Difference between revisions of "AY Honors/Power Boating/Answer Key/es"
(Created page with "{{clear}}") |
(Created page with "{{clear}}") |
||
| Line 103: | Line 103: | ||
{{clear}} | {{clear}} | ||
| − | + | {{clear}} | |
Be very careful near canal dams and waste weirs where currents and undertows can be very hazardous. Low-head dams are especially dangerous. Boaters and anglers often get too close to the downstream side of the dam, become drawn or sucked into the backwash current that takes them to the base of the dam, and are then forced under water and pushed away from the dam. After surfacing, the victim is drawn back in toward the base of the dam, starting the cycle over again. | Be very careful near canal dams and waste weirs where currents and undertows can be very hazardous. Low-head dams are especially dangerous. Boaters and anglers often get too close to the downstream side of the dam, become drawn or sucked into the backwash current that takes them to the base of the dam, and are then forced under water and pushed away from the dam. After surfacing, the victim is drawn back in toward the base of the dam, starting the cycle over again. | ||
Revision as of 03:43, 1 February 2021
| Lancha a motor | ||
|---|---|---|
| Asociación General
|
Destreza: 2 Año de introducción: 1975 |
|
Requisitos
|
La especialidad de Lancha a motor es un componente de la Maestría Acuática. |
1
Para consejos e instrucciones, véase [[AY Honors/Swimming - Advanced Beginner/es|]].
2
A summary of the boating laws for Australia, all U.S. States and Territories, and all Canadian Provinces can be found at the NASBLA website.
3
4
Be very careful near canal dams and waste weirs where currents and undertows can be very hazardous. Low-head dams are especially dangerous. Boaters and anglers often get too close to the downstream side of the dam, become drawn or sucked into the backwash current that takes them to the base of the dam, and are then forced under water and pushed away from the dam. After surfacing, the victim is drawn back in toward the base of the dam, starting the cycle over again.
Find out if there are any dams where you plan to go boating before you head out – and stay clear of them. When boating in an area with dams, be sure to follow the signage posted by dam authorities.
Safety Under Electric Lines and Under Bridges
Contact with an aerial electric line or an electric arc zone (invisible) can kill you. Hitting a bridge can damage your boat and the bridge. That is why you should:
- Know the height of your boat above water (including gear installed on top of the mast).
- Know the minimal clearance identified on marine charts and avoid electric lines when this information is not available.
- Be careful at night: electric lines are more difficult to see
Waterskiing and Other Recreational Towing Activities
The rules that govern waterskiing also apply to other recreational towing activities like barefoot skiing, tubing, kneeboarding and parasailing. Here are rules to remember when towing someone with your boat:
- You must have a spotter on board the boat who can keep watch on each
person you are towing and communicate with you.
- There must be an empty seat on your boat for each person you are
towing in case they need to come on board.
- You may only tow persons with a personal watercraft made to carry three or more people.
- If someone you tow is not wearing a lifejacket or PFD, you must have one on board for him or her.
- You may not tow anyone when visibility is poor or from one hour after sunset to sunrise.
- No towing boat may be remotely controlled.
Locks and Canals
When visiting one of Canada’s historic canals, make sure your boat has enough properly sized mooring lines and securely fastened floating fenders.
Many water activities are not allowed in a canal. Some rules include:
- no excessive noise between 11 p.m. and 6 a.m.;
- no fishing within 10 m (32’10”) of a lock or approach wharf or from a bridge that passes over a navigation channel;
- no diving, jumping, scuba diving or swimming in a navigation channel or within 40 m (131’) of a lock gate or a dam in a historic canal;
- no waterskiing or other towing activities while in a navigation channel or within 100 m (328’1”) of a lock structure; and
- no mooring a vessel to a navigation aid.
Visit Parks Canada (or whoever is in charge) to learn more about historic canals and see Historic Canal Regulations for more information about the regulations that apply.
Passage through a Lock
Obey the posted speed limits and be aware of your boat’s wake when approaching a lock. Other things to remember include:
- Keep clear of the channel near lock gates so that vessels can come and go.
- Look for the blue line on the mooring wharf that shows where to wait for the next lockage.
- Follow the instructions given by lockmasters and bridge operators (at a number of lock stations, a green traffic light is your signal to go ahead).
- Enter the lock slowly (no faster than 10 km/h) and have people at the bow and stern of your boat ready with mooring lines.
- If the lock has drop cables, loop boat lines around them, not to them, and only once your boat is safely positioned. If the lock has floating docks, lockmasters may tell you to tie up to one inside the lock chamber.
- Tend vessel lines carefully during the lockage. Looping a line around a deck cleat may provide extra leverage.
- Never leave bow or stern lines unattended.
- Switch off the engine(s) and generator. No open flames or smoking are allowed during lockage. The bilge blower must be operating during lockage.
- When the lock gates open, wait for staff to direct you to restart your engine.
- Make sure you have brought all your mooring lines back into your boat and exit slowly and in order. Watch out for wind, currents and other vessels.
Nautical Aids
5
These regulations vary by country, size of boat, and change from time to time. In Canada the regulations for Sail and Power Boats over 9 m and up to 12 m (29’6” – 39’4”) at the time this question was answered are as an example. Be sure you know the requirements for where you are operating a given size boat:
PERSONAL LIFESAVING APPLIANCES
1. One (1) lifejacket or PFD for each person on board
2. One (1) reboarding device (See Note 1)
3. One (1) buoyant heaving line at least 15 m (49’3”) long
4. One (1) lifebuoy attached to a buoyant line at least 15 m (49’3”) long
VISUAL SIGNALS
5. One (1) watertight flashlight
6. Twelve (12) flares of type A, B, C or D, not more than six (6) of which are of type D (See Note 2)
VESSEL SAFETY EQUIPMENT
7. One (1) anchor and at least 30 m (98’5”) of cable, rope or chain in any combination
8. One (1) manual bilge pump (See Note 3) OR Bilge-pumping arrangements
NAVIGATION EQUIPMENT
9. One (1) sound-signalling device or appliance
10. Navigation lights (See Note 4)
11. One (1) magnetic compass (See Note 5)
12. One (1) radar reflector (See Note 6)
FIRE FIGHTING EQUIPMENT
13. One (1) 10BC fire extinguisher if equipped with a motor
14. One (1) 10BC fire extinguisher if equipped with a fuel-burning cooking, heating or refrigerating appliance
Note 1 – Reboarding Device A reboarding device is only required if the vertical height that a person must climb to reboard the boat from the water (freeboard) is over 0.5 m (1’8”).
Note 2 – Flares Flares are not required for a boat that: • is operating on a river, canal or lake in which it can never be more than one (1) nautical mile (1.852 km) from shore; or • has no sleeping quarters and is engaged in an official competition or in final preparation for an official competition.
Note 3 – Bailer and Manual Bilge Pump A bailer or manual bilge pump is not required for a boat that cannot hold enough water to make it capsize or a boat that has watertight compartments that are sealed and not readily accessible.
Note 4 – Navigation Lights Navigation lights are only required if you operate the boat after sunset, before sunrise or in periods of restricted visibility (fog, falling snow, etc.).
Note 5 – Magnetic Compass A magnetic compass is not required if the boat is 8 m (26’3”) or less and you operate it within sight of navigation marks.
Note 6 – Radar Reflector Radar reflectors are required for boats under 20 m (65’7”) and boats built of mostly non-metallic materials. A radar reflector is not required if: • the boat is used in limited traffic conditions, daylight and favourable environmental conditions, and where having a radar reflector is not essential to the boat’s safety; or • the small size of the boat or its operation away from radar navigation makes it impossible to install or use a radar reflector.
Larger boats require additional equipment and smaller boats require less equipment.'
Radar Reflectors help larger vessels to see small boats on their radar screens, and may be the only way that they will be able to spot you. A radar reflector can enhance your safety on the water, but only if it is big enough and well placed on your boat. When buying a reflector, there is no substitute for size – so buy the biggest one that will fit your boat. There are all kinds of reflectors of varying quality on the market, so make sure you look carefully before buying. Keep in mind that placement height is also very important. Reflectors should be located above all superstructures; and at least 4 m (13’1”) above the water, if possible.
Do you know that different types of fires require different types of extinguishers? The letters on a fire extinguisher tell you what types of fires it is designed to fight. Fires are classified as follows:
- Class A: Materials that burn, such as wood, cloth, paper, rubber
and plastic
- Class B: Liquids that burn, such as gas, oil and grease
- Class C: Electrical equipment
You should buy a fire extinguisher with an ABC rating. The number before the letters on the extinguisher tells you how big a fire it will put out compared to other extinguishers. For example, a 10BC device will put out a larger fire than a 5BC device. Check your extinguishers often for correct operating pressure and make sure that you and your guests know how to use them. Have a qualified person maintain, service and recharge your extinguishers as per the manufacturer’s instructions. Take dry chemical devices out of their bracket and give them a few hard shakes in the upside down position about once a month to keep the contents active.
The fire extinguisher you choose must bear a mark that shows it is certified by:
- Underwriters Laboratories of Canada (ULC);
- Underwriters’ Laboratories Inc. (UL); or
- Unites States Coast Guard.
6
The other sections of this page cover this topic well.
7
1. Life first: Take a head count to make sure everyone is there 2. Get your life jackets on - if they have flouted out of range use anything that flouts. Treading water only lasts so long. 3. Check for injuries 4. Stay with the boat as long as it is not sinking. Rescuers will have a far easier time find near the large mass of the boat. 5. Conserve energy 6. Signal for help using available equipment such as visual distress signals, horn, mirror, radios, flares etc. 7. If practical, turn a smaller boat upright and bail it out. Once most of the water is out, climb back in. A swamped boat is much better than no boat.
8
Rule 2(b) of the International Rules and Inland Rules. Rule 2(b) states “In construing and complying with these Rules due regard shall be had to all dangers of navigation and collision and to any special circumstances, including the limitations of the vessels involved, which may make a departure from these Rules necessary to avoid immediate danger.”
This rule has remained consistent for over 100 years. In plan english it means that you must follow the rules of navigation unless special circumstances that involve immediate danger require taking a different action.
9
9a
Towards the rear, or stern, of a boat. Abaft means “in the back.”
9b
On the beam; at a right angle to the centerline or keel of a vessel. Also alongside or abreast; opposite the center of the side of the ship or aircraft.
9c
On or in a vessel
9d
1. The portion of the vessel behind the middle area of the vessel.
2. Towards the stern (of the vessel).
9e
The middle section of a vessel with reference to the athwartships plane, as distinguished from port or starboard ("Put your rudder amidships.")
9f
1. Toward the stern (rear) of a vessel.
2. Behind a vessel.
9g
The width of a vessel at the widest point, or a point alongside the ship at the midpoint of its length.
9h
Beneath the deck.
9i
A knot used to join two ropes or lines. See also hitch.
9j
The compartment at the bottom of the hull of a ship or boat where water collects and must be pumped out of the vessel.
9k
1. The front of a vessel.
2. Either side of the front (or bow) of the vessel, i.e., the port bow and starboard bow. Something ahead and to the left of the vessel is "off the port bow", while something ahead and to the right of the vessel is "off the starboard bow." When "bow" is used in this way, the front of the vessel sometimes is called her bows (plural), a collective reference to her port and starboard bows synonymous with bow (singular) as described in Definition (1).
9l
An upright wall within the hull of a ship. Particularly a watertight, load-bearing wall.
9m
A stationary device used to secure a rope aboard a vessel.
9n
The depth of a ship's keel below the waterline.
9o
The height of a ship's hull (excluding superstructure) above the waterline. The vertical distance from the current waterline to the lowest point on the highest continuous watertight deck. This usually varies from one part to another.
9p
The central structural basis of the hull.
9q
9r
The left side of the boat. Towards the left-hand side of the ship facing forward (formerly Larboard). Denoted with a red light at night.
9s
The right side of the boat. Towards the right-hand side of a vessel facing forward. Denoted with a green light at night. Derived from the old steering oar or steerboard which preceded the invention of the rudder.
9t
The rear part of a ship, technically defined as the area built up over the sternpost, extending upwards from the counter rail to the taffrail.
9u
1. Relationship of ship's hull to waterline.
9v
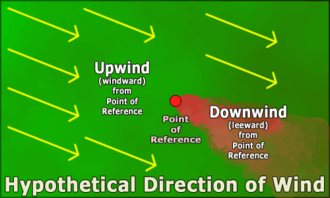
In the direction that the wind is coming from.
10
10a
Start by inspecting the boat ramp above and below the water for obstructions and to understand where to back the trailer in. Be polite to other ramp users and communicate your intentions to them. As you get into the water, but before the boat can float, undo the safety chain and loosen the cable off. Back the boat trailer into the water until the boat floats. Someone in the boat should operate the boat off the trailer while someone else unhooks the cable, deals with tying the boat to the dock with ropes (if required), and driving the truck and trailer away.
Good communication within your group and with others nearby is important to avoid damage.
10b
It is good to have a small laminated (to prevent it getting wet) card with a safety checklist appropriate to a particular boat. Checking the fuel requires either looking at the gauge (if so equipped) or opening the tank and visually looking. The motor should be tested by running it gently while unloading from the trailer.
10c
Watch where you are going. Don't go fast near the shore, and avoid making waves.
10d
This is just a simple demonstration of ability to handle the boat.
10e
The tricky part is doing this without damaging the boat. Go slow, controlling the chain/rope. A towel over the edge of the boat can help avoid damaging the fiberglass or other parts of the boat.
10f
Again, slow and controlled. If beaching you need to tie to a sturdy tree or rock, remembering that tides and waves can move your boat if not properly secured. There are a few knots every boater needs to know:
Adventist Youth Honors Answer Book/Knot/Two half hitches Adventist Youth Honors Answer Book/Knot/Bowline Adventist Youth Honors Answer Book/Knot/Double bowline Adventist Youth Honors Answer Book/Knot/Stevedore's Adventist Youth Honors Answer Book/Knot/Anchor bend Adventist Youth Honors Answer Book/Knot/Square Adventist Youth Honors Answer Book/Knot/Cleat hitch
Cleat Hitch - Use to secure the boat to a dock or secure a line to the boat Take the line to the ear of the cleat farthest from where the line comes from (the load). Take one wrap around the base of the cleat and then start a figure eight across the top of the opposite ear. Finish with a half hitch turned under so that the line is coming away from the cleat in the opposite direction from which it came in.
10g
First check for obstructions and communicate your intentions to others in the area. After one person backs the trailer into the water, slowly but forcefully drive the boat onto the trailer. Make sure your boat is straight on the trailer, which might mean letting the boat settle out before the next step. The person outside the boat should attach the cable and cinch it up before attaching the safety chain. Pull out of the water and attach safety straps at the back and anywhere else required. Check that no weeds are attached to the boat or trailer to prevent the spread of invasive species between lakes. If you have been in ocean water, rise your wheels and brakes. Attach any boat covers, and secure all ropes and equipment before driving off.
11
References
Singificant portions of these answers are from http://www.tc.gc.ca/publications/EN/TP511/PDF%5CHR/TP511E.pdf and are used here for non-commercial purposes with permission.
- Categoría: Tiene imagen de insignia
- Adventist Youth Honors Answer Book/Honors/es
- Adventist Youth Honors Answer Book/es
- Adventist Youth Honors Answer Book/Skill Level 2/es
- Categoría: Libro de respuestas de especialidades JA/Especialidades introducidas en 1975
- Adventist Youth Honors Answer Book/General Conference/es
- Adventist Youth Honors Answer Book/Recreation/es
- Adventist Youth Honors Answer Book/Recreation/Primary/es
- Adventist Youth Honors Answer Book/Stage 0/es
- Adventist Youth Honors Answer Book/Aquatic Master Award/es
- AY Honors/Prerequisite/Swimming - Advanced Beginner/es
- AY Honors/See Also/Swimming - Advanced Beginner/es
- Adventist Youth Honors Answer Book