Difference between revisions of "AY Honors/Cats/Answer Key"
Jomegat bot (talk | contribs) m (honor_header -> honor_desc) |
m |
||
| (26 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{HonorSubpage}} |
| − | | | + | <!--{{Honor_Master|honor=Cats|master=Naturalist|group=Domestic}}--> |
| − | | | + | <!--{{Honor_Master|honor=Cats|master=Zoology|group=Domestic}}--> |
| − | | | + | <section begin="Body" /> |
| − | | | ||
| − | | | ||
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | == 1. What is the scientific name of the cat family? | + | {{ansreq|page={{#titleparts:{{PAGENAME}}|2|1}}|num=1}} |
| − | + | <noinclude><translate><!--T:42--> | |
| + | </noinclude> | ||
| + | <!-- 1. What is the scientific name of the cat family? --> | ||
| + | The scientific name of the cat family is ''Felidae'' or ''Feli''. | ||
| − | == 2. How is the structure of the paw similar in all cats? | + | <!--T:43--> |
| − | + | <noinclude></translate></noinclude> | |
| + | {{CloseReq}} <!-- 1 --> | ||
| + | {{ansreq|page={{#titleparts:{{PAGENAME}}|2|1}}|num=2}} | ||
| + | <noinclude><translate><!--T:44--> | ||
| + | </noinclude> | ||
| + | <!-- 2. How is the structure of the paw similar in all cats? --> | ||
| + | Cats have five toes on each of the front paws, and four toes on each of the back paws. Their claws are retractable, and they have soft pads on the bottom of each paw. | ||
| + | <!--T:45--> | ||
| + | <noinclude></translate></noinclude> | ||
| + | {{CloseReq}} <!-- 2 --> | ||
| + | {{ansreq|page={{#titleparts:{{PAGENAME}}|2|1}}|num=3}} | ||
| + | <noinclude><translate><!--T:46--> | ||
| + | </noinclude> | ||
| + | <!-- 3. How are the eyes of all cats alike? --> | ||
| + | Cat's pupils are wide open in the dark, and contract to slits when exposed to the light. The back of the eye is coated with a reflecting surface. | ||
| − | + | <!--T:16--> | |
| − | + | In low light levels the cats pupil must be able to open as wide as possible, but also be able to contract to very small size to protect the sensitive retina in bright sunlight. In human eyes, this size variation of the pupil is controlled by a circular ciliary muscle, but this limits the amount of size variation. In cats however, the same process is controlled by two, shutter-like ciliary muscles, which gives the cat it’s characteristic slit-like pupil in bright light conditions. All cats pupils are therefore elliptical. However, the pupils of some (notably the ‘Big Cats’) appear more circular when dilated. | |
| − | == 4. What is the main food of the cat family? How are the cat's teeth fitted for this? | + | <!--T:47--> |
| − | + | <noinclude></translate></noinclude> | |
| + | {{CloseReq}} <!-- 3 --> | ||
| + | {{ansreq|page={{#titleparts:{{PAGENAME}}|2|1}}|num=4}} | ||
| + | <noinclude><translate><!--T:48--> | ||
| + | </noinclude> | ||
| + | <!-- 4. What is the main food of the cat family? How are the cat's teeth fitted for this? --> | ||
| + | The main food of the cat family is meat. They have four front canine teeth for biting and tearing, and knife-edged teeth on sides for cutting skin and muscle. | ||
| + | <!--T:49--> | ||
| + | <noinclude></translate></noinclude> | ||
| + | {{CloseReq}} <!-- 4 --> | ||
| + | {{ansreq|page={{#titleparts:{{PAGENAME}}|2|1}}|num=5}} | ||
| + | <noinclude><translate><!--T:50--> | ||
| + | </noinclude> | ||
| + | <!-- 5. Of what use are the cat's whiskers? --> | ||
| + | Cat's whiskers are connected to sensitive nerves, and act like extra fingers for feeling things. | ||
| − | + | <!--T:17--> | |
| − | + | The whiskers on the cat are specialized sensory hairs grouped in three specific locations on the cats head. The ''supercilary'' whiskers are positioned above the eyes, the ''genal'' whiskers to the rear of the cats cheek area and the ''mystacial'' whiskers, which are the longest and most prominent are located on either side of the cat's muzzle. The mystacial whiskers are primarily used as an alternative sensing mechanism when the eyes are no longer effective (i.e. in the dark). It is now believed that there is a link between sensory and visual input in the cat and that a degree of parallel processing takes place within the brain. This can be demonstrated by simply touching the end of the whiskers – the automatic response is for the cat to blink. | |
| + | <!--T:18--> | ||
| + | The extreme sensitivity of the hairs can register very small changes in air pressure thus enabling the cat to avoid objects while moving around in the dark. It is thought that the whiskers may also be used to establish the position of prey and to help locate the exact position for the killing bite. | ||
| − | + | <!--T:19--> | |
| − | + | Interestingly, cheetahs, who mainly hunt by day, have less developed whiskers than many other 'night hunting' cats. | |
| + | <!--T:20--> | ||
| + | Cats are able to change the position of their whiskers depending on what they are doing - at rest the whiskers are elongated, at 90% to the head, whilst when walking they are tilted forward to aid their sensing ability. | ||
| − | == | + | <!--T:51--> |
| − | + | <noinclude></translate></noinclude> | |
| + | {{CloseReq}} <!-- 5 --> | ||
| + | {{ansreq|page={{#titleparts:{{PAGENAME}}|2|1}}|num=6}} | ||
| + | <noinclude><translate><!--T:52--> | ||
| + | </noinclude> | ||
| + | <!-- 6. How are the cat's ears protected? --> | ||
| + | Cats have hair on the inside of their ears to catch debris. Also, their ears can be folded down flat. | ||
| − | == | + | <!--T:53--> |
| − | + | <noinclude></translate></noinclude> | |
| + | {{CloseReq}} <!-- 6 --> | ||
| + | {{ansreq|page={{#titleparts:{{PAGENAME}}|2|1}}|num=7}} | ||
| + | <noinclude><translate><!--T:54--> | ||
| + | </noinclude> | ||
| + | <!-- 7. Identify from pictures or personal observation four kinds of domesticated cats. Describe each one's temperament. --> | ||
| + | <gallery> | ||
| + | image:Abyssinian_cat.png|Abyssinian | ||
| + | Image:Koscat2.jpg|American Shorthair | ||
| + | image:Egy_mau.jpg|Egyptian Mau | ||
| + | Image:Cream tabby exotic cat.jpg|Exotic | ||
| + | Image:White Maine Coon.jpg|Maine Coon | ||
| + | Image:Gatto persiano Ettore-2.jpg|Persian | ||
| + | Image:RussianBlueCat.jpg|Russian Blue | ||
| + | Image:Traditionalsiameses.jpg|Siamese | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| − | + | <!--T:21--> | |
| − | + | ;The Abyssinian: has a distinctly ticked, tawny coat. It has large almond-shaped green or gold eyes with a fine dark line around them, and large ears. The coat is generally a warm golden color, but "Abbys" can also be blue, fawn, cinnamon and red. There is also a Silver Abyssinian variant whose coat shows shades of white, cream and grey. Abyssinians are very active, friendly, curious and playful, but are usually not "lap cats"; they are too preoccupied exploring and playing; they are "busy" cats, and can get bored and depressed without daily activity and attention. Many Abyssinians enjoy heights, and will explore their surroundings in three dimensions, from the floor to their owner's shoulders to the top of the highest furniture. They are highly intelligent, and probably the most independent of any domestic breed. | |
| − | + | <!--T:22--> | |
| − | + | ;The American Shorthair: is the most popular and most prevalent breed of American cat. American Shorthairs are medium to large sized cats, with powerful legs and strong paws. Their muzzle is squarish. Their coat is short, with the fur being thick, dense, and stiff to protect them from cold, moisture, and superficial skin injuries. Their coat thickens up in the winter and sheds in the spring but still remains lighter and slimmer than its close cousin, the British Shorthair. American Shorthairs are very affectionate, long-living, and disinclined to behavioral problems; they get along well with other family members, including dogs. The American Shorthair is also an excellent hunter, but its sunny and gentle disposition make it ideal for families with small children. Shorthairs tend to get overweight very easily. | |
| − | + | <!--T:23--> | |
| − | + | ;Egyptian Maus: are a medium-sized short-haired cat breed. They are the only naturally spotted breed of domesticated cat. The spots on an Egyptian Mau are not just on the coat; a shaved Mau has spots on its skin. Maus often possess very musical voices. They are known to chirp, chortle and emit other distinctly unusual vocalizations when stimulated. Another behavior, quite common in happy Maus, has been described as "wiggle-tail." The cat, male or female, moves its back legs up and down, and appears to be marking territory, but it is not actually releasing urine. Even veteran Mau owners are known to check after a joyous Mau does this little dance. | |
| − | + | <!--T:24--> | |
| − | + | ;The Exotic: has a compact, rounded, powerfully-built body with a short, thick "linebacker" neck. Its large round eyes, short snub nose, sweet facial expression, and small ears give it an appearance that many people consider cute. He looks like a little teddy-bear. The Exotic Shorthair has a gentle and calm personality reminiscent of the Persian, but he is livelier than his longhaired ancestor. Curious and playful, he is friendly to other cats and dogs. Easygoing and quiet, as he rarely meows. He doesn’t like being left alone, he needs the presence of his owner, but he’s always independent. They tend to show more affection and loyalty than most breeds and make excellent lap cats. Their calm and steady nature makes them ideal apartment cats for city dwellers. Nonetheless, Exotics retain some of the energetic spark of their American Shorthair forbears and they are often capable mouse hunters. | |
| − | == References == | + | <!--T:25--> |
| − | *[[Wikijunior Big Cats]] | + | ;The Maine Coon: is one of the largest breeds of domestic cat, known for its intelligence, playfulness as well as distinctive physical appearance. The breed is one of the oldest natural breeds in North America and originated from New England, making it America's first indigenous show cat.Maine Coons are a breed distinguished by intelligence, dexterity and playfulness. They have a tendency to use their front paws extensively (often curling the paw round to pick objects up) and as a consequence will easily learn to open cabinet doors, turn on water faucets, or pick up small objects. Some Maine Coons will eat with their paws, rather than eating from the bowl itself. Due to their above-average intelligence, Maine Coons are known to be one of the easiest cat breeds to train. Maine Coons are generally very quiet and do not meow much. However, they are noted for their ability to trill their meows, which sounds like a combination of a purr and a meow, and they tend to make this sound when happy or startled. Maine Coons are a very independent breed, and they do not often "beg" for attention. They are noted for rarely eating alone, preferring to eat in the company of other cats or humans. Maine Coons are usually not "lap" cats, and many Maine Coons, probably because of their size, are not comfortable with sitting on a person's lap or chest, though this may depend on the personality of the individual cat. Some Maine Coons enjoy playing with, but not usually in, water. They may dip toys in their water bowls before playing with them, or just tip the water bowl over. They may also skim their paws across the surface of their water bowl. Maine Coons occasionally engage in mischievous behavior when bored, such as deliberately pushing things off tables and the tops of fridges with their paws. Maine Coons can be very dog-like in their behavior. Playing fetch is a favorite game. As with dogs, they will bring their ball, drop it at the feet of their intended playmate and wait patiently for the ball to be thrown. Unlike other cat breeds, Main Coons tend to enjoy car rides and will often pant and be obsessed with looking out the windows. Maine Coon Cats are wonderful family cats as they enjoy "just hanging out". |
| + | |||
| + | <!--T:26--> | ||
| + | ;A Persian: has an extremely long thick coat, short legs, a wide head with the ears set far apart, large eyes, and an extremely foreshortened muzzle. The breed was originally established with a short (but not non-existent) muzzle, but over time this feature has become extremely exaggerated. Persians are very gentle and easy-going cats, adapting well to changing environments. Their hair is too long for them to groom themselves, so they do require daily brushing or their hair gets matted and tangled. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!--T:27--> | ||
| + | ;The Russian Blue: has a lean medium-sized body and a short, plush, blue coat. The colour is a blueish-gray that is the dilute expression of the black gene. The coat is unique to the breed as it is a double coat, with the undercoat being soft and downy, and the longer guard hairs an even blue with silver tips. This "tipping" gives the coat a shimmering appearance. Its eyes are green and often are dark and vivid. These cats are highly intelligent and playful but tend to be shy around strangers. They also develop a close bond with their human companions. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!--T:28--> | ||
| + | ;Siamese: cats have a creamy base coat with coloured points on their muzzles, ears, paws and lower legs, and tails. The Siamese voice, which they use frequently, is unlike that of other breeds, and has been compared to the cries of a human baby. As they are "wired for sound", they can meow loud enough to compete with fire and rescue equipment. The Siamese temperament is legendary: like all Oriental cats Siamese are active, playful, extremely vocal and persistent in demanding attention. They usually get on well with other cats, especially other Siamese or related breeds, but they also have a great need for human companionship and often will engage in crazy antics to get the attention of their people. Siamese cats are generally believed to be highly intelligent, and their behavior usually reflects this. Siamese are often described as "dog-like" because of their loyalty, often attaching themselves to one human in a household, and their trainability--they can be taught to walk on a leash, fetch and perform tricks. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!--T:29--> | ||
| + | The table below summarizes the 8 classifications of domestic cats (including the moggie, which is non-pedigreed) | ||
| + | {| border=1 cellspacing=1 cellpadding=8 align="center" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |a) ||Longhair Persian ||b) || British & American Shorthairs | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |c) ||Longhairs non-Persian ||d) || Other Shorthair breeds | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |e) ||Oriental Shorthairs ||f) || Siamese | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |g) ||Burmese ||h) || Moggie (non-pedigreed) | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!--T:55--> | ||
| + | <noinclude></translate></noinclude> | ||
| + | {{CloseReq}} <!-- 7 --> | ||
| + | {{ansreq|page={{#titleparts:{{PAGENAME}}|2|1}}|num=8}} | ||
| + | <noinclude><translate><!--T:56--> | ||
| + | </noinclude> | ||
| + | <!-- 8. Of what benefit to man are domesticated cats? --> | ||
| + | Cats catch mice and provide friendship. They are used in China and Japan to protect silkworm cocoons from rats. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!--T:57--> | ||
| + | <noinclude></translate></noinclude> | ||
| + | {{CloseReq}} <!-- 8 --> | ||
| + | {{ansreq|page={{#titleparts:{{PAGENAME}}|2|1}}|num=9}} | ||
| + | <noinclude><translate></noinclude> | ||
| + | <!-- 9. Identify from pictures or personal observation seven kinds of wild cats. Tell in what part of the world they are found. --> | ||
| + | ===Caracal=== <!--T:58--> | ||
| + | [[image:Caracal.jpg|thumb|left|400px|Caracal]] | ||
| + | Caracals are distributed over Africa and West Asia. Their habitat is dry steppes and semi-deserts, but also woodlands, savanna, and scrub forest. They are solitary, or paired, territorial cats. | ||
| + | <br style="clear:both"/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Cheetah=== <!--T:30--> | ||
| + | [[image:Cheetah_in_Kenya.jpg|thumb|left|400px|Cheetah]] | ||
| + | [[Image:cheetah range.png|thumb|right|Places where cheetahs live are colored green.]] | ||
| + | <br style="clear:both"/> | ||
| + | Today, most cheetahs are found in sub-Saharan Africa, though a few are still seen in Iran. In the past, they used to be found throughout northern India and Iran. They prefer to live in semi-deserts, savannas, prairies, and thick brush. Because they rely upon speed to hunt, they avoid dense forests. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Jaguar=== <!--T:31--> | ||
| + | [[image:Panthera_onca.jpg|thumb|400px|left|Jaguar]] | ||
| + | [[Image:jaguar range.png|thumb|right|Places where jaguars live are colored green.]] | ||
| + | <br style="clear:both"/> | ||
| + | Jaguars live in the rain forests and more open countryside in South and Central America, and are the largest members of the cat family there. Jaguars are strong swimmers and climbers, and they often prefer to live by rivers, in swamps, and in dense forest with thick cover for stalking prey. Jaguars once lived as far north as the southwestern United States. Some of these cats are once again migrating north from Mexico. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Leopard=== <!--T:32--> | ||
| + | [[image:Leopard_on_the_tree.jpg|thumb|left|400px|Leopard]] | ||
| + | [[File:Leopard prevalence.png|thumb|right|Places where leopards live are colored red.]] | ||
| + | <br style="clear:both"/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!--T:33--> | ||
| + | Leopards live in the Middle East, parts of Asia, and Africa. This means they live in more places than any other big cat. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Lion=== <!--T:34--> | ||
| + | [[File:Just one lion.jpg|thumb|400px|left|Lion]] | ||
| + | [[Image:Lion_distribution.svg|thumb|right|Places where lions live are colored green.]] | ||
| + | <br style="clear:both"/> | ||
| + | Despite the nickname ''King of the Jungle'', most lions live on the flat, grassy plains called ''savannas''. In ancient times, lions roamed nearly every continent. Today, they can commonly be found across central and southern Africa. There is also a small population in the Gir forest of India on the continent of Asia. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Lynx=== <!--T:35--> | ||
| + | [[Image:Lynx lynx poing.jpg|thumb|400px|left|Lynx]] | ||
| + | [[Image:lynx range.png|thumb|right|Places where lynx live are colored green.]] | ||
| + | The four species of lynx are very widespread. The European Lynx lives in northern Europe and Asia. The Canadian Lynx lives in North America. The Iberian (or Spanish) Lynx is one of the most highly endangered cats and only lives in wild parts of Spain. Bobcats are the smallest type of lynx, living in North America. Because they hunt small prey, they live in a wide variety of habitats. | ||
| + | <br style="clear:both"/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Ocelot=== <!--T:36--> | ||
| + | [[Image:Ocelot.jpg|thumb|400px|left|Ocelot]] | ||
| + | [[Image:Ocelot range.png|thumb|right|Places where ocelots live are colored green]] | ||
| + | Ocelots mostly live in South and Central America, but there are some as far north as the very southern reaches of the United States of America. There are eleven different types (or ''subspecies'') of ocelot. These live in different parts of the south of the Americas. | ||
| + | <br style="clear:both"/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Puma=== <!--T:37--> | ||
| + | [[Image:MountainLion.jpg|thumb|400px|left|Puma]] | ||
| + | [[Image:Puma range.png|thumb|right|Places pumas live are colored green]] | ||
| + | Pumas are widely spread in North, Central and South America. They can be seen in a variety of habitats from desert to forest all the way from northern British Columbia in the north to the southern end of the Andes mountain range. Pumas were driven out of the eastern half of North America by human pressure; a small population remains in Florida and occasionally there are puma sightings in other eastern states. Other names for Pumas are Catamount, Mountain Lion, Cougar, and Panther. | ||
| + | <br style="clear:both"/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Serval=== <!--T:38--> | ||
| + | [[Image:Serengeti Serval.jpg|thumb|400px|left|Serval]] | ||
| + | [[Image:serval range.png|thumb|right|Places where servals live are colored green.]] | ||
| + | <br style="clear:both"/> | ||
| + | Servals live in the ''savannas'' (grasslands) of Africa. This allows them to see both their prey and their predators. As a medium sized cat they have to be wary of lions and hyenas. Servals are good swimmers and often live near open water where they can take an occasional dip to hunt for fish or swipe at the birds that stop by. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Tiger=== <!--T:39--> | ||
| + | [[Image:Panthera tigris tigris.jpg|thumb|400px|left|Tiger]] | ||
| + | [[Image:Tigers.png|thumb|right|Places where tigers live are marked in dark green]] | ||
| + | <br style="clear:both"/> | ||
| + | Tigers live in forests and grasslands of eastern and southeastern Asia. They live in countries such as Bangladesh, Bhutan, China, India, Nepal, Cambodia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Thailand and Vietnam, Indonesia (Sumatra), and the Russian Far East. The Bengal Tiger is the national animal of India. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Wild cat=== <!--T:40--> | ||
| + | [[Image:Wildkatze 002.jpg|thumb|400px|left|Wild cat]] | ||
| + | The European Wild Cat lives in forests of Western, Central and Eastern Europe, as well as in Scotland and Turkey; it is not found in Scandinavia, Iceland, England, Wales, or Ireland. The African Wild Cat is found in deserts and savannas of Africa and the Arabian peninsula. The Asiatic Wild Cat primarily inhabits the scrub desert of Central Asia. | ||
| + | <br style="clear:both"/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!--T:59--> | ||
| + | <noinclude></translate></noinclude> | ||
| + | {{CloseReq}} <!-- 9 --> | ||
| + | {{ansreq|page={{#titleparts:{{PAGENAME}}|2|1}}|num=10}} | ||
| + | <noinclude><translate><!--T:60--> | ||
| + | </noinclude> | ||
| + | <!-- 10. What animal is known as the king of beasts? Why does it have that title? What is its temperament really like? --> | ||
| + | The lion is known as the ''king of the beasts''. This goes back as far as recorded history, for the Greek word for ''lion'' is translated as ''king'' in Latin. The lion gets this distinction because it fears no other animal. It is also said that the lion is named ''king of the beasts'' because of its courage and loyalty. Its courage cannot be doubted, but a lion is not particularly loyal. Male lions are known to take over another male's pride of females by chasing away (or killing) the resident male(s). They often form ''coalitions'' of two to five males and work together to oust other males. When they succeed in doing this, they then kill any cubs in the pride so that the females will be receptive to breeding sooner. The females sometimes attempt to defend their cubs, but this is rarely met with success. These coalitions of males do not limit their activities to a single pride either. A coalition may dominate several prides within their range. Not exactly a model of loyalty! (But then again, neither are human kings). | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!--T:61--> | ||
| + | <noinclude></translate></noinclude> | ||
| + | {{CloseReq}} <!-- 10 --> | ||
| + | {{ansreq|page={{#titleparts:{{PAGENAME}}|2|1}}|num=11}} | ||
| + | <noinclude><translate><!--T:62--> | ||
| + | </noinclude> | ||
| + | <!-- 11. Tell the story of Androcles and the lion. --> | ||
| + | Androcles was a Roman slave who escaped and took refuge in a cave. One day, a lion entered the cave, limping badly. Androcles examined its paw and removed a large thorn. The lion became cured and tamed by Androcles and also lived in the cave with Androcles until Androcles was later re-captured. Androcles was tried and sentenced to be torn to pieces by a hungry lion. On the fateful day, the lion, chosen to destroy him, began to lick his face and hands with obvious affection instead of eating him. It was the same lion that Androcles befriended in the cave. The authorities were moved by this show of affection. The king pardoned and set Androcles free. They also allowed Androcles to keep the lion as a companion and he walked the streets of Rome with it. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!--T:63--> | ||
| + | <noinclude></translate></noinclude> | ||
| + | {{CloseReq}} <!-- 11 --> | ||
| + | {{ansreq|page={{#titleparts:{{PAGENAME}}|2|1}}|num=12}} | ||
| + | <noinclude><translate><!--T:64--> | ||
| + | </noinclude> | ||
| + | <!-- 12. Relate four stories in the Bible in which a member of the cat family is mentioned. --> | ||
| + | * Samson and the lion. (Judges 14) | ||
| + | * David killed a lion and a bear (1 Samuel 17:36) | ||
| + | * Lion killed a disobedient prophet. (1 Kings 13) | ||
| + | * Benaiah killed a lion in a snowy pit. (1 Chronicles 11:22) | ||
| + | * Calf and the lion will lie down together in heaven. (Isaiah 11:6,7) | ||
| + | * Can a leopard change his spots? (Jeremiah 13:23) | ||
| + | * Daniel and the Lion's Den (Daniel 6) | ||
| + | * Daniel's dream of the lion with wings and leopard with four heads. (Daniel 7) | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!--T:65--> | ||
| + | <noinclude></translate></noinclude> | ||
| + | {{CloseReq}} <!-- 12 --> | ||
| + | <noinclude><translate></noinclude> | ||
| + | == References == <!--T:14--> | ||
| + | *[[wikibooks:Wikijunior Big Cats]] | ||
*Google big cat's eyes | *Google big cat's eyes | ||
| + | <noinclude></translate></noinclude> | ||
| − | [[Category:Adventist Youth Honors Answer Book | + | [[Category:Adventist Youth Honors Answer Book/Do at home{{GetLangSuffix}}]] |
| − | + | {{CloseHonorPage}} | |
Latest revision as of 17:00, 3 January 2023
1
The scientific name of the cat family is Felidae or Feli.
2
Cats have five toes on each of the front paws, and four toes on each of the back paws. Their claws are retractable, and they have soft pads on the bottom of each paw.
3
Cat's pupils are wide open in the dark, and contract to slits when exposed to the light. The back of the eye is coated with a reflecting surface.
In low light levels the cats pupil must be able to open as wide as possible, but also be able to contract to very small size to protect the sensitive retina in bright sunlight. In human eyes, this size variation of the pupil is controlled by a circular ciliary muscle, but this limits the amount of size variation. In cats however, the same process is controlled by two, shutter-like ciliary muscles, which gives the cat it’s characteristic slit-like pupil in bright light conditions. All cats pupils are therefore elliptical. However, the pupils of some (notably the ‘Big Cats’) appear more circular when dilated.
4
The main food of the cat family is meat. They have four front canine teeth for biting and tearing, and knife-edged teeth on sides for cutting skin and muscle.
5
Cat's whiskers are connected to sensitive nerves, and act like extra fingers for feeling things.
The whiskers on the cat are specialized sensory hairs grouped in three specific locations on the cats head. The supercilary whiskers are positioned above the eyes, the genal whiskers to the rear of the cats cheek area and the mystacial whiskers, which are the longest and most prominent are located on either side of the cat's muzzle. The mystacial whiskers are primarily used as an alternative sensing mechanism when the eyes are no longer effective (i.e. in the dark). It is now believed that there is a link between sensory and visual input in the cat and that a degree of parallel processing takes place within the brain. This can be demonstrated by simply touching the end of the whiskers – the automatic response is for the cat to blink.
The extreme sensitivity of the hairs can register very small changes in air pressure thus enabling the cat to avoid objects while moving around in the dark. It is thought that the whiskers may also be used to establish the position of prey and to help locate the exact position for the killing bite.
Interestingly, cheetahs, who mainly hunt by day, have less developed whiskers than many other 'night hunting' cats.
Cats are able to change the position of their whiskers depending on what they are doing - at rest the whiskers are elongated, at 90% to the head, whilst when walking they are tilted forward to aid their sensing ability.
6
Cats have hair on the inside of their ears to catch debris. Also, their ears can be folded down flat.
7
- The Abyssinian
- has a distinctly ticked, tawny coat. It has large almond-shaped green or gold eyes with a fine dark line around them, and large ears. The coat is generally a warm golden color, but "Abbys" can also be blue, fawn, cinnamon and red. There is also a Silver Abyssinian variant whose coat shows shades of white, cream and grey. Abyssinians are very active, friendly, curious and playful, but are usually not "lap cats"; they are too preoccupied exploring and playing; they are "busy" cats, and can get bored and depressed without daily activity and attention. Many Abyssinians enjoy heights, and will explore their surroundings in three dimensions, from the floor to their owner's shoulders to the top of the highest furniture. They are highly intelligent, and probably the most independent of any domestic breed.
- The American Shorthair
- is the most popular and most prevalent breed of American cat. American Shorthairs are medium to large sized cats, with powerful legs and strong paws. Their muzzle is squarish. Their coat is short, with the fur being thick, dense, and stiff to protect them from cold, moisture, and superficial skin injuries. Their coat thickens up in the winter and sheds in the spring but still remains lighter and slimmer than its close cousin, the British Shorthair. American Shorthairs are very affectionate, long-living, and disinclined to behavioral problems; they get along well with other family members, including dogs. The American Shorthair is also an excellent hunter, but its sunny and gentle disposition make it ideal for families with small children. Shorthairs tend to get overweight very easily.
- Egyptian Maus
- are a medium-sized short-haired cat breed. They are the only naturally spotted breed of domesticated cat. The spots on an Egyptian Mau are not just on the coat; a shaved Mau has spots on its skin. Maus often possess very musical voices. They are known to chirp, chortle and emit other distinctly unusual vocalizations when stimulated. Another behavior, quite common in happy Maus, has been described as "wiggle-tail." The cat, male or female, moves its back legs up and down, and appears to be marking territory, but it is not actually releasing urine. Even veteran Mau owners are known to check after a joyous Mau does this little dance.
- The Exotic
- has a compact, rounded, powerfully-built body with a short, thick "linebacker" neck. Its large round eyes, short snub nose, sweet facial expression, and small ears give it an appearance that many people consider cute. He looks like a little teddy-bear. The Exotic Shorthair has a gentle and calm personality reminiscent of the Persian, but he is livelier than his longhaired ancestor. Curious and playful, he is friendly to other cats and dogs. Easygoing and quiet, as he rarely meows. He doesn’t like being left alone, he needs the presence of his owner, but he’s always independent. They tend to show more affection and loyalty than most breeds and make excellent lap cats. Their calm and steady nature makes them ideal apartment cats for city dwellers. Nonetheless, Exotics retain some of the energetic spark of their American Shorthair forbears and they are often capable mouse hunters.
- The Maine Coon
- is one of the largest breeds of domestic cat, known for its intelligence, playfulness as well as distinctive physical appearance. The breed is one of the oldest natural breeds in North America and originated from New England, making it America's first indigenous show cat.Maine Coons are a breed distinguished by intelligence, dexterity and playfulness. They have a tendency to use their front paws extensively (often curling the paw round to pick objects up) and as a consequence will easily learn to open cabinet doors, turn on water faucets, or pick up small objects. Some Maine Coons will eat with their paws, rather than eating from the bowl itself. Due to their above-average intelligence, Maine Coons are known to be one of the easiest cat breeds to train. Maine Coons are generally very quiet and do not meow much. However, they are noted for their ability to trill their meows, which sounds like a combination of a purr and a meow, and they tend to make this sound when happy or startled. Maine Coons are a very independent breed, and they do not often "beg" for attention. They are noted for rarely eating alone, preferring to eat in the company of other cats or humans. Maine Coons are usually not "lap" cats, and many Maine Coons, probably because of their size, are not comfortable with sitting on a person's lap or chest, though this may depend on the personality of the individual cat. Some Maine Coons enjoy playing with, but not usually in, water. They may dip toys in their water bowls before playing with them, or just tip the water bowl over. They may also skim their paws across the surface of their water bowl. Maine Coons occasionally engage in mischievous behavior when bored, such as deliberately pushing things off tables and the tops of fridges with their paws. Maine Coons can be very dog-like in their behavior. Playing fetch is a favorite game. As with dogs, they will bring their ball, drop it at the feet of their intended playmate and wait patiently for the ball to be thrown. Unlike other cat breeds, Main Coons tend to enjoy car rides and will often pant and be obsessed with looking out the windows. Maine Coon Cats are wonderful family cats as they enjoy "just hanging out".
- A Persian
- has an extremely long thick coat, short legs, a wide head with the ears set far apart, large eyes, and an extremely foreshortened muzzle. The breed was originally established with a short (but not non-existent) muzzle, but over time this feature has become extremely exaggerated. Persians are very gentle and easy-going cats, adapting well to changing environments. Their hair is too long for them to groom themselves, so they do require daily brushing or their hair gets matted and tangled.
- The Russian Blue
- has a lean medium-sized body and a short, plush, blue coat. The colour is a blueish-gray that is the dilute expression of the black gene. The coat is unique to the breed as it is a double coat, with the undercoat being soft and downy, and the longer guard hairs an even blue with silver tips. This "tipping" gives the coat a shimmering appearance. Its eyes are green and often are dark and vivid. These cats are highly intelligent and playful but tend to be shy around strangers. They also develop a close bond with their human companions.
- Siamese
- cats have a creamy base coat with coloured points on their muzzles, ears, paws and lower legs, and tails. The Siamese voice, which they use frequently, is unlike that of other breeds, and has been compared to the cries of a human baby. As they are "wired for sound", they can meow loud enough to compete with fire and rescue equipment. The Siamese temperament is legendary: like all Oriental cats Siamese are active, playful, extremely vocal and persistent in demanding attention. They usually get on well with other cats, especially other Siamese or related breeds, but they also have a great need for human companionship and often will engage in crazy antics to get the attention of their people. Siamese cats are generally believed to be highly intelligent, and their behavior usually reflects this. Siamese are often described as "dog-like" because of their loyalty, often attaching themselves to one human in a household, and their trainability--they can be taught to walk on a leash, fetch and perform tricks.
The table below summarizes the 8 classifications of domestic cats (including the moggie, which is non-pedigreed)
| a) | Longhair Persian | b) | British & American Shorthairs |
| c) | Longhairs non-Persian | d) | Other Shorthair breeds |
| e) | Oriental Shorthairs | f) | Siamese |
| g) | Burmese | h) | Moggie (non-pedigreed) |
8
Cats catch mice and provide friendship. They are used in China and Japan to protect silkworm cocoons from rats.
9
Caracal
Caracals are distributed over Africa and West Asia. Their habitat is dry steppes and semi-deserts, but also woodlands, savanna, and scrub forest. They are solitary, or paired, territorial cats.
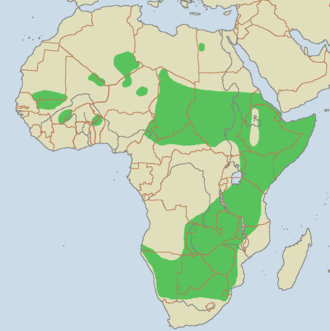
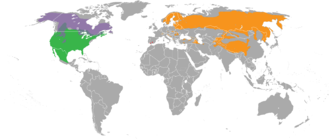
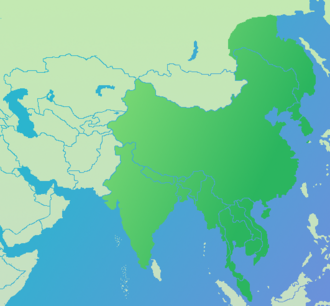
Cheetah
Today, most cheetahs are found in sub-Saharan Africa, though a few are still seen in Iran. In the past, they used to be found throughout northern India and Iran. They prefer to live in semi-deserts, savannas, prairies, and thick brush. Because they rely upon speed to hunt, they avoid dense forests.
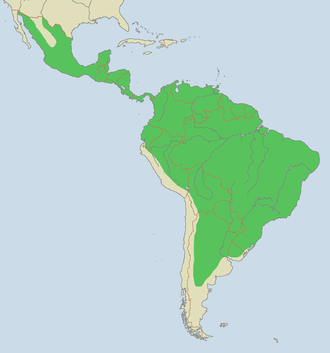
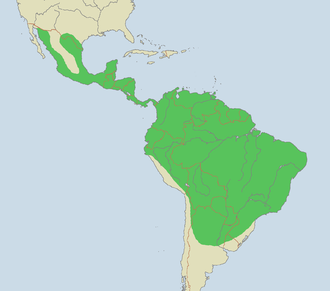
Jaguar
Jaguars live in the rain forests and more open countryside in South and Central America, and are the largest members of the cat family there. Jaguars are strong swimmers and climbers, and they often prefer to live by rivers, in swamps, and in dense forest with thick cover for stalking prey. Jaguars once lived as far north as the southwestern United States. Some of these cats are once again migrating north from Mexico.
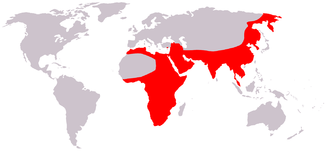
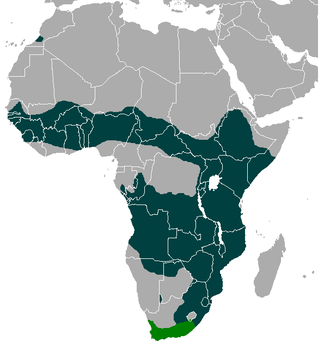
Leopard
Leopards live in the Middle East, parts of Asia, and Africa. This means they live in more places than any other big cat.
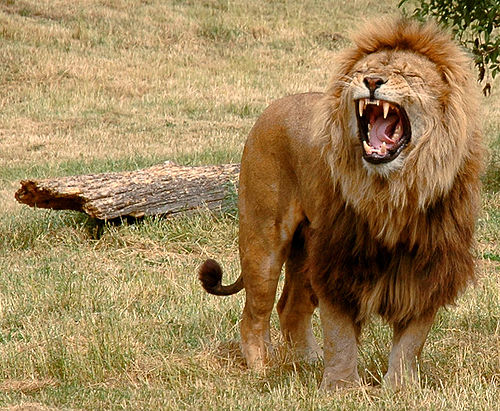
Lion
Despite the nickname King of the Jungle, most lions live on the flat, grassy plains called savannas. In ancient times, lions roamed nearly every continent. Today, they can commonly be found across central and southern Africa. There is also a small population in the Gir forest of India on the continent of Asia.
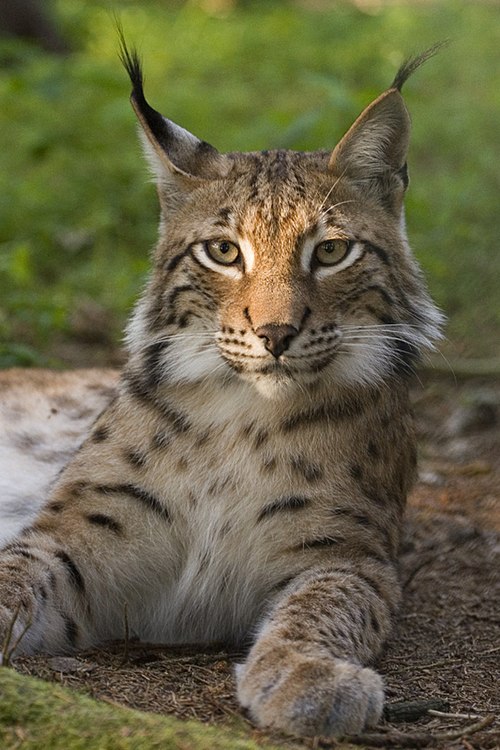
Lynx
The four species of lynx are very widespread. The European Lynx lives in northern Europe and Asia. The Canadian Lynx lives in North America. The Iberian (or Spanish) Lynx is one of the most highly endangered cats and only lives in wild parts of Spain. Bobcats are the smallest type of lynx, living in North America. Because they hunt small prey, they live in a wide variety of habitats.
Ocelot
Ocelots mostly live in South and Central America, but there are some as far north as the very southern reaches of the United States of America. There are eleven different types (or subspecies) of ocelot. These live in different parts of the south of the Americas.
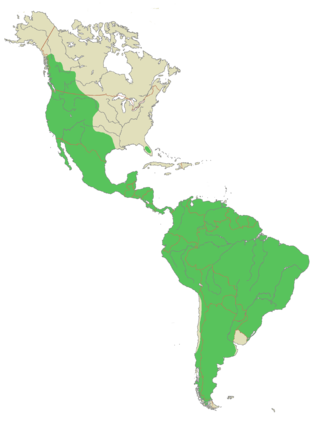
Puma
Pumas are widely spread in North, Central and South America. They can be seen in a variety of habitats from desert to forest all the way from northern British Columbia in the north to the southern end of the Andes mountain range. Pumas were driven out of the eastern half of North America by human pressure; a small population remains in Florida and occasionally there are puma sightings in other eastern states. Other names for Pumas are Catamount, Mountain Lion, Cougar, and Panther.
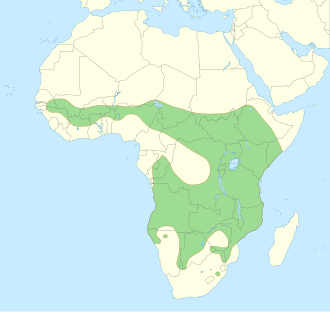
Serval
Servals live in the savannas (grasslands) of Africa. This allows them to see both their prey and their predators. As a medium sized cat they have to be wary of lions and hyenas. Servals are good swimmers and often live near open water where they can take an occasional dip to hunt for fish or swipe at the birds that stop by.
Tiger
Tigers live in forests and grasslands of eastern and southeastern Asia. They live in countries such as Bangladesh, Bhutan, China, India, Nepal, Cambodia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Thailand and Vietnam, Indonesia (Sumatra), and the Russian Far East. The Bengal Tiger is the national animal of India.
Wild cat
The European Wild Cat lives in forests of Western, Central and Eastern Europe, as well as in Scotland and Turkey; it is not found in Scandinavia, Iceland, England, Wales, or Ireland. The African Wild Cat is found in deserts and savannas of Africa and the Arabian peninsula. The Asiatic Wild Cat primarily inhabits the scrub desert of Central Asia.
10
The lion is known as the king of the beasts. This goes back as far as recorded history, for the Greek word for lion is translated as king in Latin. The lion gets this distinction because it fears no other animal. It is also said that the lion is named king of the beasts because of its courage and loyalty. Its courage cannot be doubted, but a lion is not particularly loyal. Male lions are known to take over another male's pride of females by chasing away (or killing) the resident male(s). They often form coalitions of two to five males and work together to oust other males. When they succeed in doing this, they then kill any cubs in the pride so that the females will be receptive to breeding sooner. The females sometimes attempt to defend their cubs, but this is rarely met with success. These coalitions of males do not limit their activities to a single pride either. A coalition may dominate several prides within their range. Not exactly a model of loyalty! (But then again, neither are human kings).
11
Androcles was a Roman slave who escaped and took refuge in a cave. One day, a lion entered the cave, limping badly. Androcles examined its paw and removed a large thorn. The lion became cured and tamed by Androcles and also lived in the cave with Androcles until Androcles was later re-captured. Androcles was tried and sentenced to be torn to pieces by a hungry lion. On the fateful day, the lion, chosen to destroy him, began to lick his face and hands with obvious affection instead of eating him. It was the same lion that Androcles befriended in the cave. The authorities were moved by this show of affection. The king pardoned and set Androcles free. They also allowed Androcles to keep the lion as a companion and he walked the streets of Rome with it.
12
- Samson and the lion. (Judges 14)
- David killed a lion and a bear (1 Samuel 17:36)
- Lion killed a disobedient prophet. (1 Kings 13)
- Benaiah killed a lion in a snowy pit. (1 Chronicles 11:22)
- Calf and the lion will lie down together in heaven. (Isaiah 11:6,7)
- Can a leopard change his spots? (Jeremiah 13:23)
- Daniel and the Lion's Den (Daniel 6)
- Daniel's dream of the lion with wings and leopard with four heads. (Daniel 7)
References
- wikibooks:Wikijunior Big Cats
- Google big cat's eyes