Difference between revisions of "AY Honors/Australian Birds/Answer Key"
JadeDragon (talk | contribs) |
JadeDragon (talk | contribs) m (→c. What is the term which describes this type of bird?: fix link) |
||
| Line 66: | Line 66: | ||
===c. What is the term which describes this type of bird?=== | ===c. What is the term which describes this type of bird?=== | ||
| − | Ground nesting birds often build | + | Ground nesting birds often build [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bird_nest#Scrape scrape] style nests. |
==5.== | ==5.== | ||
Revision as of 21:08, 19 September 2014
1.
a. Which is the largest of the Australian birds?
The Emu is claimed to be the second largest bird in the world and widely found in Australia. The largest emus can reach up to 1.5–1.9 m (4.9–6.2 ft) in height, 1–1.3 m (3.3–4.3 ft) at the shoulder. In length measured from the bill to the tail, emus range from 139 to 164 cm (55 to 65 in), with males averaging 148.5 cm (58.5 in) and females averaging 156.8 cm (61.7 in). Emus weigh between 18 and 60 kg (40 and 132 lb), with an average of 31.5 and 36.9 kg (69 and 81 lb) in males and females, respectively. Females are usually larger than males by a small amount, and are substantially wider across the rump.
However, according to this list of the largest birds, the Southern and Northern Cassowary are both on average heavier and larger than the Emu.
b. Describe its nest, including number, size and colour eggs and how incubated.
Male Emu lose their appetite and construct a rough nest in a semi-sheltered hollow on the ground from bark, grass, sticks, and leaves.[3] The nest is almost always a flat surface rather than a segment of a sphere, although in cold conditions the nest is taller, up to 7 cm tall, and more spherical to provide more insulation. When other material is lacking, it can also use spinifex grass bushes more than a metre across, despite the prickly nature. The nest can be placed in open ground or near scrubs and rocks, although thick grass is usually present if the emu takes the former option. The nests are usually placed in an area where the emu has a clear view of the surrounds and can detect predators.
The pair mates every day or two, and every second or third day the female lays one of an average of 11 (and as many as 20) very large, thick-shelled, dark-green eggs. The shell is around 1 mm thick although indigenous Australians say that northern eggs are thinner. The number of eggs varies with rainfall. The eggs are on average 134 by 89 millimetres (5.3 in × 3.5 in) and weigh between 700 and 900 grams (1.5 and 2.0 lb),[49] which is roughly equivalent to 10–12 chicken eggs in volume and weight. The egg surface is granulated and pale green. During the incubation period, the egg turns dark green, although if the egg never hatches, it will turn white from the bleaching effect of the sun.
The male Eu becomes broody after his mate starts laying, and begins to incubate the eggs before the laying period is complete. From this time on, he does not eat, drink, or defecate, and stands only to turn the eggs, which he does about 10 times a day. Sometimes he will walk away at night; he chooses such a time as most predators of emu eggs are not nocturnal. Over eight weeks of incubation, he will lose a third of his weight and will survive only on stored body-fat and on any morning dew that he can reach from the nest.
The male cassowary builds a nest on the ground; a mattress of herbaceous plant material 5 to 10 centimetres (2–4 in) thick and up to 100 centimetres (39 in) wide. This is thick enough to let moisture drain away from the eggs. The male also incubates the eggs and raises the chicks alone. A clutch of three or four eggs are laid measuring 138 by 95 millimetres (5.4 in × 3.7 in). They have a granulated surface and are initially bright pea-green in colour although they fade with age.
c. How fast can this bird run?
Emu can sprint at 50 km/h (31 mph). Cassowary are also fast runners, attaining speeds up to 48 km (30 mi) per hr. Both birds are flightless.
d. Which is the tallest 'flying' bird?
Sarus crane (Grus antigone) is a large non-migratory crane found in parts of the Indian Subcontinent, Southeast Asia and Australia. The tallest of the flying birds, standing at a height of up to 1.8 m (5.9 ft).
e. Can you name Australia's only native stork?
Black-necked stork
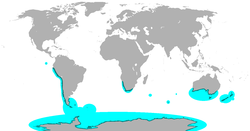
2. Are penguins found naturally in Australia and if so, where would you go to observe penguins?
Penguins live along the southern coast of Australia. Check ocean beaches.
3.
a. Which bird is known as the "Laughing Jackass"?
The laughing kookaburra
b. To which species does it belong?
D. novaeguineae
c. What is unusual about the family makeup of this bird?
Most species of kookaburra tend to live in family units, with offspring helping the parents hunt and care for the next generation of offspring.
4.
a. Name at least 2 birds who incubate their eggs in the ground.
All flightless birds including the emu, cassowary, and penguin (and some flying birds) incubate on the grounds.
b. Describe how the nest is built and eggs are laid and incubated for one of these birds.
Emu and cassowary nests and eggs and described in Question 1
Penguins form monogamous pairs for a breeding season, though the rate the same pair recouples varies drastically. Most penguins lay two eggs in a clutch, although the two largest species, the emperor and the king penguins, lay only one. With the exception of the emperor penguin, where the male does it all, all penguins share the incubation duties. These incubation shifts can last days and even weeks as one member of the pair feeds at sea. If they make a nest (some just hold the eggs with their feet) they make the nest among and from rocks, generally as part of a large colony of nesting penguins.
c. What is the term which describes this type of bird?
Ground nesting birds often build scrape style nests.
5.
a. What does the Bower Bird use his bower for and what colour is the Satin Bower Bird known to 'steal' to decorate the bower?
A bower is large structure made of grass and bright objects, used by the bower bird during courtship displays to attract a mate. They prefer blue items.
b. Can you name a Bower Bird which lives in your state?
Check the ranges of the [various species] to find one that loves in your state.