer, [[Liquid Capacitive Basics |Liquid Capacitive]], electrolytic, gas bubble in liquid, and pendulum. | Common sensor technologies for tilt sensors and inclinometers are accelerometer, [[Liquid Capacitive Basics |Liquid Capacitive]], electrolytic, gas bubble in liquid, and pendulum. | ||
| − | Tilt sensor technology has also been implemented in video games. ''[[Yoshi Topsy-Turvy]]'' and ''[[Kirby Tilt 'n' Tumble]]'' are both built around a tilt sensor mechanism, which is built into the cartridge. The [[PlayStation 3]] | + | Tilt sensor technology has also been implemented in video games. ''[[Yoshi Topsy-Turvy]]'' and ''[[Kirby Tilt 'n' Tumble]]'' are both built around a tilt sensor mechanism, which is built into the cartridge. The [[PlayStation 3]] and [[Wii]] game controllers also use tilt as a means to play video games. |
Inclinometers are also used in Engineering fields where it's used to measure the inclination of a land to build on. | Inclinometers are also used in Engineering fields where it's used to measure the inclination of a land to build on. | ||
Revision as of 06:47, 24 February 2009
An inclinometer or clinometer is an instrument for measuring angles of slope (or tilt), elevation or inclination of an object with respect to gravity. It is also known as a tilt meter, tilt indicator, slope alert, slope gauge, gradient meter, gradiometer, level gauge, level meter, declinometer, and pitch & roll indicator. Clinometers measure both inclines (positive slopes, as seen by an observer looking upwards) and declines (negative slopes, as seen by an observer looking downward).
History
Early inclinometers include examples such as Well's inclinometer, the essential parts of which are a flat side, or base, on which it stands, and a hollow disk just half filled with some heavy liquid. The glass face of the disk is surrounded by a graduated scale that marks the angle at which the surface of the liquid stands, with reference to the flat base. The line 0.——0. being parallel to the base, when the liquid stands on that line, the flat side is horizontal; the line 90.——90. being perpendicular to the base, when the liquid stands on that line, the flat side is perpendicular or plumb. Intervening angles are marked, and, by the aid of simple conversion tables, the instrument indicates the rate of fall per set distance of horizontal measurement, and set distance of the sloping line.
The earliest electronic inclinometers used a weight, an extension, and a potentiometer. Early in the 1900's (circa 1917) precision curved glass tubes filled with a damping liquid and steel ball were introduced to provide accurate visual angle indication. Common sensor technologies for electronic tilt sensors and inclinometers are accelerometer, liquid capacitive, electrolytic, gas bubble in liquid, and pendulum. MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems) technology is becoming the new standard due to their tiny size and low cost.
Accuracy
Certain highly sensitive electronic inclinometer sensors can achieve an output accurate to .001 degrees. An inclinometer sensor's true or absolute accuracy (which is the combined total error), however, is a combination of initial sets of sensor zero offset and sensitivity, sensor linearity, hysteresis, repeatability, and the temperature drifts of zero and sensitivity - electronic inclinometers accuracy can typically range from .01º to ±2º depending on the sensor and situation. Typically in room ambient conditions the accuracy is limited to the sensor linearity specification.
Sensor technology
Tilt sensors and inclinometers generate an artificial horizon and measure angular tilt with respect to this horizon. They are used in cameras, aircraft flight controls, automobile security systems, and special switches. Also used for platform leveling, boom angle indication, anywhere tilt requires measuring. Important specifications to consider when searching for tilt sensors and inclinometers are the tilt angle range and number of axes. The tilt angle range is the range of desired linear output measured in degrees. The number of axes the inclinometer and tilt sensor measure on is another important specification.
Common sensor technologies for tilt sensors and inclinometers are accelerometer, Liquid Capacitive, electrolytic, gas bubble in liquid, and pendulum.
Tilt sensor technology has also been implemented in video games. Yoshi Topsy-Turvy and Kirby Tilt 'n' Tumble are both built around a tilt sensor mechanism, which is built into the cartridge. The PlayStation 3 and Wii game controllers also use tilt as a means to play video games.
Inclinometers are also used in Engineering fields where it's used to measure the inclination of a land to build on.
Usages
Inclinometers are used for:
- Determining the angle of the earth's magnetic field in respect to the horizontal plane.
- Showing the inclination of an aircraft or ship relative to the horizontal. An airplane instrument. See turn coordinator or slip indicator[1].
- Showing a deviation from the true vertical or horizontal.
- Surveying, in order to measure an angle of inclination or elevation.
- Rollover warning, to alert equipment operator of possible tip over condition.[2]
- Measuring angles of elevation, slope, or incline, as of an embankment. Also called an inclinometer.
- Measuring slight differences in slopes, particularly for geophysics. Such inclinometers are, for instance, used for monitoring volcanoes, or for measuring the depth and rate of landslide movement.
- Measuring movements in walls and/or the ground in civil engineering projects.[3]
- Determining the dip of beds or strata, or the slope of an embankment or cutting; a kind of plumb level.
- Some automotive safety systems.
- Indicating pitch and roll of vehicles, sail boats, and aircraft.
- Monitoring boom angle of cranes and material handlers.
- Measuring the "look angle" of a satellite antenna towards a satellite.
- Measuring the slope angle of a tape or chain during distance measurement.
- Estimating the height of a building, tree, or other feature using a vertical angle and a distance (determined by taping or pacing).
- Measuring the angle of drilling in well-logging applications.
- Measuring the height of trees or other poles.
- Measuring steepness of a ski slope.
- Measuring the orientation of planes and lineations in rocks, in combination with a compass. (see structural geology)
- Measuring Range of Motion in the joints of the body
Survey methods
- Inclinometers are used for the measurement of angles in reference to gravity.
- The USDA Forest Service uses inclinometers to measure tree height in its Forest Inventory and Analysis program.
- Using Range of Motion instruments such as Titronics R&D's.
See also
External links
ar:مميال de:Neigungsmesser es:Clinómetro fr:Inclinomètre it:Clinometro ja:クリノメーター no:Klinometer pt:Inclinômetro sl:Klinometer sv:Inklinometer