Difference between revisions of "AY Honors/Parrots and Cockatoos/Answer Key"
m (- Category of AYHAB) |
|||
| (147 intermediate revisions by 13 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{HonorSubpage}} |
| − | | | + | <!--{{Honor_Master|honor=Parrots and Cockatoos|master=Zoology|group=Domestic}}--> |
| − | | | + | <section begin="Body" /> |
| − | | | + | {{ansreq|page={{#titleparts:{{PAGENAME}}|2|1}}|num=1}} |
| − | + | <noinclude><translate></noinclude> | |
| − | | | + | <!-- 1. Name 15 species of parrot and five species of cockatoo that are common to Australia and be able to identify them from real life or pictures. --> |
| − | | | + | ===Parrots=== <!--T:43--> |
| − | + | <gallery perrow="3" width=90%> | |
| − | + | Image:Psephotus chrysopterygius1.jpg|Golden-shouldered Parrot<br>''Psephotus chrysopterygius'' | |
| − | + | Image:Longbilledcorella.jpg|Long-billed Corella<br>''Cacatua tenuirostris'' | |
| − | + | File:Neophema chrysogaster male - Melaleuca.jpg|Orange-bellied Parrot<br>''Neophema chrysogaster'' | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | | | ||
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | <!--T:2--> | |
| + | Image:Eclectus Parrot02 - melbourne zoo.jpg|Eclectus Parrot (Male)<br>''Eclectus roratus'' | ||
| + | Image:Eclectus roratus -female side2.jpg|Eclectus Parrot (Female)<br>''Eclectus roratus'' | ||
| + | Image:Alisterus scapularis - Australian King Parrot pair.jpg|Australian King Parrot<br>''Alisterus scapularis'' | ||
| − | + | <!--T:3--> | |
| + | Image:Double-Eyed Fig Parrot.JPG|Double-Eyed Fig-Parrot<br>''Cyclopsitta diophthalma'' | ||
| + | Image:Redrumpedparrot.jpg|Red-rumped Parrot<br>''Psephotus haematonotus'' | ||
| + | Image:Turquoise Parrot-01.jpg|Turquoise Parrot<br>''Neophema pulchella'' | ||
| − | + | <!--T:4--> | |
| + | Image:Mallee Ringneck Bowra.jpg|Australian Ringneck<br>''Barnardius zonarius'' | ||
| + | Image:Rock Parrot Cape Leeuwin 2 email.jpg|Rock Parrot<br>''Neophema petrophila'' | ||
| + | Image:Red Shining-parrot.jpg|Red Shining-parrot<br>''Prosopeia tabuensis'' | ||
| − | + | <!--T:5--> | |
| + | Image:Platycercus icterotis1.jpg|Western Rosella<br>''Platycercus icterotis'' | ||
| + | Image:Crimson Rosella (Platycercus elegans) -Mt Buffalo2.jpg|Crimson Rosella<br>''Platycercus elegans'' | ||
| + | Image:Platycercus venustus.jpg|Northern Rosella<br>''Platycercus venustus'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!--T:6--> | ||
| + | Image:Red-Capped-Parrot 0004 flat web.jpg|Red-capped Parrot<br>''Purpureicephalus spurius'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!--T:7--> | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Cockatoos=== <!--T:8--> | ||
| + | Cockatoos share many features with other parrots including the characteristic curved beak shape and a zygodactyl foot, with two forward toes and two backwards toes. They differ, however in a number of characteristics, including the often spectacular movable headcrest, the presence of a gall bladder and some other anatomical details, and their lack of the Dyck texture feather composition which causes the bright blues and greens seen in true parrots. Also Cockatoo species are, on average, larger than the average size of true parrots. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!--T:9--> | ||
| + | <gallery perrow="3" width=90%> | ||
| + | Image:Palm Cockatoo.JPG|Palm Cockatoo<br>''Probosciger aterrimus'' | ||
| + | Image:Gang-gang female MJC01.jpg|Gang-gang Cockatoo<br> ''Callocephalon fimbriatum'' | ||
| + | Image:Cockatoo.1.arp.500pix.jpg|Umbrella Cockatoo<br>''Cacatua alba'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!--T:10--> | ||
| + | Image:Glossy black cockatoo male kobble08.JPG|Glossy Black Cockatoo<br>''Calyptorhynchus lathami'' | ||
| + | Image:Cacatua leadbeateri.jpg|Major Mitchell's Cockatoo<br>''Lophocroa leadbeateri'' | ||
| + | Image:Sulphur Crested 02.jpg|Sulphur-crested Cockatoo<br>''Cacatua galerita'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!--T:11--> | ||
| + | Image:Red-tailed Black Cockatoo (Calyptorhynchus banksii) on Casuarina tree.jpg|Red-tailed Black Cockatoo<br>''Calyptorhynchus banksii'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!--T:12--> | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!--T:44--> | ||
| + | <noinclude></translate></noinclude> | ||
| + | {{CloseReq}} <!-- 1 --> | ||
| + | {{ansreq|page={{#titleparts:{{PAGENAME}}|2|1}}|num=2}} | ||
| + | <noinclude><translate></noinclude> | ||
| + | <!-- 2. Name two species of parrot that builds its nest in a termite mound and tell where each is found. --> | ||
| + | ===Golden-shouldered Parrot=== <!--T:45--> | ||
| + | [[Image:Psephotus chrysopterygius1.jpg|thumb|200px|left|Male and female Golden-shouldered Parrots in an aviary at the Queensland Museum]] | ||
| + | The Golden-shouldered Parrot (''Psephotus chrysopterygius'') is a rare bird of southern Cape York Peninsula, in Queensland, Australia. It measures 26 cm long and weighs between 54-56 g. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!--T:14--> | ||
| + | The Golden-shouldered Parrot lives in open forest, where it feeds on small grass seeds, principally those of firegrass. An important habitat requirement is the provision of terrestrial termite mounds, which the bird uses for nesting. This has led to the parrot also being known as the Antbed Parrot. They will preferentially seek out taller mounds (up to 2 m high), and will dig a burrow into them when the mound has been softened by the rains. A long tunnel is dug down into the mound, and capped off by a nesting chamber. The clutch size is between 3-6 eggs, which are incubated for 20 days. The mound regulates the temperature in the chamber, keeping it high enough that the eggs can be left unattended while the parents feed. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!--T:15--> | ||
| + | The Golden-shouldered Parrot is listed as endangered (CITES I). The species has a restricted range and suffers from a variety of threats, including predation by feral cats, tourist disturbance, and a change in burning regime in the grasslands upon whose seeds it depends. The wild population is around 3000 birds, with around 1500 held in captivity in Australia. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Grey-cheeked Parakeet=== <!--T:16--> | ||
| + | The Grey-cheeked parakeet (Brotogeris pyrrhoptera), less commonly known as fire-winged parakeet, is a species of parrot in the Psittacidae family. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!--T:17--> | ||
| + | The grey-cheeked parakeet is indigenous to northwestern Peru and western Ecuador, living in subtropical or tropical regions encompassing dry forests, moist lowland forests, shrubland, and arable land.[2] Grey-cheeked parakeets do not build their nests in the canopies of trees. Rather, they prefer to build their nests in protected areas such as active termite mounds or tree hollows. It is yet unknown why termites tolerate their presence. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!--T:18--> | ||
| + | The grey-cheeked parakeet now faces habitat loss due to the irresponsible smuggling of pet birds and hunting due to their destruction of banana plantations. The species is now endangered with most populations existing within the homes of private individuals as pets. Because of this, efforts have been undertaken to save this and several other species of Brotogeris endemic to the region. It is protected by the Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species of Wild Animals (also called the Bonn Convention or CMS). | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!--T:19--> | ||
| + | Even in its native home, the grey-cheeked parakeet is widely kept as a pet. With patience, these birds may be taught to mimic human sounds, albeit without the clarity of larger parrots. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Green-rumped Parrotlet=== <!--T:20--> | ||
| + | [[Image:GR parrotlet.jpg|thumb|200px|left|Green-rumped Parrotlet]] | ||
| + | The Green-rumped Parrotlet, ''Forpus passerinus'', is a small parrot. It is a resident breeding bird in tropical South America, from Caribbean regions of Colombia, Venezuela and Trinidad south and east to the Guianas and Brazil, on the downstream Amazon River. It has been introduced in Jamaica, Curaçao, Barbados and Tobago, and was not recorded on Trinidad prior to 1916. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!--T:21--> | ||
| + | Its habitat is open forest and scrub. The female lays five to seven white eggs in a hole in a termite nest, tree cavity, or even hollow pipe, and incubates the clutch for 18 days to hatching, with about another five weeks to fledging. | ||
| + | {{clear}} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | <!--T:46--> | |
| + | <noinclude></translate></noinclude> | ||
| + | {{CloseReq}} <!-- 2 --> | ||
| + | {{ansreq|page={{#titleparts:{{PAGENAME}}|2|1}}|num=3}} | ||
| + | <noinclude><translate><!--T:47--> | ||
| + | </noinclude> | ||
| + | <!-- 3. Where in Australia would you find each of the following and describe the natural diet of each. --> | ||
| + | <noinclude></translate></noinclude> | ||
| + | {{ansreq|page={{#titleparts:{{PAGENAME}}|2|1}}|num=3a}} | ||
| + | <noinclude><translate><!--T:48--> | ||
| + | </noinclude> | ||
| + | [[Image:Longbilledcorella.jpg|thumb|200px|left|Long Billed Corella]][[Image:Bird range long-billed corella.png|thumb|200px|right|Long Billed Corella range (in red)]] | ||
| + | The Long-billed Corella, ''Cacatua tenuirostris'', is a cockatoo native to Australia. Species are mostly white, with a pink face and forehead. They also have faintly pink feathers on the breast and belly, and yellow on the underside of the wings and tail. The birds have a long white beak, which is used to dig for roots and seeds. | ||
| − | + | <!--T:23--> | |
| − | + | {{clear}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | == | + | <!--T:49--> |
| + | <noinclude></translate></noinclude> | ||
| + | {{CloseReq}} <!-- 3a --> | ||
| + | {{ansreq|page={{#titleparts:{{PAGENAME}}|2|1}}|num=3b}} <!--T:24--> | ||
| + | <noinclude><translate><!--T:50--> | ||
| + | </noinclude> | ||
| + | [[Image:Palm Cockatoo.JPG|thumb|200px|left|Great Palm Cackatoo]] | ||
| + | [[Image:Bird range palm cockatoo.png|thumb|200px|right|Range of the Great Palm Cackatoo (in red)]] | ||
| + | The Palm Cockatoo (''Probosciger aterrimus'') is distributed in rainforests and woodlands of New Guinea and northern Queensland, Australia. It measures around 55-60 cm in length and weighs between 500-1,000 g. It is a distinctive bird with a large crest and has one of the largest bills of any parrots (only the Hyacinth Macaw's is larger). The bill is unusual as the lower and upper mandibles do not meet for much of its length, allowing the tongue to hold a nut against the top mandible while the lower mandible works to open it. | ||
| + | {{clear}} | ||
| − | < | + | <!--T:51--> |
| − | Image: | + | <noinclude></translate></noinclude> |
| − | Image:Gang-gang male | + | {{CloseReq}} <!-- 3b --> |
| − | Image: | + | {{ansreq|page={{#titleparts:{{PAGENAME}}|2|1}}|num=3c}} <!--T:25--> |
| + | <noinclude><translate><!--T:52--> | ||
| + | </noinclude> | ||
| + | [[Image:Gang-gang female MJC01.jpg|thumb|200px|left|Gang-gang Cockatoo]] | ||
| + | [[Image:Bird range gang-gang cockatoo.png|thumb|200px|right|Range of the Gang-gang Cockatoo (in red)]] | ||
| + | The Gang-gang Cockatoo, Callocephalon fimbriatum, is found in the cooler and wetter forests and woodlands of Australia, particularly alpine bushland. Mostly mild grey in colour with some lighter scalloping (more pronounced and buffish in females) the male has a red head and crest, while the female has a small fluffy grey crest. It ranges throughout south-eastern Australia and Tasmania. The Gang-gang Cockatoo is the faunal emblem of the Australian Capital Territory. It is easily identified by its distinctive call, which is described as resembling a creaky gate, or the sound of a cork being pulled from a bottle. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!--T:26--> | ||
| + | Gang-gang cockatoos eat fruits, and seem to have a particular weakness for Hawthorn berries (though Hawthorns are an introduced species, and not part of the cockatoo's natural diet). | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!--T:53--> | ||
| + | <noinclude></translate></noinclude> | ||
| + | {{CloseReq}} <!-- 3c --> | ||
| + | {{CloseReq}} <!-- 3 --> | ||
| + | {{ansreq|page={{#titleparts:{{PAGENAME}}|2|1}}|num=4}} | ||
| + | <noinclude><translate><!--T:54--> | ||
| + | </noinclude> | ||
| + | <!-- 4. Which three species of cockatoo are known as the most rare? --> | ||
| + | <gallery perrow=3 widths=200px> | ||
| + | Image:Yellow-crested Cockatoo.jpg|Yellow-crested Cockatoo<br>''Cacatua sulphurea'' | ||
| + | Image:Cacatua-haematuropygia.jpg|Red-vented Cockatoo<br>''Cacatua haematuropygia'' | ||
| + | Image:Moluccan cockatoo 31l07.JPG|Moluccan Cockatoo<br>''Cacatua moluccensis'' | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| + | ;Yellow-crested Cockatoo: The Yellow-crested Cockatoo, ''Cacatua sulphurea,'' is critically endangered. Numbers have declined dramatically due to illegal trapping for the cage-bird trade. The current population is estimated at less than 10,000. It is listed on Appendix I of CITES. | ||
| + | ;Red-vented Cockatoo: This bird, ''Cacatua haematuropygia'', is critically endangered. Populations have decreased dramatically due to illegal trapping for the cage-bird trade. The high price fetched per bird (c.US$160 in Manila in 1997) means that chicks are taken from virtually every accessible nest. Loss of habitat may also have contributed to its decline. The current population is estimated at less than 4,000 birds. | ||
| + | ;Moluccan Cockatoo: The Moluccan Cockatoo, ''Cacatua moluccensis,'' is an endangered species, and has been listed on appendix I of CITES since 1989, which makes trade in wild-caught birds illegal. Trade in captive bred birds is legal only with appropriate CITES certification. Numbers have declined due to illegal trapping for the cage-bird trade and habitat loss. During the height of the trapping of this species over 6,000 birds were being removed from the wild per year. It has a stronghold in Manusela National Park on Seram, although even today some illegal trapping continues. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!--T:55--> | ||
| + | <noinclude></translate></noinclude> | ||
| + | {{CloseReq}} <!-- 4 --> | ||
| + | {{ansreq|page={{#titleparts:{{PAGENAME}}|2|1}}|num=5}} | ||
| + | <noinclude><translate><!--T:56--> | ||
| + | </noinclude> | ||
| + | <!-- 5. Which is the largest species in the Rosella family? Where does it come from and what is its usual food? --> | ||
| + | [[Image:Green Rosella eating plucked flowers.jpg|thumb|200px|Green Rosella]] | ||
| + | The Green Rosella or Tasmanian Rosella (Platycercus caledonicus) is endemic to Tasmania. The largest of the Rosellas it is predominantly green and yellow in plumage with blue cheeks. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!--T:29--> | ||
| + | Its diet consists mostly of seeds, fruits, and berries, and it will sometimes feed on the ground. | ||
| + | {{clear}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!--T:57--> | ||
| + | <noinclude></translate></noinclude> | ||
| + | {{CloseReq}} <!-- 5 --> | ||
| + | {{ansreq|page={{#titleparts:{{PAGENAME}}|2|1}}|num=6}} | ||
| + | <noinclude><translate><!--T:58--> | ||
| + | </noinclude> | ||
| + | <!-- 6. Every State of Australia has a Rosella that is common to that State. Some are found in more than one State but there is one that is commonly associated with your State. Which is it? --> | ||
| + | {| border=1 cellspacing=1 cellpadding=5 width=90% align="center" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | !style="background:#00e0e0"|State of Australia | ||
| + | !style="background:#00e0e0"| Associated Rosella | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |style="background:#80dfdf"|New South Wales | ||
| + | |style="background:#80dfdf"| Crimson Rosella | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |style="background:#a0ffff"|Queensland | ||
| + | |style="background:#a0ffff"|Pale-headed Rosella | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |style="background:#80dfdf"|South Australia | ||
| + | |style="background:#80dfdf"|Adelaide Rosella | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |style="background:#a0ffff"|Tasmania | ||
| + | |style="background:#a0ffff"| Green Rosella | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |style="background:#80dfdf"|Victoria | ||
| + | |style="background:#80dfdf"|Crimson Rosella | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |style="background:#a0ffff"|Western Australia | ||
| + | |style="background:#a0ffff"|Western Rosella | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!--T:59--> | ||
| + | <noinclude></translate></noinclude> | ||
| + | {{CloseReq}} <!-- 6 --> | ||
| + | {{ansreq|page={{#titleparts:{{PAGENAME}}|2|1}}|num=7}} | ||
| + | <noinclude><translate><!--T:60--> | ||
| + | </noinclude> | ||
| + | <!-- 7. When the Eclectus parrot was first found it was thought that the Male and Female were of different species. Why was this? Where are they found and what is their usual diet? --> | ||
| + | [[Image:Eclectus Parrot02 - melbourne zoo.jpg|thumb|200px|left|Male Eclectus Parrot]] | ||
| + | [[Image:Eclectus roratus -female side2.jpg|thumb|200px|right|Female Ecletus Parrot]] | ||
| + | The Eclectus Parrot, Eclectus roratus, is a parrot native to the Solomon Islands, New Guinea, northeastern Australia and the Maluku Islands (Moluccas). It is unusual in the parrot family the males and females are so different from one another. The males of the species are bright green, having bright candy-corn-colored upper mandibles and black lower mandibles, and blue or red tail and wing feathers; while the females have red heads and blue to purple breasts, with black beaks. Joseph Forshaw, in his book Parrots of the World, noted that the first European ornithologists to see Eclectus Parrots thought they were of two distinct species. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!--T:32--> | ||
| + | The diet of the eclectus in the wild consists of mainly fruits, unripe nuts, flower and leaf buds, and some seeds. Two favorite fruits are the pomegranate and the papaya (pawpaw) with seeds. In captivity, they will eat most fruits including mangos, figs, guavas, bananas, any melons, stone fruits (peaches etc.), grapes, citrus fruits, pears and apples. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!--T:61--> | ||
| + | <noinclude></translate></noinclude> | ||
| + | {{CloseReq}} <!-- 7 --> | ||
| + | {{ansreq|page={{#titleparts:{{PAGENAME}}|2|1}}|num=8}} | ||
| + | <noinclude><translate><!--T:62--> | ||
| + | </noinclude> | ||
| + | <!-- 8. What Australian cockatoo is regarded as the most beautiful in the world? Describe what it looks like and where it is found. --> | ||
| + | [[Image:Leadbeater cockatoo 31l07.JPG|thumb|200px|left|Major Mitchell's Cockatoo]] | ||
| + | [[Image:Bird range major mitchells cockatoo.png|thumb|200px|right|Range of Major Mitchell's Cockatoo]] | ||
| + | With its soft-textured white and salmon-pink plumage and large, bright red and yellow crest, Major Mitchell's Cockatoo is generally recognised as the most beautiful of all cockatoos. It is named in honour of Major Sir Thomas Mitchell, who wrote "Few birds more enliven the monotonous hues of the Australian forest than this beautiful species whose pink-coloured wings and flowing crest might have embellished the air of a more voluptuous region". | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!--T:34--> | ||
| + | It is restricted to arid and semi-arid inland areas of Australia (see map). | ||
| + | {{clear}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!--T:63--> | ||
| + | <noinclude></translate></noinclude> | ||
| + | {{CloseReq}} <!-- 8 --> | ||
| + | {{ansreq|page={{#titleparts:{{PAGENAME}}|2|1}}|num=9}} | ||
| + | <noinclude><translate><!--T:64--> | ||
| + | </noinclude> | ||
| + | <!-- 9. Name four different Lorikeets and tell why they all have brush tongues. --> | ||
| + | Lories and lorikeets are small to medium-sized arboreal parrots which comprise the subfamily Loriinae. They are widely distributed throughout the Australasian region, including south-eastern Asia, Polynesia, Papua New Guinea and Australia, and the majority have very brightly colored plumage. | ||
| + | <gallery perrow=4 width=90%> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!--T:36--> | ||
| + | Image:BlackWingedLorikeet.jpg|Black-winged Lory | ||
| + | Image:RainbowLorikeetOregonZoo.jpg|Green-naped Lorikeet (subspecies of Rainbow Lorikeet) | ||
| + | Image:Scalybreastedlorikeet.jpg|Scaly-breasted Lorikeet | ||
| + | Image:PerfectLorikeetHead.jpg|Olive-headed Lorikeet | ||
| + | Image:Chalcopsitta sintillata - Yellow-streaked Lory at Fuengirola Zoo.jpg|Yellow-streaked Lory | ||
| + | Image:Musklorikeet.jpg|Musk Lorikeet | ||
| + | Image:Louisa - Dusky Lory.JPG|Dusky Lory | ||
| + | Image:BlueStreakedLory.jpg|Blue-streaked Lory | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | [[Image:LoryTongueLyd4.png|thumb|left|Tongue of a Lory]] | ||
| + | Lories and lorikeets have specialized brush-tipped tongues for feeding on nectar and soft fruits. They can feed from the flowers of about 5,000 species of plants and use their specialised tongues to take the nectar. The tip of their tongues have tufts of papillae (extremely fine hairs), which collect nectar and pollen. | ||
| + | {{clear}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!--T:65--> | ||
| + | <noinclude></translate></noinclude> | ||
| + | {{CloseReq}} <!-- 9 --> | ||
| + | {{ansreq|page={{#titleparts:{{PAGENAME}}|2|1}}|num=10}} | ||
| + | <noinclude><translate><!--T:66--> | ||
| + | </noinclude> | ||
| + | <!-- 10. Be able to describe the nest of any one of the above parrots or cockatoos and also tell the color of the egg. --> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!--T:38--> | ||
| + | Here are a couple examples. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!--T:39--> | ||
| + | The '''Musk Lorikeet''' breeds mainly from August to January. Their nest are usually built in a hollow limb of a tree. Two white 25 mm × 20 mm (0.98 in × 0.79 in) eggs are laid. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!--T:40--> | ||
| + | '''Golden-shouldered Parrot''' lives in open forest. An important habitat requirement is the provision of terrestrial termite mounds, which the bird uses for nesting. This has led to the parrot also being known as the Antbed Parrot. They will preferentially seek out taller mounds (up to 2 m high), and will dig a burrow into them when the mound has been softened by the rains. A long tunnel is dug down into the mound, and capped off by a nesting chamber. The mound regulates the temperature in the chamber, keeping it high enough that the eggs can be left unattended while the parents feed. A borrow and nesting chamber are dug from a termite mound, normally by the female, between March and June. Mounds are usually only sufficiently large enough for nesting when they are 30 to 50+ years old, and are rarely occupied more than once, possibly due to the persistence of nest parasites, such as lice, or because mounds repaired by termites are difficult to excavate. Thus there are problems in some areas where most mounds of a suitable size have already been used | ||
| + | The clutch size is between 3-6 eggs which are white and almost spherical and incubated for 20 days. | ||
| − | + | <!--T:67--> | |
| − | + | <noinclude></translate></noinclude> | |
| − | + | {{CloseReq}} <!-- 10 --> | |
| − | + | {{ansreq|page={{#titleparts:{{PAGENAME}}|2|1}}|num=11}} | |
| + | <noinclude><translate><!--T:68--> | ||
| + | </noinclude> | ||
| + | <!-- 11. Make a list of all the parrots and cockatoos that are common to your area. --> | ||
| + | If there are no parrots and cockatoos in your area, make a list for an area where they do live. | ||
| − | + | <!--T:69--> | |
| − | + | <noinclude></translate></noinclude> | |
| − | + | {{CloseReq}} <!-- 11 --> | |
| − | + | <noinclude><translate></noinclude> | |
| − | + | ==References== <!--T:42--> | |
| − | + | * http://vtpb-www2.cvm.tamu.edu/brightsmith/Wild%20Parrots.htm | |
| − | + | <noinclude></translate></noinclude> | |
| + | {{CloseHonorPage}} | ||
Latest revision as of 21:24, 14 July 2022
1
Parrots
Cockatoos
Cockatoos share many features with other parrots including the characteristic curved beak shape and a zygodactyl foot, with two forward toes and two backwards toes. They differ, however in a number of characteristics, including the often spectacular movable headcrest, the presence of a gall bladder and some other anatomical details, and their lack of the Dyck texture feather composition which causes the bright blues and greens seen in true parrots. Also Cockatoo species are, on average, larger than the average size of true parrots.
2
Golden-shouldered Parrot
The Golden-shouldered Parrot (Psephotus chrysopterygius) is a rare bird of southern Cape York Peninsula, in Queensland, Australia. It measures 26 cm long and weighs between 54-56 g.
The Golden-shouldered Parrot lives in open forest, where it feeds on small grass seeds, principally those of firegrass. An important habitat requirement is the provision of terrestrial termite mounds, which the bird uses for nesting. This has led to the parrot also being known as the Antbed Parrot. They will preferentially seek out taller mounds (up to 2 m high), and will dig a burrow into them when the mound has been softened by the rains. A long tunnel is dug down into the mound, and capped off by a nesting chamber. The clutch size is between 3-6 eggs, which are incubated for 20 days. The mound regulates the temperature in the chamber, keeping it high enough that the eggs can be left unattended while the parents feed.
The Golden-shouldered Parrot is listed as endangered (CITES I). The species has a restricted range and suffers from a variety of threats, including predation by feral cats, tourist disturbance, and a change in burning regime in the grasslands upon whose seeds it depends. The wild population is around 3000 birds, with around 1500 held in captivity in Australia.
Grey-cheeked Parakeet
The Grey-cheeked parakeet (Brotogeris pyrrhoptera), less commonly known as fire-winged parakeet, is a species of parrot in the Psittacidae family.
The grey-cheeked parakeet is indigenous to northwestern Peru and western Ecuador, living in subtropical or tropical regions encompassing dry forests, moist lowland forests, shrubland, and arable land.[2] Grey-cheeked parakeets do not build their nests in the canopies of trees. Rather, they prefer to build their nests in protected areas such as active termite mounds or tree hollows. It is yet unknown why termites tolerate their presence.
The grey-cheeked parakeet now faces habitat loss due to the irresponsible smuggling of pet birds and hunting due to their destruction of banana plantations. The species is now endangered with most populations existing within the homes of private individuals as pets. Because of this, efforts have been undertaken to save this and several other species of Brotogeris endemic to the region. It is protected by the Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species of Wild Animals (also called the Bonn Convention or CMS).
Even in its native home, the grey-cheeked parakeet is widely kept as a pet. With patience, these birds may be taught to mimic human sounds, albeit without the clarity of larger parrots.
Green-rumped Parrotlet
The Green-rumped Parrotlet, Forpus passerinus, is a small parrot. It is a resident breeding bird in tropical South America, from Caribbean regions of Colombia, Venezuela and Trinidad south and east to the Guianas and Brazil, on the downstream Amazon River. It has been introduced in Jamaica, Curaçao, Barbados and Tobago, and was not recorded on Trinidad prior to 1916.
Its habitat is open forest and scrub. The female lays five to seven white eggs in a hole in a termite nest, tree cavity, or even hollow pipe, and incubates the clutch for 18 days to hatching, with about another five weeks to fledging.
3
3a
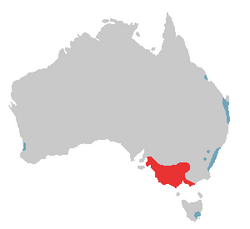
The Long-billed Corella, Cacatua tenuirostris, is a cockatoo native to Australia. Species are mostly white, with a pink face and forehead. They also have faintly pink feathers on the breast and belly, and yellow on the underside of the wings and tail. The birds have a long white beak, which is used to dig for roots and seeds.
3b
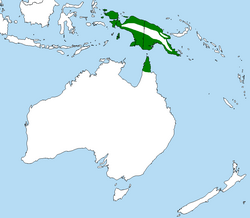
The Palm Cockatoo (Probosciger aterrimus) is distributed in rainforests and woodlands of New Guinea and northern Queensland, Australia. It measures around 55-60 cm in length and weighs between 500-1,000 g. It is a distinctive bird with a large crest and has one of the largest bills of any parrots (only the Hyacinth Macaw's is larger). The bill is unusual as the lower and upper mandibles do not meet for much of its length, allowing the tongue to hold a nut against the top mandible while the lower mandible works to open it.
3c
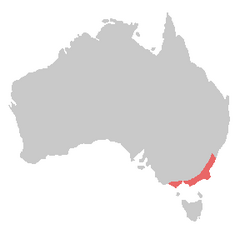
The Gang-gang Cockatoo, Callocephalon fimbriatum, is found in the cooler and wetter forests and woodlands of Australia, particularly alpine bushland. Mostly mild grey in colour with some lighter scalloping (more pronounced and buffish in females) the male has a red head and crest, while the female has a small fluffy grey crest. It ranges throughout south-eastern Australia and Tasmania. The Gang-gang Cockatoo is the faunal emblem of the Australian Capital Territory. It is easily identified by its distinctive call, which is described as resembling a creaky gate, or the sound of a cork being pulled from a bottle.
Gang-gang cockatoos eat fruits, and seem to have a particular weakness for Hawthorn berries (though Hawthorns are an introduced species, and not part of the cockatoo's natural diet).
4
- Yellow-crested Cockatoo
- The Yellow-crested Cockatoo, Cacatua sulphurea, is critically endangered. Numbers have declined dramatically due to illegal trapping for the cage-bird trade. The current population is estimated at less than 10,000. It is listed on Appendix I of CITES.
- Red-vented Cockatoo
- This bird, Cacatua haematuropygia, is critically endangered. Populations have decreased dramatically due to illegal trapping for the cage-bird trade. The high price fetched per bird (c.US$160 in Manila in 1997) means that chicks are taken from virtually every accessible nest. Loss of habitat may also have contributed to its decline. The current population is estimated at less than 4,000 birds.
- Moluccan Cockatoo
- The Moluccan Cockatoo, Cacatua moluccensis, is an endangered species, and has been listed on appendix I of CITES since 1989, which makes trade in wild-caught birds illegal. Trade in captive bred birds is legal only with appropriate CITES certification. Numbers have declined due to illegal trapping for the cage-bird trade and habitat loss. During the height of the trapping of this species over 6,000 birds were being removed from the wild per year. It has a stronghold in Manusela National Park on Seram, although even today some illegal trapping continues.
5
The Green Rosella or Tasmanian Rosella (Platycercus caledonicus) is endemic to Tasmania. The largest of the Rosellas it is predominantly green and yellow in plumage with blue cheeks.
Its diet consists mostly of seeds, fruits, and berries, and it will sometimes feed on the ground.
6
| State of Australia | Associated Rosella |
|---|---|
| New South Wales | Crimson Rosella |
| Queensland | Pale-headed Rosella |
| South Australia | Adelaide Rosella |
| Tasmania | Green Rosella |
| Victoria | Crimson Rosella |
| Western Australia | Western Rosella |
7
The Eclectus Parrot, Eclectus roratus, is a parrot native to the Solomon Islands, New Guinea, northeastern Australia and the Maluku Islands (Moluccas). It is unusual in the parrot family the males and females are so different from one another. The males of the species are bright green, having bright candy-corn-colored upper mandibles and black lower mandibles, and blue or red tail and wing feathers; while the females have red heads and blue to purple breasts, with black beaks. Joseph Forshaw, in his book Parrots of the World, noted that the first European ornithologists to see Eclectus Parrots thought they were of two distinct species.
The diet of the eclectus in the wild consists of mainly fruits, unripe nuts, flower and leaf buds, and some seeds. Two favorite fruits are the pomegranate and the papaya (pawpaw) with seeds. In captivity, they will eat most fruits including mangos, figs, guavas, bananas, any melons, stone fruits (peaches etc.), grapes, citrus fruits, pears and apples.
8
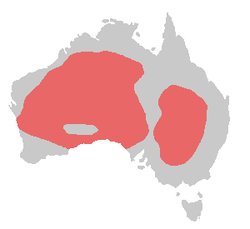
With its soft-textured white and salmon-pink plumage and large, bright red and yellow crest, Major Mitchell's Cockatoo is generally recognised as the most beautiful of all cockatoos. It is named in honour of Major Sir Thomas Mitchell, who wrote "Few birds more enliven the monotonous hues of the Australian forest than this beautiful species whose pink-coloured wings and flowing crest might have embellished the air of a more voluptuous region".
It is restricted to arid and semi-arid inland areas of Australia (see map).
9
Lories and lorikeets are small to medium-sized arboreal parrots which comprise the subfamily Loriinae. They are widely distributed throughout the Australasian region, including south-eastern Asia, Polynesia, Papua New Guinea and Australia, and the majority have very brightly colored plumage.
Lories and lorikeets have specialized brush-tipped tongues for feeding on nectar and soft fruits. They can feed from the flowers of about 5,000 species of plants and use their specialised tongues to take the nectar. The tip of their tongues have tufts of papillae (extremely fine hairs), which collect nectar and pollen.
10
Here are a couple examples.
The Musk Lorikeet breeds mainly from August to January. Their nest are usually built in a hollow limb of a tree. Two white 25 mm × 20 mm (0.98 in × 0.79 in) eggs are laid.
Golden-shouldered Parrot lives in open forest. An important habitat requirement is the provision of terrestrial termite mounds, which the bird uses for nesting. This has led to the parrot also being known as the Antbed Parrot. They will preferentially seek out taller mounds (up to 2 m high), and will dig a burrow into them when the mound has been softened by the rains. A long tunnel is dug down into the mound, and capped off by a nesting chamber. The mound regulates the temperature in the chamber, keeping it high enough that the eggs can be left unattended while the parents feed. A borrow and nesting chamber are dug from a termite mound, normally by the female, between March and June. Mounds are usually only sufficiently large enough for nesting when they are 30 to 50+ years old, and are rarely occupied more than once, possibly due to the persistence of nest parasites, such as lice, or because mounds repaired by termites are difficult to excavate. Thus there are problems in some areas where most mounds of a suitable size have already been used The clutch size is between 3-6 eggs which are white and almost spherical and incubated for 20 days.
11
If there are no parrots and cockatoos in your area, make a list for an area where they do live.