Difference between revisions of "AY Honors/Christian Citizenship/Answer Key 9"
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
Image:Flag of Johor.svg|Sultanate of '''Johor''' (Johor Bahru) - The white crescent and star of five points denote royal sovereignty. The red represents a warrior and the blue represents the universe | Image:Flag of Johor.svg|Sultanate of '''Johor''' (Johor Bahru) - The white crescent and star of five points denote royal sovereignty. The red represents a warrior and the blue represents the universe | ||
Image:Flag of Kedah.svg|Sultanate of '''Kedah''' (Alor Star) - The state flag features a red crescent moon below a green shield and is enveloped by a yellow wreath against a red background. Red is the traditional colour of the state and also signifies prosperity while the crescent moon is symbolic of Islam. The shield symbolises the Sultan of the state as the protector and guardian of his subjects. | Image:Flag of Kedah.svg|Sultanate of '''Kedah''' (Alor Star) - The state flag features a red crescent moon below a green shield and is enveloped by a yellow wreath against a red background. Red is the traditional colour of the state and also signifies prosperity while the crescent moon is symbolic of Islam. The shield symbolises the Sultan of the state as the protector and guardian of his subjects. | ||
| − | Image:Flag of Kelantan.svg|Sultanate of '''Kelantan''' (Kota Bharu) | + | Image:Flag of Kelantan.svg|Sultanate of '''Kelantan''' (Kota Bharu) - The state flag features a white crest against a red background. The colour red symbolizes the loyalty of the Kelantanese people and white represents the sanctity of the Ruler. |
| − | Image:Flag of Pahang.svg|Sultanate of '''Pahang''' (Kuantan) | + | Image:Flag of Pahang.svg|Sultanate of '''Pahang''' (Kuantan) - The white crescent and star of five points denote royal sovereignty. The red represents a warrior and the blue represents the universe |
Image:Flag of Perak.svg|Sultanate of '''Perak''' (Ipoh) - The State Flag is divided into three equal horizontal stripes. The three colours represent the three branches of the royal family whereby the throne is shared in rotation. The white stripe symbolises the Sultan while the yellow stripe is that of the Raja Muda. The black stripe represents the Raja DiHilir. | Image:Flag of Perak.svg|Sultanate of '''Perak''' (Ipoh) - The State Flag is divided into three equal horizontal stripes. The three colours represent the three branches of the royal family whereby the throne is shared in rotation. The white stripe symbolises the Sultan while the yellow stripe is that of the Raja Muda. The black stripe represents the Raja DiHilir. | ||
Image:Flag of Selangor.svg|Sultanate of '''Selangor''' (Shah Alam) - The flag is divided into four equal-sized sections. The red sections denote the courage of the people of Selangor while the yellow sections are representative of the royal status of the head of state, the Sultan. The crescent moon and star on the upper left section are the symbols of Islam, the official religion of the state. | Image:Flag of Selangor.svg|Sultanate of '''Selangor''' (Shah Alam) - The flag is divided into four equal-sized sections. The red sections denote the courage of the people of Selangor while the yellow sections are representative of the royal status of the head of state, the Sultan. The crescent moon and star on the upper left section are the symbols of Islam, the official religion of the state. | ||
| − | Image:Flag of Terengganu.svg|Sultanate of '''Terengganu''' (Kuala Terengganu) | + | Image:Flag of Terengganu.svg|Sultanate of '''Terengganu''' (Kuala Terengganu) - The white background denotes the Ruler and the black field represents the people; the white surrounding the black signifies the protection of the Ruler over his subjects. The crescent and the star represent Islam, the State religion. |
Image:Flag of Negeri Sembilan.svg|Elective Monarchy of '''Negeri Sembilan''' (Seremban) - The yellow field of the flag represents the State Ruler. The canton in the top left-hand corner has two colours which divide it diagonally. The colour red represents the rakyat (citizens); and black is the symbol of the four undangs (traditional chiefs). | Image:Flag of Negeri Sembilan.svg|Elective Monarchy of '''Negeri Sembilan''' (Seremban) - The yellow field of the flag represents the State Ruler. The canton in the top left-hand corner has two colours which divide it diagonally. The colour red represents the rakyat (citizens); and black is the symbol of the four undangs (traditional chiefs). | ||
Image:Flag of Perlis.svg|Kingdom of '''Perlis''' (Kangar) - The top half of the flag, which is yellow in colour, represents the royal status of the Ruler of Perlis. The bottom half of the flag, on the other hand, is blue and stands for the people of Perlis. The two colours lay close and in tangent with each other, reflecting the cordial and close relationship between the Ruler and his people. | Image:Flag of Perlis.svg|Kingdom of '''Perlis''' (Kangar) - The top half of the flag, which is yellow in colour, represents the royal status of the Ruler of Perlis. The bottom half of the flag, on the other hand, is blue and stands for the people of Perlis. The two colours lay close and in tangent with each other, reflecting the cordial and close relationship between the Ruler and his people. | ||
Image:Flag of Malacca.svg|'''Melaka''' (Bandar Melaka) - The colours blue, yellow, red and white on the Melaka flag reflect the exact colours of the flag of Malaysia. This marks Melaka as a Malaysian state. The crescent moon and star are the symbols of Islam, the official religion of the state and country. | Image:Flag of Malacca.svg|'''Melaka''' (Bandar Melaka) - The colours blue, yellow, red and white on the Melaka flag reflect the exact colours of the flag of Malaysia. This marks Melaka as a Malaysian state. The crescent moon and star are the symbols of Islam, the official religion of the state and country. | ||
Image:Flag of Penang (Malaysia).svg|'''Pulau Pinang''' (George Town) - The tricolour flag features vertical stripes of equal width with an areca nut tree on the white centre panel. Light blue represents the sea surrounding the island; white stands for its serenity and yellow signifies prosperity. Pulau Pinang (Penang Island) derives its name from the arecanut tree, called pokok pinang in Malay. | Image:Flag of Penang (Malaysia).svg|'''Pulau Pinang''' (George Town) - The tricolour flag features vertical stripes of equal width with an areca nut tree on the white centre panel. Light blue represents the sea surrounding the island; white stands for its serenity and yellow signifies prosperity. Pulau Pinang (Penang Island) derives its name from the arecanut tree, called pokok pinang in Malay. | ||
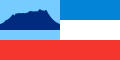
| − | Image:Flag of Sabah.svg|'''Sabah''' (Kota Kinabalu) | + | Image:Flag of Sabah.svg|'''Sabah''' (Kota Kinabalu) - The red stripe represents courage and the willingness to sacrifice for the state of Sabah. White is the colour of purity while dark blue is the colour of peace and prosperity. The light blue denotes Sabah's status as a young state. The silhouette of Mount Kinabalu is the symbol of the unity of the people. |
| − | Image:Flag of Sarawak.svg|'''Sarawak''' (Kuching) | + | Image:Flag of Sarawak.svg|'''Sarawak''' (Kuching) - Red symbolises the courage, confidence and sacrifices of the people in their efforts to achieve and maintain progress in the state. Yellow represents the supremacy of the law and the unity found amongst Sarawak's diverse races. Black denotes the abundant natural resources of Sarawak: petroleum and timber. The yellow nine-pointed star represents the nine divisions and the aspirations of the people to improve their quality of life. |
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Revision as of 00:17, 18 April 2008
1. Describe the national, state or provincial, AY, Pathfinder, and Christian flags.
Current state/provincial flags
- States of Malaysia
Sultanate of Kedah (Alor Star) - The state flag features a red crescent moon below a green shield and is enveloped by a yellow wreath against a red background. Red is the traditional colour of the state and also signifies prosperity while the crescent moon is symbolic of Islam. The shield symbolises the Sultan of the state as the protector and guardian of his subjects.
Sultanate of Perak (Ipoh) - The State Flag is divided into three equal horizontal stripes. The three colours represent the three branches of the royal family whereby the throne is shared in rotation. The white stripe symbolises the Sultan while the yellow stripe is that of the Raja Muda. The black stripe represents the Raja DiHilir.
Sultanate of Selangor (Shah Alam) - The flag is divided into four equal-sized sections. The red sections denote the courage of the people of Selangor while the yellow sections are representative of the royal status of the head of state, the Sultan. The crescent moon and star on the upper left section are the symbols of Islam, the official religion of the state.
Elective Monarchy of Negeri Sembilan (Seremban) - The yellow field of the flag represents the State Ruler. The canton in the top left-hand corner has two colours which divide it diagonally. The colour red represents the rakyat (citizens); and black is the symbol of the four undangs (traditional chiefs).
Kingdom of Perlis (Kangar) - The top half of the flag, which is yellow in colour, represents the royal status of the Ruler of Perlis. The bottom half of the flag, on the other hand, is blue and stands for the people of Perlis. The two colours lay close and in tangent with each other, reflecting the cordial and close relationship between the Ruler and his people.
Pulau Pinang (George Town) - The tricolour flag features vertical stripes of equal width with an areca nut tree on the white centre panel. Light blue represents the sea surrounding the island; white stands for its serenity and yellow signifies prosperity. Pulau Pinang (Penang Island) derives its name from the arecanut tree, called pokok pinang in Malay.
Sabah (Kota Kinabalu) - The red stripe represents courage and the willingness to sacrifice for the state of Sabah. White is the colour of purity while dark blue is the colour of peace and prosperity. The light blue denotes Sabah's status as a young state. The silhouette of Mount Kinabalu is the symbol of the unity of the people.
Sarawak (Kuching) - Red symbolises the courage, confidence and sacrifices of the people in their efforts to achieve and maintain progress in the state. Yellow represents the supremacy of the law and the unity found amongst Sarawak's diverse races. Black denotes the abundant natural resources of Sarawak: petroleum and timber. The yellow nine-pointed star represents the nine divisions and the aspirations of the people to improve their quality of life.
- Federal Territory of Malaysia
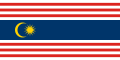
Federal Territory of Kuala Lumpur - The Kuala Lumpur Federal Territory flag comprises 14 alternating white and red stripes divided equally by a field of dark blue. The stripes represent the 13 states and the Federal Territory in the Malaysian Federation. The crescent moon and star are the symbols of Islam, the official religion of the country; dark blue represents the ethnic diversity of Kuala Lumpur. The colour white signifies purity and cleanliness, while red stands for courage, and yellow is the colour of peace and prosperity.
- Image:Flag of Labuan.svg
Federal Territory of Labuan (Bandar Labuan)
2. Know how to display the national flag with two other flags under the following situations:
a. Camp out/camporee
b. Fair
c. Pathfinder Day program
d. Parade
3. Demonstrate how to fold and salute your national flag. Mention when and how it should be displayed.
Folding
Flag Protocol
4. Explain the meaning of and reason for the National Anthem, and recite the words from memory.
5. Give the rights and responsibilities of a citizen of your country.
Rights
Responsibilities
6. Have an interview with a local, regional, or national official of your country, and learn about his duties.
It is generally easier to get a local official to agree to an interview, though it is often more exciting to interview a more prominent person. The interview can be accomplished during a club meeting, and multiple Pathfinders can ask questions. Invite your guest well ahead of time, and make sure everyone in the club is on time. A visit by an official would be a very good reason to have everyone in the club wear their class A uniforms. If desired, you can make up several questions ahead of time, writing them on index cards, and distributing them to the members of your club. But do not be so rigid as to not allow them to ask spontaneous questions. Having questions prepared ahead of time on index cards are a good way to get things rolling. Here are some suggested questions:
- Could you describe a typical day at work?
- What is the most difficult part of your job?
- What is the most satisfying aspect of your job?
- To whom do you report?
- How did you get your position? Were you elected, appointed, or hired?
- How should a young person prepare for a life of public service?
7. Write a one-page essay or give a two-minute oral report about a famous person in your country. Mention what he has done to gain his recognition.
This would be an excellent opportunity to present a worship during the opening exercises of a regular club meeting. Encourage your Pathfinder to choose a person they are personally interested in. If they cannot think of anyone themselves, have a list of suggested persons at hand and encourage them to choose from the list. Famous people might be historical figures, politicians, actors, sports stars, or anyone else. It would be preferable to choose a person who has been a positive influence on the country.
Although the requirement asks that you "mention what he has done to gain his recognition," this should not be interpreted as excluding women. Men are not the only famous people in a country.
8. Do one of the following:
a. Make a list of ten famous quotations from leaders of your country.
b. Make a list of ten famous historic places in your country.
c. Make a list of ten famous historic events in your country.
9. Describe what you can do as a citizen to help your church and country.
The best way to help either your church or your country is by getting involved. Edmund Burke, an English philosopher summed this up when he said "The only thing necessary for the triumph of evil is for good men to do nothing."
In your church, this means that you will show up for services on a regular basis. It also means you will support it with your tithes and offering, show up for business meetings, and not wait to be asked before you volunteer your services. If you see something that needs done, do it. If you do not have the skill to do it, or you think that you need permission first, talk to your pastor, an elder, deacon, or deaconess. Find your ministry!
For your country, it is much the same. Show up for public meetings, stay informed about the issues of the day, vote if you are eligible, and pay your taxes fairly and promptly.
10. Go through the steps of an individual acquiring citizenship in the country and learn how this is done.
11. Know how to explain the process of government in your country.
12. Explain the meaning of this statement Jesus made in Matthew 22:21: "Render therefore unto Caesar the things which are Caesar's, and unto God the things that are God's.
This verse teaches that governmental authority is to be respected, as long as it does not conflict with the moral obligations of being a Christian. Government serves a holy purpose; preserving social order, promoting the well-being of its citizens, and protecting their safety. If you believe that this does not apply today because you see the government as corrupt, you are urged to research the Roman government of the first century A.D. when these words were spoken by Jesus. Was Herod corrupt? Was Pilate just?