Difference between revisions of "AY Honors/Flags/Answer Key/es"
(Created page with "; Estados Unidos") |
(Updating to match new version of source page) |
||
| (9 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{HonorSubpage}} | {{HonorSubpage}} | ||
<!--{{Honor Master|honor={{#titleparts:{{PAGENAME}}|1|3}}|master=Family, Origins, and Heritage|group=options}}--> | <!--{{Honor Master|honor={{#titleparts:{{PAGENAME}}|1|3}}|master=Family, Origins, and Heritage|group=options}}--> | ||
| − | <section begin="Body" /> | + | <section begin="Body" /> |
{{ansreq|page={{#titleparts:{{PAGENAME}}|2|1}}|num=1}} | {{ansreq|page={{#titleparts:{{PAGENAME}}|2|1}}|num=1}} | ||
<noinclude></noinclude> | <noinclude></noinclude> | ||
| Line 147: | Line 147: | ||
{{ansreq|page={{#titleparts:{{PAGENAME}}|2|1}}|num=6c}} | {{ansreq|page={{#titleparts:{{PAGENAME}}|2|1}}|num=6c}} | ||
<noinclude></noinclude> | <noinclude></noinclude> | ||
| − | {{: | + | {{:AY Honors/Pathfinder Emblem Meaning/es}} |
<noinclude></noinclude> | <noinclude></noinclude> | ||
| Line 253: | Line 253: | ||
{{clear}} | {{clear}} | ||
| − | + | {{clear}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | {{clear}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
{{clear}} | {{clear}} | ||
| − | + | {{clear}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | {{clear}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | {{clear}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| Line 297: | Line 272: | ||
{{clear}} | {{clear}} | ||
| − | + | {{clear}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | {{clear}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | {{clear}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | {{clear}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | {{clear}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
{{clear}} | {{clear}} | ||
| Line 364: | Line 323: | ||
[[File:Flag of Canada.svg|thumb|Bandera de Canadá]] | [[File:Flag of Canada.svg|thumb|Bandera de Canadá]] | ||
| − | + | {{clear}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | {{clear}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | {{clear}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | {{clear}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | {{clear}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ====Los Estados Unidos (excluyendo a Puerto Rico y las Islas Vírgenes de los EE.UU., que son parte de la División Interamericana)==== | |
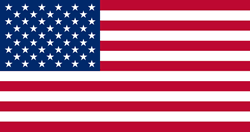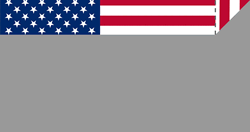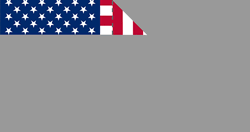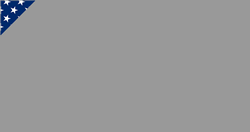
| − | === | + | [[File:Flag of the United States.svg|thumb|Bandera de los Estados Unidos]] |
| − | [[File:Flag of the United States.svg|thumb| | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | {{clear}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | {{clear}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | {{clear}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | {{clear}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | {{clear}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | {{clear}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | {{clear}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | {{clear}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | {{clear}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | (estos tres últimos países se encuentran en libre asociación con los Estados Unidos, y junto con los tres territorios de los Estados Unidos del Pacífico forman la Misión de Guam-Micronesia, que se convirtió en parte de la División Norteamericana en 2011.) | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ===Otras partes del mundo=== | |
| − | + | Puede ver una lista de países asociadas actualmente con otras divisiones y regiones adjuntas [http://www.adventist.org/es/iglesia-mundial aquí]. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | <noinclude></noinclude> | |
| − | <noinclude | ||
| − | |||
{{CloseReq}} <!-- 10 --> | {{CloseReq}} <!-- 10 --> | ||
| − | <noinclude> | + | <noinclude></noinclude> |
| − | </noinclude> | + | ==Referencias== |
| − | == | + | <noinclude></noinclude> |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | <noinclude | ||
| − | |||
| − | [[Category:Adventist Youth Honors Answer Book/Do at home | + | [[Category:Adventist Youth Honors Answer Book/Do at home{{GetLangSuffix}}]] |
{{CloseHonorPage}} | {{CloseHonorPage}} | ||
Latest revision as of 01:48, 4 January 2023
1
Una bandera es una pieza de material con un diseño distintivo que es generalmente rectangular y se utiliza como un símbolo, como un dispositivo de señalización o decoración adjunto a una orilla de un poste o una cuerda.
2
2a
Es la para superior de la bandera cerca del asta, o una bandera con un diseño en el área del cantón. La parte azul con estrellas en la bandera de los Estados Unidos es el cantón, pero no hay cantón en la bandera canadiense.
2b
Es el color de fondo de la bandera, la parte entre al asta y el pendiente.
2c
Un ornamento encima del asta, sea en un poste fijo - como en una escuela - o un poste diseñado para llevar la bandera en un desfile.
2d
Generalmente cuando una bandera se usa al aire libre, está en un mástil o un asta.
2e
La parte de la bandera que está más lejos del asta.
2f
La parte de la bandera que aletea en el viento y a veces se deteriora.
2g
Es una cuerda o cable que se utiliza para subir y bajar una bandera en un asta.
2h
La parte de la bandera que está más cercano a la asta de bandera.
2i
El mecanismo que conecta el pináculo al poste.
3
Mientras que algunas instrucciones específicas difieren un poco entre los países, lo que sigue es casi una verdad universal:
- La bandera nacional debe estar por encima de cualquier otra bandera
- La bandera nacional nunca debe tocar el suelo
- Se debe mostrar respeto a la bandera - incluyendo el saludo a la bandera
- Banderas hechas andrajos no se deben mostrar o exhibir pero deberán eliminarse de forma privada, preferiblemente con fuego
4
El procedimiento para doblar la bandera nacional varía según el país. Si su país y bandera no está en esta lista, por favor siéntase libre de investigar y agregarlo a la lista.
Bermuda
El protocolo de la bandera para Bermuda debe seguir el mismo que del Reino Unido porque es un territorio británico.
Canadá
No existe un método oficial de doblar la bandera para el uso diario. Hay, sin embargo, un método similar a la utilizada en los Estados Unidos cuando se dobla una bandera para fines ceremoniales tal como un funeral. Más información (sólo disponibles en inglés) se puede encontrar en la página web de Canadian Directorate of History and Heritage (Dirección Canadiense de Historia y Patrimonio).
Reino Unido
Hay dos métodos utilizados generalmente en doblar la bandera británica. El primero se llama Romper y se usa generalmente durante izamiento de la bandera. La bandera británica se dobla por la mitad a lo largo (a lo largo de la franja roja central de la Cruz de San Jorge) y luego por la mitad, con el doblez llegando al borde. El último tercio de la bandera se dobla hacia dentro y luego el resto se enrolla hacia el lado al asta. La bandera se fija con un pedazo de algodón ligero o cuerda. Cuando izada, un fuerte tirón de la driza se romperá la cadena y permitirá que la bandera vuele libre.
El otro método es generalmente usado cuando la bandera cubre a un ataúd. La manera de doblarla es similar al que se usa en los Estados Unidos. Además de estos, no hay otros métodos oficiales para doblar la bandera británica. Debe ser izada y bajada con respeto, y que no toque el suelo.
Los Estados Unidos
Title 4 Chapter 1 of the United States Code, conocido como el protocolo de la bandera estadounidense, adoptado por primera vez en 1924 y modificado hasta el presente, regula la etiqueta de la bandera para una variedad de circunstancias que garantiza que el símbolo nacional sea tratado adecuadamente.
5
5a
5b
5c
5d
5e
6
6a
Elena Hobbs creó la bandera de Conquistadores. El escudo del Club de Conquistadores fue diseñado por Juan H. Hancock.
6b
Vea la bandera al lado para una guía.
6c
- Rojo (Sacrificio)
- Nos recuerda a Cristo. Juan 3:16, Romanos 12:1
- Dorado (Excelencia)
- Medida estándar. El Club de Conquistadores tiene altos estándares para ayudar a edificar un carácter fuerte para el reino de los cielos. Apocalipsis 3:18
- Blanco (Pureza)
- Deseamos tener la pureza y rectitud de la vida de Cristo en nuestras vidas. Apocalipsis 3:5
- Azul (Lealtad)
- Es el propósito del Club de Conquistadores ayudar a enseñarnos a ser leales a nuestro Dios en el cielo, a nuestros padres y a nuestra iglesia.
- Tres Lados (Totalidad)
- Divinidad Total - Padre, Hijo, Espíritu Santo. Mateo 28:19-20
- Triple base educativa:
- Mental - Niveles progresivos y especialidades
- Física - Campamentos, obreros, enfoque de salud
- Espiritual - Actividades misioneras, testificación
- Escudo (Protección)
- En las Escrituras, Dios es frecuentemente llamado el Escudo de su pueblo. Génesis 15:1, Efesios 6:16
- Espada (Biblia)
- La espada es usada en la guerra. Una batalla es siempre ganada por ofensa. Nosotros estamos en una batalla contra el pecado y nuestra arma es la Palabra de Dios. Efesios 6:17
- Triángulo Invertido
- El orden inverso de importancia enseñado por Jesús, que es contrario a las enseñanzas del mundo.
- El sacrificio del «yo» al colocar las necesidades de los otros delante de las nuestras.
- Club de Conquistadores
- El Club de Conquistadores es una de las organizaciones del ministerio juvenil de la Iglesia Adventista del Séptimo Día.
7
La simplicidad de la bandera cristiana hace esta parte fácil.
7a
La bandera tiene un campo blanco, con una cruz latina roja dentro de un cantón azul. El tono del color rojo en la cruz simboliza la sangre que Cristo derramó en el Calvario. El color azul representa las aguas del bautismo, así como la fidelidad de Cristo. El color blanco representa la pureza de Cristo. En la vexilología convencional, una bandera blanca significa rendirse, una referencia a la descripción bíblica de la actitud pacífica y la rendición de Cristo. Las dimensiones de la bandera y el cantón no tienen especificaciones oficiales.
7b
La cruz representa la muerte de Jesús, para que podamos vivir para siempre. La cruz es un símbolo reconocible instantáneo del cristianismo.
8
8a
Cuando se muestra la bandera nacional en campamentos, debe colocarse a la izquierda de los que entran al campamento y a la derecha de los que están acampando. Cuando todas las banderas se muestran en un asta, la bandera nacional está en la parte superior, y después la bandera JA y la bandera de Conquistadores.
8b
Para un programa de Día del Conquistador, la bandera nacional se debe mostrar a la derecha del orador si está en la plataforma. Otras banderas deben mostrarse a la izquierda del orador.
8c
Si se muestran las banderas en otro lugar, con excepción de la plataforma, la bandera nacional debe aparecer a la derecha de la audiencia, mirando hacia la plataforma. Otras banderas deben estar a la izquierda de la audiencia.
8d
Banderas deben colocarse a la derecha de la caseta y a la izquierda del inspector. Si la bandera nacional es parte de un grupo de banderas, debe estar en el centro y un poco hacia adelante o en relieve. En las ferias públicas, banderas pueden estar puestos dentro de la caseta, pero la bandera nacional está siempre a la izquierda del espectador.
8e
A la derecha de la audiencia.
9
- Estados Unidos
Las rayas rojas y blancas representan las 13 colonias originales. Las 50 estrellas representan los 50 estados. El número de estrellas aumenta si se agrega más estados.
- Otros países
Si su país no está alistado aquí, puede investigar la información y agregarla aquí. La historia de las banderas nacionales es fácil de encontrar por medio de Internet.
10
La Igesia Adventista ha dividido el mundo en 13 distritos administrativos llamadas Divisiones.
División Norteamericana
La División Norteamericana está compuesta de 10 naciones y territorios:
Bermuda
Canadá
Los Estados Unidos (excluyendo a Puerto Rico y las Islas Vírgenes de los EE.UU., que son parte de la División Interamericana)
(estos tres últimos países se encuentran en libre asociación con los Estados Unidos, y junto con los tres territorios de los Estados Unidos del Pacífico forman la Misión de Guam-Micronesia, que se convirtió en parte de la División Norteamericana en 2011.)
Otras partes del mundo
Puede ver una lista de países asociadas actualmente con otras divisiones y regiones adjuntas aquí.