Difference between revisions of "AY Honors/Flags/Answer Key/es"
(Created page with "{{clear}}") |
(Created page with "{{clear}}") |
||
| Line 217: | Line 217: | ||
{{clear}} | {{clear}} | ||
| − | + | {{clear}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
Revision as of 21:56, 26 March 2021
1
Una bandera es una pieza de material con un diseño distintivo que es generalmente rectangular y se utiliza como un símbolo, como un dispositivo de señalización o decoración adjunto a una orilla de un poste o una cuerda.
2
2a
Es la para superior de la bandera cerca del asta, o una bandera con un diseño en el área del cantón. La parte azul con estrellas en la bandera de los Estados Unidos es el cantón, pero no hay cantón en la bandera canadiense.
2b
Es el color de fondo de la bandera, la parte entre al asta y el pendiente.
2c
Un ornamento encima del asta, sea en un poste fijo - como en una escuela - o un poste diseñado para llevar la bandera en un desfile.
2d
Generalmente cuando una bandera se usa al aire libre, está en un mástil o un asta.
2e
La parte de la bandera que está más lejos del asta.
2f
La parte de la bandera que aletea en el viento y a veces se deteriora.
2g
Es una cuerda o cable que se utiliza para subir y bajar una bandera en un asta.
2h
La parte de la bandera que está más cercano a la asta de bandera.
2i
El mecanismo que conecta el pináculo al poste.
3
Mientras que algunas instrucciones específicas difieren un poco entre los países, lo que sigue es casi una verdad universal:
- La bandera nacional debe estar por encima de cualquier otra bandera
- La bandera nacional nunca debe tocar el suelo
- Se debe mostrar respeto a la bandera - incluyendo el saludo a la bandera
- Banderas hechas andrajos no se deben mostrar o exhibir pero deberán eliminarse de forma privada, preferiblemente con fuego
4
El procedimiento para doblar la bandera nacional varía según el país. Si su país y bandera no está en esta lista, por favor siéntase libre de investigar y agregarlo a la lista.
Bermuda
El protocolo de la bandera para Bermuda debe seguir el mismo que del Reino Unido porque es un territorio británico.
Canadá
No existe un método oficial de doblar la bandera para el uso diario. Hay, sin embargo, un método similar a la utilizada en los Estados Unidos cuando se dobla una bandera para fines ceremoniales tal como un funeral. Más información (sólo disponibles en inglés) se puede encontrar en la página web de Canadian Directorate of History and Heritage (Dirección Canadiense de Historia y Patrimonio).
Reino Unido
Hay dos métodos utilizados generalmente en doblar la bandera británica. El primero se llama Romper y se usa generalmente durante izamiento de la bandera. La bandera británica se dobla por la mitad a lo largo (a lo largo de la franja roja central de la Cruz de San Jorge) y luego por la mitad, con el doblez llegando al borde. El último tercio de la bandera se dobla hacia dentro y luego el resto se enrolla hacia el lado al asta. La bandera se fija con un pedazo de algodón ligero o cuerda. Cuando izada, un fuerte tirón de la driza se romperá la cadena y permitirá que la bandera vuele libre.
El otro método es generalmente usado cuando la bandera cubre a un ataúd. La manera de doblarla es similar al que se usa en los Estados Unidos. Además de estos, no hay otros métodos oficiales para doblar la bandera británica. Debe ser izada y bajada con respeto, y que no toque el suelo.
Los Estados Unidos
Title 4 Chapter 1 of the United States Code, conocido como el protocolo de la bandera estadounidense, adoptado por primera vez en 1924 y modificado hasta el presente, regula la etiqueta de la bandera para una variedad de circunstancias que garantiza que el símbolo nacional sea tratado adecuadamente.
5
5a
5b
5c
5d
5e
6
6a
Elena Hobbs creó la bandera de Conquistadores. El escudo del Club de Conquistadores fue diseñado por Juan H. Hancock.
6b
Vea la bandera al lado para una guía.
6c
7
La simplicidad de la bandera cristiana hace esta parte fácil.
7a
La bandera tiene un campo blanco, con una cruz latina roja dentro de un cantón azul. El tono del color rojo en la cruz simboliza la sangre que Cristo derramó en el Calvario. El color azul representa las aguas del bautismo, así como la fidelidad de Cristo. El color blanco representa la pureza de Cristo. En la vexilología convencional, una bandera blanca significa rendirse, una referencia a la descripción bíblica de la actitud pacífica y la rendición de Cristo. Las dimensiones de la bandera y el cantón no tienen especificaciones oficiales.
7b
La cruz representa la muerte de Jesús, para que podamos vivir para siempre. La cruz es un símbolo reconocible instantáneo del cristianismo.
8
8a
Cuando se muestra la bandera nacional en campamentos, debe colocarse a la izquierda de los que entran al campamento y a la derecha de los que están acampando. Cuando todas las banderas se muestran en un asta, la bandera nacional está en la parte superior, y después la bandera JA y la bandera de Conquistadores.
8b
Para un programa de Día del Conquistador, la bandera nacional se debe mostrar a la derecha del orador si está en la plataforma. Otras banderas deben mostrarse a la izquierda del orador.
8c
Si se muestran las banderas en otro lugar, con excepción de la plataforma, la bandera nacional debe aparecer a la derecha de la audiencia, mirando hacia la plataforma. Otras banderas deben estar a la izquierda de la audiencia.
8d
Banderas deben colocarse a la derecha de la caseta y a la izquierda del inspector. Si la bandera nacional es parte de un grupo de banderas, debe estar en el centro y un poco hacia adelante o en relieve. En las ferias públicas, banderas pueden estar puestos dentro de la caseta, pero la bandera nacional está siempre a la izquierda del espectador.
8e
A la derecha de la audiencia.
9
- Canada
Canadian Heritage is responsible for flag promotion and protocol. Explore their page here for everything you need to know about the Maple Leaf.
- United Kingdom
All UK specific answers and other general info. http://www.flaginstitute.org/pdfs/Flying_Flags_in_the_United_Kingdom.pdf
- United States
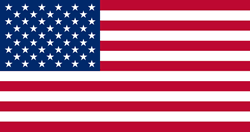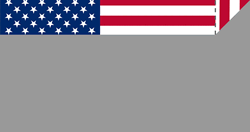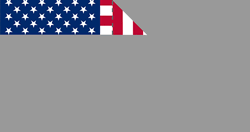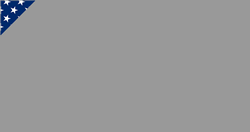
The red and white stripes represent the original 13 colonies. The (current) 50 stars represent the current 50 states, the number being increased as states were added.
- Other Countries
If your country is not listed here, please research and add the info here. The history of national flags is easy to find online.
The national flag of Burundi was adopted on June 28, 1967 after the country's independence from Belgium on 1 July 1962. It consists of a white saltire which divides the field into alternating red and green areas. The center of the saltire merges into a white disk, on which there are three red solid six-pointed stars outlined in green.
The flag is divided into four parts by a white cross. The upper and lower parts are red in color while the left and right ones are green in color. White color of the cross represents peace, green represents the nation's hopes placed on future development and red symbolizes the suffering of the nation during its freedom struggle.[2] The three stars in triangular configuration stand for the three major ethnic groups of Burundi: the Hutu, the Twa and the Tutsi.[2] The three stars also stand for the three elements of the national motto: Unité, Travail, Progrès ("Unity, Work and Progress"), which can be seen on the Coat of arms of Burundi.[3] They also represent the loyalty that the citizens of the nations have pledged to their God, king and country. Flag of Burundi
The flag of Rwanda was adopted on October 25, 2001. The flag has four colours: blue, green, and two forms of yellow[1] (standard yellow for the middle band and what the Pantone system calls "sun yellow" for the sun). The blue band represents happiness and peace, the yellow band symbolizes economic development, and the green band symbolizes the hope of prosperity. The sun represents enlightenment. The new flag represents national unity, respect for work, heroism, and confidence in the future. It was adopted to avoid connotations to the 1994 genocide. The flag was designed by Alphonse Kirimobenecyo. When hung vertically, the flag should be displayed as the horizontal version rotated clockwise 90 degrees. Flag of Rwanda
The flag of Zambia was adopted upon independence on October 24, 1964. Before that, Zambia was the British protectorate of Northern Rhodesia and used a defaced Blue Ensign as its flag. The current flag is used as both national flag and ensign. It is green with an orange-coloured African fish eagle in flight over a rectangular block of three vertical stripes, coloured, from left to right: red, black and orange. The placement of the eagle and block of stripes at the flag's fly is notable as most emblems and devices on flags are placed at centre or at the hoist.
The colours used in the flag of Zambia are rich in symbolism. Green stands for the nation's lush flora, red for the nation's struggle for freedom, black for the Zambian people, and orange for the land's natural resources and mineral wealth. Additionally, the eagle flying above the coloured stripes is intended to represent the people's ability to rise above the nation's problems.
The Zambian flag was slightly modified in 1996. The shade of green used in the 1964 flag was replaced with a brighter and lighter green and the eagle was slightly altered so as to be more like the one used in the Zambian coat of arms.
The design of the national flag of Zambia is described in National Flag and Armorial Ensigns Act of 4 June 1965.[1] Green with an orange coloured eagle in flight over a rectangular block of three vertical stripes coloured from left to right in red, black and orange; of overall dimensions 3:2; and to the following colour specifications: "Spectrum Green", British Colour Council Shade reference 100. "Union Jack Red", British Colour Council Shade reference 210. "Jet Black", British Colour Council Shade reference 220. "Spectrum Orange", British Colour Council Shade reference 57.
Colours
The green was adjusted in 1996 to a lighter and brighter green. In 2012 The London Organising Committee of the Olympic and Paralympic Games solicited advice from each participating nation the correct Pantone colours for its flag. Once confirmed, the results were published in a guide.
Symbolism
The flag's colours and emblems are rich in symbolism. Each of the four colours represents an aspect of Zambia: green for the country's natural resources and vegetation; red for its struggle for freedom; black for its people and orange for its mineral wealth (primarily copper). The eagle is an African fish eagle, which also appears in the national coat of arms and represents the people's ability to rise above the nation's problems.
Flag protocol
By law, the Zambian flag should be flown only between the hours of sunrise and sunset and may be flown: - at buildings or premises owned or occupied by the Government; - at buildings or premises owned or occupied by local government authorities; - at buildings or premises owned or occupied by any statutory board or statutory corporation; - at state-aided schools; - on any motor car, boat or ship in or by which a Minister of Government is for the time being travelling; - on any ship registered as Zambian.
The flag is not allowed to be flown by any other individual or institution without express written permission from the Minister except on the following occasions: - on the following public holidays, namely: Africa Freedom Day, Heroes Day, Unity Day, and Independence Day; - on such other days or occasions as the Minister may declare for this purpose. Flag of Zambia
The flag of South Sudan was adopted following the signing of the Comprehensive Peace Agreement that ended the Second Sudanese Civil War. The flag was previously used as the flag of the Sudan People's Liberation Movement.
The flag bears striking similarities with those of Sudan (from whom Southern Sudan seceded in 2011), and Kenya. It shares the black, white, red, and green of the Sudanese flag (though different symbolism is given to the colours), in addition to having a triangle along the hoist. The horizontal black, white, red, and green bands, fimbriated white, are the same design as the Kenyan flag, and the Pan-African symbolism it conveys.
The Southern Sudanese government also specifies that the colours of the flag are to represent:
- Black: Black African skin. - Red: Blood that was shed by the liberation struggle martyrs. - Green: The country's natural resources and verdant land. - White: Peace attained after many years of the liberation struggle. - Blue: Waters of the Nile River, a source of life for the country. - Yellow: The unity of the states making up South Sudan. Flag of South Sudan
The flag of Tanzania consists of a yellow-edged black diagonal band divided diagonally from the lower hoist-side corner, with a green upper triangle and blue lower triangle. Adopted in 1964 to replace the individual flags of Tanganyika and Zanzibar, it has been the flag of the United Republic of Tanzania since the two states merged that year. The design of the present flag incorporates the elements from the two former flags.
The United Kingdom – together with its dominion South Africa and fellow Allied power Belgium – occupied the majority of German East Africa in 1916 during the East African Campaign. Three years later, the British were tasked with administering the Tanganyika Territory as a League of Nations mandate. It was turned into a UN Trust Territory after World War II, when the LN dissolved in 1946 and the United Nations was formed. In 1954, the Tanganyika African Association – which spoke out against British colonial rule – became the Tanganyika African National Union (TANU) under the leadership of Julius Nyerere and Oscar Kambona. The aim of the political party was to attain independence for the territory; its flag was a tricolour consisting of three horizontal green, black and green bands.Shortly before independence in 1961, elections were held in Tanganyika. After the TANU won comprehensively, the British colonial leaders advised them to utilize the design of their party's flag as inspiration for a new national flag. As a result, yellow stripes were added, and Tanganyika became independent on 9 December 1961.
In April 1964, both Tanganyika and Zanzibar united in order to form a single country – the United Republic of Tanzania. Consequently, the flag designs of the two states were amalgamated to establish a new national flag. The green and black colours from the flag of Tanganyika were retained along with the blue from Zanzibar's flag, with a diagonal design used "for distinctiveness".[3] This combined design was adopted on 30 June 1964. It was featured on the first set of stamps issued by the newly unified country.
Symbolism
The colors and symbols of the flag carry cultural, political, and regional meanings. The green alludes to the natural vegetation and "rich agricultural resources" of the country, while black represents the Swahili people who are native to Tanzania. The blue epitomizes the Indian Ocean, as well as the nation's numerous lakes and rivers. The thin stripes stand for Tanzania's mineral wealth, derived from the "rich deposits" in the land. While Whitney Smith in the Encyclopædia Britannica and Dorling Kindersley's Complete Flags of the World describe the fimbriations as yellow, other sources – such as The World Factbook and Simon Clarke in the journal Azania: Archaeological Research in Africa – contend that it is actually gold. Flag of Tanzania
The flag of Uganda was adopted on 9 October 1962, the date that Uganda became independent from the United Kingdom. It consists of six equal horizontal bands of black (top), yellow, red, black, yellow, and red (bottom); a white disc is superimposed at the centre and depicts the national symbol, a grey crowned crane, facing the hoist side.
History
When the Democratic Party ruled the country, a design for flag was proposed. It had vertical stripes of green-blue-green, separated by narrower yellow stripes, and in the centre had the silhouette of a yellow crane. After the party lost the national elections on April 25, 1962 the newly elected Uganda People’s Congress (UPC) rejected the former design and instead proposed the current design. It was based on the flag of UPC– a tricolor having horizontal strips of red, yellow and black. The British administration gave their approval to this design before the country's independence. The flag was designed by the Ugandan Minister of Justice, Grace Ibingira.
Symbolism
The three colours are representative of African peoples (black), Africa's sunshine (yellow), and African brotherhood (red being the colour of blood, through which all Africans are connected). The grey crowned crane is fabled for its gentle nature and was also the military badge of Ugandan soldiers during British rule. The raised leg of the crane symbolizes the forward movement of the country.
The flag of the Democratic Republic of the Congo is a sky blue flag, adorned with a yellow star in the upper left canton and cut diagonally by a red stripe with a yellow fimbriation. It was adopted on 20 February 2006. A new constitution, ratified in December 2005 and which came into effect in February 2006, promoted a return to a flag similar to that flown between 1963 and 1971, with a change from a royal blue to sky blue background. Blue represents peace. Red stands for "the blood of the country's martyrs, yellow the country's wealth; and the star a radiant future for the country."
Previous flags
The previous flag was adopted in 2003. It is similar to the flag used between 1960 and 1963. The flag is based on the flag which was originally used by King Leopold's Association Internationale Africaine and was first used in 1877. The design was then implemented as the flag of the Congo Free State after the territory was recognized as an official possession of Leopold II at the Berlin Conference. After gaining independence from Belgium on 30 June 1960, the same basic design was maintained. However, six stars were incorporated to symbolise the six provinces of the country at the time. This design was used only from 1960 to 1963.
The flag of the first Republic of Mobutu Sese Seko became the official banner after Mobutu established his dictatorship. This flag was used from 1966–1971 and consisted of the same yellow star, now made smaller, situated in the top corner of the hoist side, with a red, yellow-lined band running diagonally across the center. The red symbolized the people's blood; the yellow symbolized prosperity; the blue symbolized hope; and the star represented unity. This flag was changed when the country was renamed Zaire in 1971. The Zaire flag was created as part of Mobutu's attempted re-Africanization of the nation and was used officially until Mobutu's overthrow in the First Congo War. Flag of the Democratic Republic of the Congo
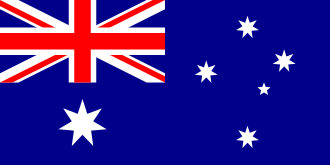
The Australian National Flag (the flag) was first flown in 1901. It is Australia's foremost national symbol and has become an expression of Australian identity and pride.The flag is paraded by our defense forces and displayed around the country at sporting events and by service organisations, schools, community groups and private citizens. The flag has three elements on a blue background: the Union Jack, the Commonwealth Star and the Southern Cross. The Union Jack in the upper left corner represents the history of British settlement. Below the Union Jack is a white Commonwealth, or Federation, star. It has seven points representing the unity of the six states and the territories of the Commonwealth of Australia. The star is also featured on the Commonwealth Coat of Arms. The Southern Cross is shown on the flag in white. It is a constellation of five stars that can only be seen from the southern hemisphere and is a reminder of Australia’s geography.
10
The Adventist Church has divided the world into 13 administrative districts it calls Divisions.
North American Division
The North American Division comprises 10 countries and territories:
Bermuda
The current Bermuda flag was adopted in the 1910. As a British overseas territory, Bermuda's flag features the United Kingdom flag upper left. The green and white badge displays a red lion holding a shield that symbolizes the sinking of the Sea Venture about one mile off the coastline of Bermuda in the summer of 1609 by the founders of Bermuda. The ship was caught in a hurricane, so the captain intentionally struck a reef near the island saving all lives on board. &
Canada
The flag of Canada was officially adopted on February 15, 1965. The Canadian Red Ensign, bearing the Union Jack and the shield of the royal arms of Canada, was lowered and then, on the stroke of noon, the new maple leaf flag was raised. The crowd sang the national anthem O Canada, followed by the royal anthem, God Save the Queen.
The following words, spoken on that momentous day by the Honourable Maurice Bourget, Speaker of the Senate, added further symbolic meaning to the flag: "The flag is the symbol of the nation's unity, for it, beyond any doubt, represents all the citizens of Canada without distinction of race, language, belief or opinion." The stylish red maple leaf has been the national symbol of Canada for over 150 years. Red and white are the official colors of Canada, proclaimed by King George V in 1921.&
St.Pierre and Miquelon (French islands close to Newfoundland with no Adventist presence)
Saint Pierre and Miquelon are a self-governing territory of France. The stylish flag features a red sailing ship on a blue field. The three-part verticle band on the left side displays the heraldic arms of local settlements established by French colonists from the Basque Country (top), Brittany (center), and Normandy (bottom).&
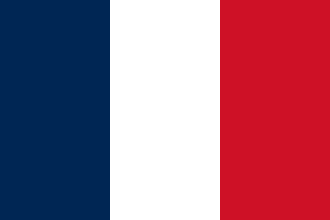
The Flag of France also flies in Saint Pierre and Miquelon.
Blue and red are the traditional colours of Paris, used on the city's coat of arms. Blue is identified with Saint Martin, red with Saint Denis. At the storming of the Bastille in 1789, the Paris militia wore blue and red cockades on their hats. White had long featured prominently on French flags and is described as the "ancient French colour" by Lafayette.[1] White was added to the "revolutionary" colors of the militia cockade to "nationalise" the design, thus creating the tricolour cockade.[1] Although Lafayette identified the white stripe with the nation, other accounts identify it with the monarchy.[3] Lafayette denied that the flag contains any reference to the red-and-white livery of the Duc d'Orléans. Despite this, Orléanists adopted the tricolour as their own.
Blue and red are associated with the Virgin Mary the patron saint of France, and were the colours of Charlemagne's ensign and war cry, "Montjoie". The colours of the French flag may also represent the three main estates of the Ancien Régime (the clergy: white, the nobility: red and the bourgeoisie: blue). Blue, as the symbol of class, comes first and red, representing the nobility, comes last. Both extreme colours are situated on each side of white referring to a superior order.[4] Lafayette's tricolour cockade was adopted in July 1789, a moment of national unity that soon faded. Royalists began wearing white cockades and flying white flags, while the Jacobins, and later the Socialists, flew the red flag. The tricolour, which combines royalist white with republican red, came to be seen as a symbol of moderation and of a nationalism that transcended factionalism.
The three colours are occasionally taken to represent the three elements of the revolutionary motto, liberté (freedom: blue), égalité (equality: white), fraternité (brotherhood: red); this symbolism was referenced in Krzysztof Kieślowski's three colours film trilogy, for example.
United States (excluding Puerto Rico and the US Virgin Islands which are in IAD)
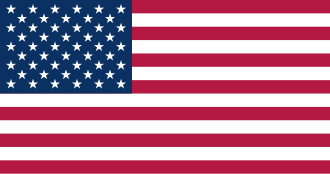
The flag of the United States features thirteen equal horizontal stripes of red (top and bottom) alternating with white; there is a blue rectangle in the upper hoist-side corner bearing 50 small, white, five-pointed stars arranged in nine offset horizontal rows of six stars (top and bottom) alternating with rows of five stars; the 50 stars represent the 50 states; the 13 stripes the 13 original colonies. The flag is known as Old Glory, and no one knows for certain who designed it. Most historians believe that U.S. Congressman, Francis Hopkinson was the original designer, while a few still believe that Betsy Ross, a Philadelphia seamstress, made the first one.&
US Pacific territories of Guam, Northern Marianas, and Wake Island
The flag of Guam was designed on the island, and officially adopted in 1917. As a territory of the United States it features traditional U.S. colors, along with a symbolic seal that includes a swaying palm tree, sand, and the waters of the Pacific Ocean.&
The flag of Northern Mariana Islands was officially adopted in 1972. The islands are a territory of the United States, symbolized by the centered white star. Under that star, a gray latte stone is representative of a traditional foundation stone, one used in building. The surrounding wreath is comprised of colorful local flowers.&
The Wake Island flag includes the colors of the US flag, a maps of the 3 islands that make up the territory and three white stars representing those islands. The flag clearly conveys the connection to the United States.
Palau
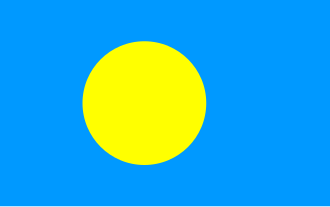
The flag of Palau was adopted on 1 January 1981, when the island group separated from the United Nations Trust Territory and became a republic. Previously, the flag of the Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands was flown jointly with the United Nations and American flags. Like some other flags of several other Pacific island groups, blue is the colour used to represent the ocean and the nation's place within it.
The flag's very simple design belies the depth of meaning attributed to it. The explanation for the choice of colours is rooted in the history and customs of the Palauan people. The bright blue of the field, which might be assumed to be symbolic of the Pacific Ocean, is in fact a representation of the transition from foreign domination to self-government. The golden disk, which sits slightly off centre toward the hoist, represents the full moon. The Palauans consider the full moon to be the optimum time for human activity. At this time of the month, celebrations, fishing, sowing, harvesting, tree-felling, and the carving of traditional canoes are carried out. The moon is a symbol of peace, love, and tranquility.
The Marshall Islands
The flag of the Marshall Islands was adopted upon the start of self-governance, May 1, 1979. The flag was designed by Emlain Kabua, who served as the first First Lady of the republic.
The Marshall Islands were part of the Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands administered by the United States, from which the Marshall Islands, Palau, and the Federated States of Micronesia split. In common with other island nations in the region, this flag features the symbolic representation of the islands' place within the ocean. The rising diagonal band represents the equator, the star above representing this Northern Hemisphere archipelago. The white and orange portions of the band represent, respectively, the Ratak Chain ("sunrise") and the Ralik Chain ("sunset"), as well as symbolizing peace and courage. The star's 24 points represent the number of electoral districts, while the four elongated points represent the principal cultural centers of Majuro, Jaluit, Wotje and Ebeye.
The Federated States of Micronesia
The flag of the Federated States of Micronesia (FSM) was adopted on 10 November 1979. The blue field represents the Pacific Ocean, while the four stars represent the states in the federation: Chuuk, Pohnpei, Kosrae and Yap, with the stars arranged like the points of the compass.
The flag brings together element of previous flags flown over the islands. The Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands used a six star flag however the current flag excludes the stars representing Palau, the Marshall Islands and Northern Mariana, which chose not to participate in the Federation, and adds back a star because the Trust Territory flag combined two islands in the group in one of the six stars. The blue and white colors are those of the UN flag which flew over the islands from 1947 - 1965. The idea of stars representing states echos the US flag, which also flew over the islands for many years.
(these last three countries are in free association with the United States and with the three US Pacific territories form the Guam-Micronesia Mission, which became part of the North American Division in 2011.)
Other Parts of the World
You can see a list of countries currently associated with the other Divisions and attached regions here. http://www.adventist.org/world-church/world-divisions/index.html From that list you can assemble a collection of the required flags.
References
- ↑ http://www.worldatlas.com/webimage/flags/countrys/europe/bermuda.htm
- ↑ http://www.worldatlas.com/webimage/flags/countrys/namerica/canada/caflag.htm
- ↑ http://www.worldatlas.com/webimage/flags/countrys/assorted/stpierre.htm
- ↑ http://www.worldatlas.com/webimage/countrys/namerica/usstates/usflags.htm
- ↑ http://www.worldatlas.com/webimage/flags/countrys/pacific/guam.htm
- ↑ http://www.worldatlas.com/webimage/flags/countrys/pacific/marianas.htm
- Wikipedia - Flags
- http://www.flaginstitute.org/pdfs/Flying_Flags_in_the_United_Kingdom.pdf. All UK specific answers here and other general info.