Difference between revisions of "AY Honors/Bamboo Craft/Answer Key"
Jomegat bot (talk | contribs) (Bot: Automated import of articles *** existing text overwritten ***) |
JadeDragon (talk | contribs) m (minor copy edit) |
||
| (8 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | < | + | {{HonorSubpage}} |
| − | <noinclude><translate><!--T: | + | <section begin="Body" /> |
| + | {{ansreq|page={{#titleparts:{{PAGENAME}}|2|1}}|num=1}} | ||
| + | <noinclude><translate><!--T:48--> | ||
</noinclude> | </noinclude> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<!-- 1. How is bamboo classified scientifically? --> | <!-- 1. How is bamboo classified scientifically? --> | ||
<!--T:4--> | <!--T:4--> | ||
| − | Bamboo belongs to the grass family Gramineae (also called Poaceae), subfamily Bambusoideae. There are about 60 to 70 genera and over 1200 species in the world of bamboo. The bamboo plant is a fast growing giant grass with woody stems. It is an evergreen that grow all year round. | + | Bamboo belongs to the grass family Gramineae (also called Poaceae), subfamily Bambusoideae. There are about 60 to 70 genera and over 1200 species in the world of bamboo. The bamboo plant is a fast growing giant grass with woody stems. It is an evergreen that will grow all year round. |
<!--T:5--> | <!--T:5--> | ||
| − | According to the [[w:Guinness_World_Records|Guinness Book of World’s Records]], bamboo is the fastest growing plant on earth. Although | + | According to the [[w:Guinness_World_Records|Guinness Book of World’s Records]], bamboo is the fastest growing plant on earth. Although Guinness does not identify a particular species, they report a growth rate of 35 inches a day. Other sources claim that bamboo can grow more than a meter in a day. |
| + | <!--T:49--> | ||
<noinclude></translate></noinclude> | <noinclude></translate></noinclude> | ||
{{CloseReq}} <!-- 1 --> | {{CloseReq}} <!-- 1 --> | ||
{{ansreq|page={{#titleparts:{{PAGENAME}}|2|1}}|num=2}} | {{ansreq|page={{#titleparts:{{PAGENAME}}|2|1}}|num=2}} | ||
| − | <noinclude><translate></noinclude> | + | <noinclude><translate><!--T:50--> |
| + | </noinclude> | ||
<!-- 2. Name the parts of a bamboo plant. --> | <!-- 2. Name the parts of a bamboo plant. --> | ||
| Line 37: | Line 23: | ||
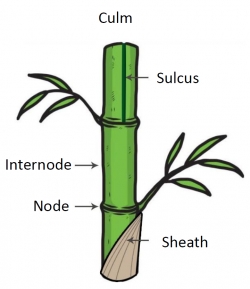
[[File:Parts of bamboo.png|250px]] | [[File:Parts of bamboo.png|250px]] | ||
| + | <!--T:51--> | ||
<noinclude></translate></noinclude> | <noinclude></translate></noinclude> | ||
{{CloseReq}} <!-- 2 --> | {{CloseReq}} <!-- 2 --> | ||
{{ansreq|page={{#titleparts:{{PAGENAME}}|2|1}}|num=3}} | {{ansreq|page={{#titleparts:{{PAGENAME}}|2|1}}|num=3}} | ||
| − | <noinclude><translate></noinclude> | + | <noinclude><translate><!--T:52--> |
| + | </noinclude> | ||
<!-- 3. Under what condition does the bamboo plant grow best? --> | <!-- 3. Under what condition does the bamboo plant grow best? --> | ||
<!--T:9--> | <!--T:9--> | ||
| − | Bamboo grows in both tropical and temperate climates in Asia, on islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans, and also in Africa and South America. It requires a fertile moisture retentive soil that doesn’t get waterlogged. It will grow well in most soil except alkaline soils, dry desert and marsh. Only a few species can grow in fairly cold weather that is below 20 | + | Bamboo grows in both tropical and temperate climates in Asia, on islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans, and also in Africa and South America. It requires a fertile moisture retentive soil that doesn’t get waterlogged. It will grow well in most soil except alkaline soils, dry desert and marsh. Only a few species can grow in fairly cold weather that is below 20 degrees Celsius. |
<!--T:10--> | <!--T:10--> | ||
The adaptability of the bamboo is admirable as you can find them growing in plains, hilly regions, and even high altitude mountainous areas. | The adaptability of the bamboo is admirable as you can find them growing in plains, hilly regions, and even high altitude mountainous areas. | ||
| + | <!--T:53--> | ||
<noinclude></translate></noinclude> | <noinclude></translate></noinclude> | ||
{{CloseReq}} <!-- 3 --> | {{CloseReq}} <!-- 3 --> | ||
{{ansreq|page={{#titleparts:{{PAGENAME}}|2|1}}|num=4}} | {{ansreq|page={{#titleparts:{{PAGENAME}}|2|1}}|num=4}} | ||
| − | <noinclude><translate></noinclude> | + | <noinclude><translate><!--T:54--> |
| + | </noinclude> | ||
<!-- 4. How high can the bamboo plant grow? --> | <!-- 4. How high can the bamboo plant grow? --> | ||
<!--T:12--> | <!--T:12--> | ||
| − | The giant bamboo species can reach a height of 20 to 40 meters (130 feet). The culms of some bamboo species grow as quickly as 1 foot or 0.3 meters per day. Some | + | The giant bamboo species can reach a height of 20 to 40 meters (130 feet). The culms of some bamboo species grow as quickly as 1 foot or 0.3 meters per day. Some are capable of growing 2 feet (24 inches or 60 cm) or more per day. |
| − | are capable of growing 2 feet (24 inches or 60 cm) or more per day. | ||
<!--T:13--> | <!--T:13--> | ||
[[File:Giant bamboo with person.png|300px]] | [[File:Giant bamboo with person.png|300px]] | ||
| + | <!--T:55--> | ||
<noinclude></translate></noinclude> | <noinclude></translate></noinclude> | ||
{{CloseReq}} <!-- 4 --> | {{CloseReq}} <!-- 4 --> | ||
{{ansreq|page={{#titleparts:{{PAGENAME}}|2|1}}|num=5}} | {{ansreq|page={{#titleparts:{{PAGENAME}}|2|1}}|num=5}} | ||
| − | <noinclude><translate></noinclude> | + | <noinclude><translate><!--T:56--> |
| + | </noinclude> | ||
<!-- 5. How often does the bamboo plant flower? --> | <!-- 5. How often does the bamboo plant flower? --> | ||
<!--T:15--> | <!--T:15--> | ||
| − | Most bamboos rarely flower and they produce seeds only after | + | Most bamboos rarely flower and they produce seeds only after 30-60 years and sometimes after over 120 years of growth. Some only flower once in their lifetime. A few bamboo species do flower annually. |
<!--T:16--> | <!--T:16--> | ||
[[File:BambooFlowering.jpg|thumb|left|Bamboo flowering]]{{clear}} | [[File:BambooFlowering.jpg|thumb|left|Bamboo flowering]]{{clear}} | ||
| + | <!--T:57--> | ||
<noinclude></translate></noinclude> | <noinclude></translate></noinclude> | ||
{{CloseReq}} <!-- 5 --> | {{CloseReq}} <!-- 5 --> | ||
{{ansreq|page={{#titleparts:{{PAGENAME}}|2|1}}|num=6}} | {{ansreq|page={{#titleparts:{{PAGENAME}}|2|1}}|num=6}} | ||
| − | <noinclude><translate></noinclude> | + | <noinclude><translate><!--T:58--> |
| + | </noinclude> | ||
<!-- 6. What are the special qualities of the bamboo plant that have inspired many artists and poets in their works of art? --> | <!-- 6. What are the special qualities of the bamboo plant that have inspired many artists and poets in their works of art? --> | ||
| Line 92: | Line 85: | ||
[[File:Xia Chang - Bamboo in Wind - 1989.235.1 - Metropolitan Museum of Art.jpg|thumb|left|Bamboo in Wind - Metropolitan Museum of Art]]{{clear}} | [[File:Xia Chang - Bamboo in Wind - 1989.235.1 - Metropolitan Museum of Art.jpg|thumb|left|Bamboo in Wind - Metropolitan Museum of Art]]{{clear}} | ||
| + | <!--T:59--> | ||
<noinclude></translate></noinclude> | <noinclude></translate></noinclude> | ||
{{CloseReq}} <!-- 6 --> | {{CloseReq}} <!-- 6 --> | ||
{{ansreq|page={{#titleparts:{{PAGENAME}}|2|1}}|num=7}} | {{ansreq|page={{#titleparts:{{PAGENAME}}|2|1}}|num=7}} | ||
| − | <noinclude><translate></noinclude> | + | <noinclude><translate><!--T:60--> |
| + | </noinclude> | ||
<!-- 7. What are the different uses of bamboo? --> | <!-- 7. What are the different uses of bamboo? --> | ||
| Line 123: | Line 118: | ||
<!--T:30--> | <!--T:30--> | ||
| − | Bamboo rods are often used | + | Bamboo rods are often used as fishing poles. |
| + | <!--T:61--> | ||
<noinclude></translate></noinclude> | <noinclude></translate></noinclude> | ||
{{CloseReq}} <!-- 7 --> | {{CloseReq}} <!-- 7 --> | ||
{{ansreq|page={{#titleparts:{{PAGENAME}}|2|1}}|num=8}} | {{ansreq|page={{#titleparts:{{PAGENAME}}|2|1}}|num=8}} | ||
| − | <noinclude><translate></noinclude> | + | <noinclude><translate><!--T:62--> |
| + | </noinclude> | ||
<!-- 8. What are some of the tools needed in working with bamboo? --> | <!-- 8. What are some of the tools needed in working with bamboo? --> | ||
<!--T:32--> | <!--T:32--> | ||
| − | Because bamboo is tough and durable, it needs to be handled properly with the right tools like axes, saws , coping saws and splitters. Sandpaper is needed to polish off the sharp edges of cut bamboo so as to prevent injury. Glue | + | Because bamboo is tough and durable, it needs to be handled properly with the right tools like axes, saws, coping saws and splitters. Sandpaper is needed to polish off the sharp edges of cut bamboo so as to prevent injury. Glue can be used to join different parts of the bamboo together. A drill will be needed to make any items that have holes in it such as a flute. |
| + | <!--T:63--> | ||
<noinclude></translate></noinclude> | <noinclude></translate></noinclude> | ||
{{CloseReq}} <!-- 8 --> | {{CloseReq}} <!-- 8 --> | ||
{{ansreq|page={{#titleparts:{{PAGENAME}}|2|1}}|num=9}} | {{ansreq|page={{#titleparts:{{PAGENAME}}|2|1}}|num=9}} | ||
| − | <noinclude><translate></noinclude> | + | <noinclude><translate><!--T:64--> |
| + | </noinclude> | ||
<!-- 9. What are the hazards involved when working with bamboo? --> | <!-- 9. What are the hazards involved when working with bamboo? --> | ||
<!--T:34--> | <!--T:34--> | ||
| − | When bamboo is split open, it can be very sharp at the edges and | + | When bamboo is split open, it can be very sharp at the edges and the edges can cut you easily. Bamboo dust can cause irritation to the eyes. Upon skin contact, it may also cause allergic contact dermatitis in sensitized individuals. |
<!--T:35--> | <!--T:35--> | ||
Upon inhalation, bamboo dust may also cause nasal obstruction and dryness as well as irritation leading to coughing, sneezing, wheezing and sinusitis. It may also aggravate pre-existing respiratory conditions or allergies. | Upon inhalation, bamboo dust may also cause nasal obstruction and dryness as well as irritation leading to coughing, sneezing, wheezing and sinusitis. It may also aggravate pre-existing respiratory conditions or allergies. | ||
| + | <!--T:65--> | ||
<noinclude></translate></noinclude> | <noinclude></translate></noinclude> | ||
{{CloseReq}} <!-- 9 --> | {{CloseReq}} <!-- 9 --> | ||
{{ansreq|page={{#titleparts:{{PAGENAME}}|2|1}}|num=10}} | {{ansreq|page={{#titleparts:{{PAGENAME}}|2|1}}|num=10}} | ||
| − | <noinclude><translate></noinclude> | + | <noinclude><translate><!--T:66--> |
| + | </noinclude> | ||
<!-- 10. Make four different bamboo craft items from four of the following categories (all four items must NOT be from the same category): --> | <!-- 10. Make four different bamboo craft items from four of the following categories (all four items must NOT be from the same category): --> | ||
| − | |||
<noinclude></translate></noinclude> | <noinclude></translate></noinclude> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | <noinclude>< | + | <noinclude><translate><!--T:80--> |
| − | + | </noinclude> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<!--T:44--> | <!--T:44--> | ||
| Line 205: | Line 176: | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| + | <!--T:81--> | ||
<noinclude></translate></noinclude> | <noinclude></translate></noinclude> | ||
| − | |||
{{CloseReq}} <!-- 10 --> | {{CloseReq}} <!-- 10 --> | ||
<noinclude><translate></noinclude> | <noinclude><translate></noinclude> | ||
==References== <!--T:46--> | ==References== <!--T:46--> | ||
| + | <noinclude></translate></noinclude> | ||
| − | + | [[Category:AY Honors/noindex{{GetLangSuffix}}|{{SUBPAGENAME}}]] | |
| − | [[Category: | + | {{CloseHonorPage}} |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 00:15, 18 August 2024
1
Bamboo belongs to the grass family Gramineae (also called Poaceae), subfamily Bambusoideae. There are about 60 to 70 genera and over 1200 species in the world of bamboo. The bamboo plant is a fast growing giant grass with woody stems. It is an evergreen that will grow all year round.
According to the Guinness Book of World’s Records, bamboo is the fastest growing plant on earth. Although Guinness does not identify a particular species, they report a growth rate of 35 inches a day. Other sources claim that bamboo can grow more than a meter in a day.
2
3
Bamboo grows in both tropical and temperate climates in Asia, on islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans, and also in Africa and South America. It requires a fertile moisture retentive soil that doesn’t get waterlogged. It will grow well in most soil except alkaline soils, dry desert and marsh. Only a few species can grow in fairly cold weather that is below 20 degrees Celsius.
The adaptability of the bamboo is admirable as you can find them growing in plains, hilly regions, and even high altitude mountainous areas.
4
The giant bamboo species can reach a height of 20 to 40 meters (130 feet). The culms of some bamboo species grow as quickly as 1 foot or 0.3 meters per day. Some are capable of growing 2 feet (24 inches or 60 cm) or more per day.
5
Most bamboos rarely flower and they produce seeds only after 30-60 years and sometimes after over 120 years of growth. Some only flower once in their lifetime. A few bamboo species do flower annually.
6
Bamboo stands for elasticity, resilience, endurance and tenacity (strength). The bamboo stem bends in the breeze but does not break. The leaves are moved by the wind but do not fall. The plant always survives and conquers even a storm.
The plant reminds us of the need to compromise when it is necessary, to yield for the moment but eventually to go forward unbroken from all opposition.
In the Chinese culture, the bamboo is a symbol of modest virtue because of its humble droopy leaves and empty culm (stem).
7
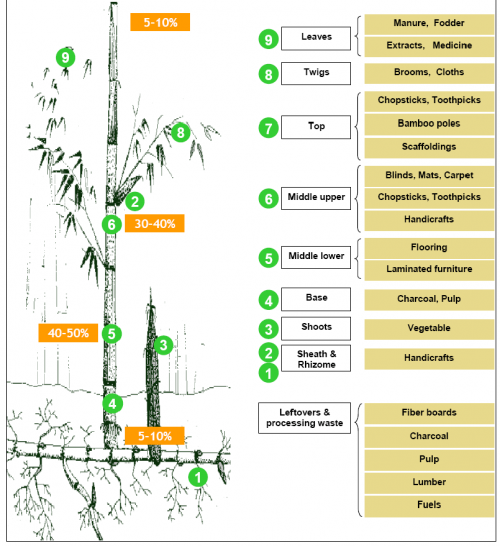
Almost every part of the bamboo can be used either as food, fodder, medicine, paper, fuel, lumber or to be made into useful objects. Seeds are eaten as grain and the young shoots of the some bamboos are eaten, especially in East Asian cuisines. The raw leaves are a fodder for livestock.
The Panda bear feeds exclusively on bamboo.
The pulped fibres are used to make fine quality paper.
Bamboo can be made into charcoal. Bamboo charcoal comes from pieces of bamboo plants, harvested after at least five years, and burned in ovens at temperatures ranging from 800 to 1200 °C.
The jointed stems of bamboo provide materials for houses and rafts.
The hollow quality of the bamboo is ideal for making wind instruments like the flute and Sompoton, as well as percussion instruments like the Angklung.
Bamboo rods are often used as fishing poles.
8
Because bamboo is tough and durable, it needs to be handled properly with the right tools like axes, saws, coping saws and splitters. Sandpaper is needed to polish off the sharp edges of cut bamboo so as to prevent injury. Glue can be used to join different parts of the bamboo together. A drill will be needed to make any items that have holes in it such as a flute.
9
When bamboo is split open, it can be very sharp at the edges and the edges can cut you easily. Bamboo dust can cause irritation to the eyes. Upon skin contact, it may also cause allergic contact dermatitis in sensitized individuals.
Upon inhalation, bamboo dust may also cause nasal obstruction and dryness as well as irritation leading to coughing, sneezing, wheezing and sinusitis. It may also aggravate pre-existing respiratory conditions or allergies.
10
- A decorative item. Example: candle holder, picture frame, flower pot holder (planter), water wheel, wind chime
- A kitchen utensil item. Example: cup, ladle, spoon, butter knife, basket, tea cup, mug, mat, tray, pot holder, chopsticks, food cover
- A stationery item. Example: letter opener, pencil container, coin container
- A musical instrument. Example: flute, whistle, rattler, xylophone, percussion instrument
- A piece of furniture. Example: chair, stool, table, divider, bar set
- A utility item. Example: back scratcher, clothes hanger, cloth peg, lamp shade, rope ladder, basket, hat, identification tag
- A toy item. Example: miniature furniture, animals, plane, car
- Different Bamboo Crafts