Difference between revisions of "AY Honors/Brain and Behavior/Answer Key/es"
(Created page with "</noinclude>") |
(Created page with "{{clear}}") |
||
| Line 162: | Line 162: | ||
<noinclude></noinclude> | <noinclude></noinclude> | ||
| − | + | {{clear}} | |
<noinclude></noinclude> | <noinclude></noinclude> | ||
Revision as of 10:02, 8 March 2021
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
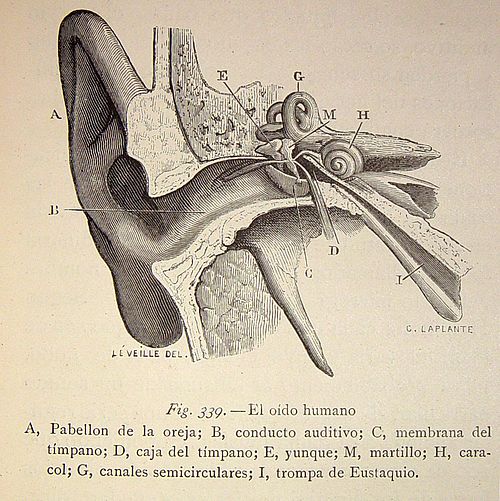
Las tres partes básicas del oído son el oído externo, el oído medio y el oído interno.
- The outer ear is the external portion of the ear and includes the eardrum. The pinna, which is the external portion of the ear, captures the sound and transfers them through the auditory canal to the eardrum, which vibrates and transfers the sound to the tiny bones in the middle ear.
9
9a
9b
9c
9d
9e
9f
Now this sounds like FUN!
10
- Wear a helmet. Many work and recreational activities can subject a person to head injury. It is best to not take chances - wear a helmet when it's called for! Do not enter a hard-hat area without a hardhat. Put on your helmet every time you ride your bike, go rock climbing, play football, or paddle a kayak. Why risk it?
- Exercise your brain. The more you use your brain, the better it works. The saying "practice makes perfect" is very true. Any activity that involves the brain can be improved with practice.
- Get plenty of fresh air. Your brain needs oxygen.
- Say "No" to drugs. Most of the illegal "street drugs" are popular because they affect the way people feel. The only way they can do this is by affecting the brain, and these effects are never harmless. Drugs can do permanent damage to the brain.
- Eat healthy food. Junk foods cloud the brain. Healthy foods are just as good for the brain as they are for the body.
- Live by Christian principles. Viewing inappropriate television programs, listening to music that promotes sin, and indulging in indecent reading material has a permanent effect on the brain. Memorized song lyrics stick with a person for a long time, even when that person no longer wishes to remember them.
11
11a
11b
11bi
Alzheimer's disease is a degenerative disease of the brain. It is the most common cause of dementia and is characterized by progressive intellectual deterioration together with declining activities of daily living and behavioral changes. The most striking early symptom is memory loss (amnesia), usually in the form of minor forgetfulness that becomes steadily worse as the illness progresses, with relative preservation of older memories. As the disorder progresses, intellectual impairment extends to language, coordinated movement, recognition and functions such as decision-making and planning.
11bii
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic disease that affects the brain and spinal cord. MS can cause a variety of symptoms, including changes in sensation, visual problems, muscle weakness, depression, and difficulties with coordination and speech. Although many patients lead full and rewarding lives, MS can cause impaired mobility and disability in the more severe cases.
Multiple sclerosis affects neurons, the cells of the brain and spinal cord that carry information, create thought and perception and allow the brain to control the body.
11biii
Epilepsy is a chronic neurological condition characterized by recurrent unprovoked seizures. It has been described as electrical storms in the brain's circuitry.
All the causes of epilepsy are not known, but many predisposing factors have been identified, including brain damage resulting from malformations during brain development, head trauma, neurosurgical operations, other penetrating wounds of the brain, brain tumor, high fever, bacterial or viral encephalitis, stroke, intoxication, or acute or inborn disturbances of metabolism.
11biv
Major depression is a state of sadness or melancholia that has advanced to the point of being disruptive to an individual's social functioning and/or activities of daily living. It is caused by chemical imbalances in the brain.
11bv
Down syndrome encompasses a number of chromosomal abnormalities causing highly variable degrees of learning difficulties as well as physical disabilities. While most children with Down syndrome have a lower than average cognitive function, some have earned college degrees, and nearly all will learn to read, write and do simple mathematics.
11bvi
Huntington's disease (HD) is an inherited disorder characterized by abnormal body movements called chorea, and a reduction of various mental abilities. Symptoms of the disorder include loss of cognitive ability (thinking, speaking), changes in personality, jerking movements of the face and body in general and unsteady walking. These symptoms develop into dementia and cognitive decline, and an advanced form of rapid jerking.
11bvii
Quadriplegia is a symptom in which a human experiences partial or complete paralysis from the neck down. It is caused by damage to the brain or to the spinal cord at a high level. The injury causes the victim to lose total or partial use of the arms and legs.
11bviii
Paraplegia is a condition in which the lower part of a patient's body is paralyzed and cannot move. It is usually the result of spinal cord injury or a congenital condition such as spina bifida.
12
An excellent place to find Biblical references on making decisions is Week 23 of the IA weekly devotional guide (required for Companions and Voyagers):
References
- http://staff.washington.edu/chudler/synapse.html
- http://nobelprize.org/medicine/educational/synapse/intro.html
- http://www.txtwriter.com/backgrounders/Drugaddiction/drugs1.html