Jomegat bot (talk | contribs) m (Fix Tab Name transclusion) |
Jomegat bot (talk | contribs) (Convert honor_tab to honor_landing *** existing text overwritten ***) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<translate> | <translate> | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{honor_landing |
|honorname=Sight | |honorname=Sight | ||
|skill=1 | |skill=1 | ||
| Line 10: | Line 8: | ||
|insignia=Sight AY Honour.png | |insignia=Sight AY Honour.png | ||
|insignia_source=British Union | |insignia_source=British Union | ||
| + | |overview= | ||
| + | |challenge= | ||
| + | <b>{{reqreq|page={{PAGENAME}}|num=18}}</b> | ||
}} | }} | ||
</translate> | </translate> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Revision as of 01:21, 20 January 2021
| Sight | |
|---|---|
| Regional | |
Skill Level 123 | |
Approval authority British Union | Year of Introduction 2020 |
The most challenging requirement of this honor is probably this:
18. Watch the video on how to do an origami eye. Make an origami eye.
1. Complete the following:
- a. Perform this activity.
Be blindfolded. Let someone place an item between 15 metres to 20 metres away from you. Now search for the item. Record the time you found the item. Now, be blindfolded again. Let someone place the item somewhere else but within the same distance as before. Take off your blindfold. Search for the item. Record the time you found the item.
- b. Watch the video: https://youtu.be/syaQgmxb5i0. Now answer the following questions:
- What is the sense of sight used for?
- How important is it?
- c. How big is the human eye?
2. Anatomy of the eye. Label the parts.
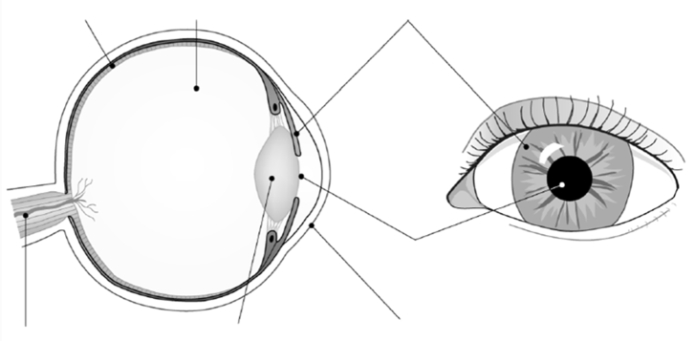
Eye Function Drag
Click on the link provided above and do the exercise on the functions of the parts of the eye. When complete check your answer. The system will then mark your work. Print and paste your work.
3. How does a lens work? Complete the sentence below using the words from the box.
We have a lens in each of our _______________. This is a ______________ lens. The job of this lens is to ______________ the ________________ so we can_____________________. The point at which the rays cross is called the focus or the ____________________. The light is ________________________as it goes into the and as it comes back out.
| eyes | refracted | light | focal point | |||
| focus | see | convex |
4. Watch video:
- a. Below are the steps in how humans see. Arrange them in a chronological order by putting numbers (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6) in the “position” column to reflect the right order in which they should be.
| Position | Steps |
| When you look at an object, light reflected from the object goes through the pupil of your eye. | |
| Your brain sorts the image out so you see it the right way round. | |
| The cornea and the lens focus the light onto the retina. | |
| An inverted image is formed on the retina. The retina is made of light sensitive cells called photoreceptors. | |
| The iris, a muscle that controls the size of the pupil, allows the correct amount of light to enter your eye. | |
| When the image forms on the photoreceptors in the retina, chemical reactions produce and electrical impulse that travels up the optic nerve to your brain. |
- b. Fill in the blank: A medical doctor who specialises in examining, diagnosing, and treating eyes and eye diseases is called a/an ____________________.
- c. Visual acuity test, visual field test and tonometry test are tests that an ophthalmologist performs on the eye. Match the name of the term to its meaning:
| Visual acuity test | ????? | A person reads an eye chart to measure how well he or she sees at various distances. |
| Visual field test | ????? | This test determines the fluid pressure inside the eye to evaluate for glaucoma. |
| Tonometry test | ????? | Ophthalmologists use this test to measure side, or peripheral, vision. |
- d. What are the roles of:
- i. Rods
- ii. Cones
5. How does the eyesight of humans compare with other creatures? Compare with any three of the following animals: eagles, owls, mantis shrimp, deer, goat, horse, elk, sheep, goat.
6. Complete the following:
- a. Compare the key features of the eye and a camera by finishing the table.
| Feature in a camera | Feature in an eye | Use |
| Pupil | ||
| Lens | ||
| Shutter | ||
| Retina | Receives light |
- b. Write a paragraph below to compare how the eye and the camera work. Cover the following factors in your answer:
- i. Similarities: What features do they have in common? What does each convert the light energy into when it is processed? Which way up does the image form in both?
- ii. Differences: How does the lens change in each to produce an image? How do the types of image made by each compare? How are the images captured and kept?
7. With reference to the eye chart explain:
- a. 20/20 vision
- b. 20/70 vision
8. What is visual impairment?
9. Define these eye problems and state their "cures".
- a. Glaucoma
- b. Cataracts
- c. Strabismus
- d. "Sore eyes"/conjunctivitis
- e. Colour blindness
10. Fill in the blanks: (Watch the video - https://youtu.be/ypF037wlYZg)
- a. ________________ is the bending of light when it passes through a transparent medium such as glass, lens or water.
- b. The refractive errors are _______________, ___________________, ____________ and _______________.
- c. _________________is also known as near-sightedness. People with this have eyes that are a little longer than normal, measuring from the front of the eyeball to the back. Therefore, light focuses in front of the retina instead of on it.
- d. ___________________ is also known as farsightedness. People with this have trouble focusing on things close up because their eyes are too "short" from front to back. Therefore, light focuses behind the retina instead of on it, causing blurry vision.
- e. _____________________ is a condition in which your eye isn’t completely round. Therefore, light gets bent more in one direction than another. That means only part of an object is in focus so things at a distance may look blurry and wavy.
- f. _________________ is the normal loss of near focusing ability that occurs with age. Most people begin to notice the effects of presbyopia sometime after age 40, when they start having trouble seeing small print clearly.
- g. Read Genesis 48:10. Which of the refractive errors did Israel have?
- h. State if the following statement below is true or false: “All the refractive errors can be corrected by wearing the right glasses or contact lens.”
11. Eye care:
- a. How should I clean my eyes?
- b. Write one sentence on how we can strain our eyes.
- c. How should we rest them?
- d. Matthew has been using a computer continuously for 4 hours! Now he is complaining of eye strain. Give Matthew three pieces of advice to help him relax his eyes.
- e. Explain the 20-20-20 rule of eye relaxation.
- f. What do I do if I cannot see very well?
12. Give two meanings to the expression “The eyes are a window to the soul.”
13. What are the effects of exposing ourselves to watching:
- a. Violence/pornography (mention three)
- b. Video games: Give three advantages and disadvantages
- c. Social media: Give three advantages and disadvantages
14. Explain 1 Samuel 16:7.
15. Explain “fixing our eyes on Jesus.” (Hebrews 12:2)
16. Mention four ways that life can be made easier for the visually impaired.
17. Optical illusion:
- a. Fill in the blanks using the word bank in the box below the passage.
_____________ Illusions can use colour, ______________ and patterns to create ___________ that can be deceptive or misleading to our _____________. The information gathered by the eye is processed by the brain, creating a perception that in reality, does not match the true image. Perception refers to the interpretation of what we take in through our _____________. Optical illusions occur because our brain is trying to _______________ what we see and make sense of the world around us. Optical illusions simply trick our brains into seeing things which may or may not be _____________.
| images | eyes | brains | optical | real | light | interpret |
- b. Provide the answers to the optical illusions below.
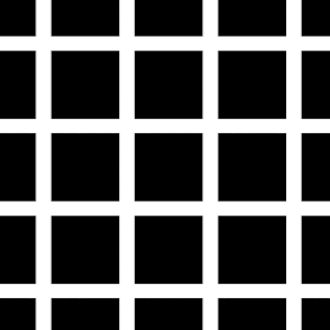
- Hermann Grid Illusion
- How many black dots are in this image?
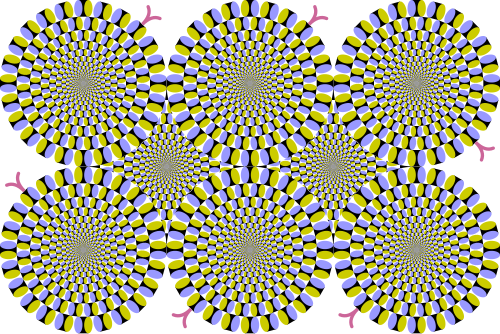
- Rotating Snakes Illusion
- Are the circles moving in the image?
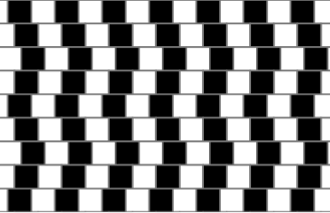
- Café Wall Illusion
- Are the horizontal lines sloping or straight?
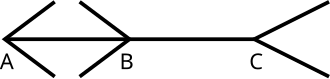
- Müller-Lyer Illusion
- Take a very close look at the 2 line segments. Do you think one line is longer than the other?
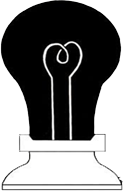
- Lightbulb Illusion
- Stare closely at this lightbulb for 25 seconds. Then immediately stare at a white wall or sheet of paper. What do you see?
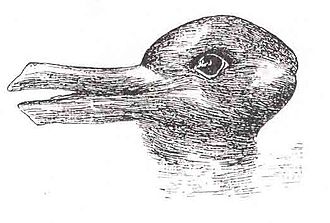
- Shepard's Elephant Illusion
- How many legs do I have?
- Teach or Learn
- In this illusion you can see the word Teach and its reflection. Can you read the reflection too? What does it say?
- Animal Illusion
- How many animals do you see in the image?
18. Watch the video on how to do an origami eye. Make an origami eye.
1
1a
Be blindfolded. Let someone place an item between 15 metres to 20 metres away from you. Now search for the item. Record the time you found the item. Now, be blindfolded again. Let someone place the item somewhere else but within the same distance as before. Take off your blindfold. Search for the item. Record the time you found the item.
| Distance of item from you (metres) | Time you found the item (seconds) | |
| When blindfolded | ||
| When not blindfolded |
1b
- What is the sense of sight used for?
- How important is it?
What is the sense of sight used for?
How important is it?
1c
2
Eye Function Drag
Click on the link provided above and do the exercise on the functions of the parts of the eye. When complete check your answer. The system will then mark your work. Print and paste your work.
3
We have a lens in each of our _______________. This is a ______________ lens. The job of this lens is to ______________ the ________________ so we can_____________________. The point at which the rays cross is called the focus or the ____________________. The light is ________________________as it goes into the and as it comes back out.
| eyes | refracted | light | focal point | |||
| focus | see | convex |
4
4a
| Position | Steps |
| When you look at an object, light reflected from the object goes through the pupil of your eye. | |
| Your brain sorts the image out so you see it the right way round. | |
| The cornea and the lens focus the light onto the retina. | |
| An inverted image is formed on the retina. The retina is made of light sensitive cells called photoreceptors. | |
| The iris, a muscle that controls the size of the pupil, allows the correct amount of light to enter your eye. | |
| When the image forms on the photoreceptors in the retina, chemical reactions produce and electrical impulse that travels up the optic nerve to your brain. |
4b
4c
| Visual acuity test | ????? | A person reads an eye chart to measure how well he or she sees at various distances. |
| Visual field test | ????? | This test determines the fluid pressure inside the eye to evaluate for glaucoma. |
| Tonometry test | ????? | Ophthalmologists use this test to measure side, or peripheral, vision. |
4d
i
ii
5
6
6a
| Feature in a camera | Feature in an eye | Use |
| Pupil | ||
| Lens | ||
| Shutter | ||
| Retina | Receives light |
6b
i
ii
7
7a
7b
8
9
9a
9b
9c
9d
9e
10
10a
10b
10c
10d
10e
10f
10g
Now the eyes of Israel were dim with age, so that he could not see. Then Joseph brought them near him, and he kissed them and embraced them.
10h
11
11a
11b
11c
11d
11e
11f
12
13
13a
13b
13c
14
But the Lord said to Samuel, “Do not look at his appearance or at his physical stature, because I have refused him. For the Lord does not see as man sees; for man looks at the outward appearance, but the Lord looks at the heart.”
15
looking unto Jesus, the author and finisher of our faith, who for the joy that was set before Him endured the cross, despising the shame, and has sat down at the right hand of the throne of God.
16
17
17a
_____________ Illusions can use colour, ______________ and patterns to create ___________ that can be deceptive or misleading to our _____________. The information gathered by the eye is processed by the brain, creating a perception that in reality, does not match the true image. Perception refers to the interpretation of what we take in through our _____________. Optical illusions occur because our brain is trying to _______________ what we see and make sense of the world around us. Optical illusions simply trick our brains into seeing things which may or may not be _____________.
| images | eyes | brains | optical | real | light | interpret |
17b
- Hermann Grid Illusion
- How many black dots are in this image?
- Rotating Snakes Illusion
- Are the circles moving in the image?
- Café Wall Illusion
- Are the horizontal lines sloping or straight?
- Müller-Lyer Illusion
- Take a very close look at the 2 line segments. Do you think one line is longer than the other?
- Lightbulb Illusion
- Stare closely at this lightbulb for 25 seconds. Then immediately stare at a white wall or sheet of paper. What do you see?
- Shepard's Elephant Illusion
- How many legs do I have?
- Teach or Learn
- In this illusion you can see the word Teach and its reflection. Can you read the reflection too? What does it say?
- Animal Illusion
- How many animals do you see in the image?
18
References
Content on this wiki is generated by people like you, and no one has created a lesson plan for this honor yet. You could do that and make the world a better place.
See AY Honors/Model Lesson Plan if you need ideas for creating one.