Difference between revisions of "AY Honors/Mammals/Answer Key"
(+ translate tags) |
(Marked this version for translation) |
||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
{{Honor_Master|honor=Mammals|master=Naturalist|core=Options}} | {{Honor_Master|honor=Mammals|master=Naturalist|core=Options}} | ||
{{Honor_Master|honor=Mammals|master=Zoology}} | {{Honor_Master|honor=Mammals|master=Zoology}} | ||
| − | ==1. What Bible verse gives the day mammals were created?== | + | ==1. What Bible verse gives the day mammals were created?== <!--T:1--> |
| + | <!--T:2--> | ||
Genesis 1:24,25, 31 | Genesis 1:24,25, 31 | ||
{{Bible verse | {{Bible verse | ||
| Line 22: | Line 23: | ||
<sup>24</sup>And God said, "Let the land produce living creatures according to their kinds: livestock, creatures that move along the ground, and wild animals, each according to its kind." And it was so. | <sup>24</sup>And God said, "Let the land produce living creatures according to their kinds: livestock, creatures that move along the ground, and wild animals, each according to its kind." And it was so. | ||
| + | <!--T:3--> | ||
<sup>25</sup>God made the wild animals according to their kinds, the livestock according to their kinds, and all the creatures that move along the ground according to their kinds. And God saw that it was good. | <sup>25</sup>God made the wild animals according to their kinds, the livestock according to their kinds, and all the creatures that move along the ground according to their kinds. And God saw that it was good. | ||
| + | <!--T:4--> | ||
<sup>26</sup>Then God said, "Let us make man in our image, in our likeness, and let them rule over the fish of the sea and the birds of the air, over the livestock, over all the earth, and over all the creatures that move along the ground." | <sup>26</sup>Then God said, "Let us make man in our image, in our likeness, and let them rule over the fish of the sea and the birds of the air, over the livestock, over all the earth, and over all the creatures that move along the ground." | ||
| + | <!--T:5--> | ||
<sup>27</sup>So God created man in his own image, in the image of God he created him; male and female he created them. | <sup>27</sup>So God created man in his own image, in the image of God he created him; male and female he created them. | ||
| + | <!--T:6--> | ||
<sup>28</sup>God blessed them and said to them, "Be fruitful and increase in number; fill the earth and subdue it. Rule over the fish of the sea and the birds of the air and over every living creature that moves on the ground." | <sup>28</sup>God blessed them and said to them, "Be fruitful and increase in number; fill the earth and subdue it. Rule over the fish of the sea and the birds of the air and over every living creature that moves on the ground." | ||
| + | <!--T:7--> | ||
<sup>29</sup>Then God said, "I give you every seed-bearing plant on the face of the whole earth and every tree that has fruit with seed in it. They will be yours for food. | <sup>29</sup>Then God said, "I give you every seed-bearing plant on the face of the whole earth and every tree that has fruit with seed in it. They will be yours for food. | ||
| + | <!--T:8--> | ||
<sup>30</sup>And to all the beasts of the earth and all the birds of the air and all the creatures that move on the ground—everything that has the breath of life in it—I give every green plant for food." And it was so. | <sup>30</sup>And to all the beasts of the earth and all the birds of the air and all the creatures that move on the ground—everything that has the breath of life in it—I give every green plant for food." And it was so. | ||
| + | <!--T:9--> | ||
<sup>31</sup>God saw all that he had made, and it was very good. And there was evening, and there was morning—the sixth day. | <sup>31</sup>God saw all that he had made, and it was very good. And there was evening, and there was morning—the sixth day. | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | ==2. List four characteristics of a mammal. == | + | ==2. List four characteristics of a mammal. == <!--T:10--> |
| + | <!--T:11--> | ||
::1. Endothermic (Warm-blooded) | ::1. Endothermic (Warm-blooded) | ||
| + | <!--T:12--> | ||
::2. Hair or Fur | ::2. Hair or Fur | ||
| + | <!--T:13--> | ||
::3. Mammary (milk producing) glands | ::3. Mammary (milk producing) glands | ||
| + | <!--T:14--> | ||
::4. Sebaceous (fat-secreting) glands | ::4. Sebaceous (fat-secreting) glands | ||
| + | <!--T:15--> | ||
::5. Heterodont Dentition (Different shapes of teeth in their mouths) | ::5. Heterodont Dentition (Different shapes of teeth in their mouths) | ||
| − | ==3. Give one or more identifying characteristics of each of the following orders of mammals, and name one or more species of mammals found in each order:== | + | ==3. Give one or more identifying characteristics of each of the following orders of mammals, and name one or more species of mammals found in each order:== <!--T:16--> |
===a. Marsupialia=== | ===a. Marsupialia=== | ||
| + | <!--T:17--> | ||
Marsupials have a pouch that protects the young as they are developing. The infant is born at very early stage of development and crawls out of the womb and across the mothers belly to the pouch where the baby finds a nipple that it attaches to as it continues to grow. | Marsupials have a pouch that protects the young as they are developing. The infant is born at very early stage of development and crawls out of the womb and across the mothers belly to the pouch where the baby finds a nipple that it attaches to as it continues to grow. | ||
| + | <!--T:18--> | ||
{| border ="0" | {| border ="0" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 64: | Line 79: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | ===b. Insectivora=== | + | ===b. Insectivora=== <!--T:19--> |
| + | <!--T:20--> | ||
Insectivora means literally insect eater and that is the main connecting feature of the animals in this order. Many of the animals that were once a part of this order have been moved to other orders based on DNA analysis. The order Insectivora has been replaced by the orders Erinaceomorpha and Soricomorpha. | Insectivora means literally insect eater and that is the main connecting feature of the animals in this order. Many of the animals that were once a part of this order have been moved to other orders based on DNA analysis. The order Insectivora has been replaced by the orders Erinaceomorpha and Soricomorpha. | ||
| + | <!--T:21--> | ||
{| border ="0" | {| border ="0" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 76: | Line 93: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | ===c. Chiroptera=== | + | ===c. Chiroptera=== <!--T:22--> |
| + | <!--T:23--> | ||
:The order of flying mammals commonly called "bats". | :The order of flying mammals commonly called "bats". | ||
| + | <!--T:24--> | ||
Bats are mammals. Though sometimes called "flying rodents", "flying mice," or even mistaken for invertebrate bugs and birds, bats are neither rodents nor arthropods. | Bats are mammals. Though sometimes called "flying rodents", "flying mice," or even mistaken for invertebrate bugs and birds, bats are neither rodents nor arthropods. | ||
There are two suborders of bats: | There are two suborders of bats: | ||
| Line 85: | Line 104: | ||
# Microbat Microchiroptera (microbats/echolocating bats) | # Microbat Microchiroptera (microbats/echolocating bats) | ||
| + | <!--T:25--> | ||
Despite the name, not all megabats are larger than microbats. The major distinction between the two suborders is based on other factors: | Despite the name, not all megabats are larger than microbats. The major distinction between the two suborders is based on other factors: | ||
* Microbats use Animal echolocation, whereas megabats do not (except for ''Rousettus'' and relatives, which do). | * Microbats use Animal echolocation, whereas megabats do not (except for ''Rousettus'' and relatives, which do). | ||
| + | <!--T:26--> | ||
* Microbats lack the claw at the second toe of the forelimb. | * Microbats lack the claw at the second toe of the forelimb. | ||
* The ears of microbats do not form a closed ring, but the edges are separated from each other at the base of the ear. | * The ears of microbats do not form a closed ring, but the edges are separated from each other at the base of the ear. | ||
* Microbats lack underfur; they have only guard hairs or are naked. | * Microbats lack underfur; they have only guard hairs or are naked. | ||
| + | <!--T:27--> | ||
Megabats eat fruit, nectar or pollen while microbats eat insects, blood (small quantities of blood of animals), small mammals, and fish, relying on animal echolocation for navigation and finding prey. | Megabats eat fruit, nectar or pollen while microbats eat insects, blood (small quantities of blood of animals), small mammals, and fish, relying on animal echolocation for navigation and finding prey. | ||
| + | <!--T:28--> | ||
{| border ="0" | {| border ="0" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 102: | Line 125: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | ===d. Carnivora === | + | ===d. Carnivora === <!--T:29--> |
| + | <!--T:30--> | ||
Carnivora are meat eaters, and have canine teeth that are especially adapted for this behavior. They tend to have good eye sight, a good sense of smell and a well developed brain, all working together to improve their hunting ability. | Carnivora are meat eaters, and have canine teeth that are especially adapted for this behavior. They tend to have good eye sight, a good sense of smell and a well developed brain, all working together to improve their hunting ability. | ||
| + | <!--T:31--> | ||
The order carnivora is not the only order that has carnivores or hunters. Many other orders have creatures that hunt their prey. For example marsupialia contains the ''Sarcophilus harrisii'' (Tasmanian Devil) and the now extinct ''Thylacinus cynocephalus'' (Tasmanian wolf). Insectivora species hunt, but they primarily hunt and eat insects or worms. Bats hunt insects, and the Vampire bat stalks many mammals to drink blood as they sleep. | The order carnivora is not the only order that has carnivores or hunters. Many other orders have creatures that hunt their prey. For example marsupialia contains the ''Sarcophilus harrisii'' (Tasmanian Devil) and the now extinct ''Thylacinus cynocephalus'' (Tasmanian wolf). Insectivora species hunt, but they primarily hunt and eat insects or worms. Bats hunt insects, and the Vampire bat stalks many mammals to drink blood as they sleep. | ||
| + | <!--T:32--> | ||
It should also be said that there are a number of species included in the order carnivora that are not carnivores. ''Ailurus''s (Pandas) are a good example as they primarily eat bamboo, using their canines to rip the hard bamboo apart. Many or the ursas (bears) will have a diet higher in berries than meat. | It should also be said that there are a number of species included in the order carnivora that are not carnivores. ''Ailurus''s (Pandas) are a good example as they primarily eat bamboo, using their canines to rip the hard bamboo apart. Many or the ursas (bears) will have a diet higher in berries than meat. | ||
| + | <!--T:33--> | ||
The skull of carnivora often has a ridge that runs along the top from front to back. This ridge is where the powerful muscles that work the jaw is attached to provide the maximum force. The Panthera leo (lion) has a jaw force of {{H:title|397.4 pounds force|1768N}}, Pathera tigris (Tiger) {{H:title|342.8 pounds force|1525N}}, Ursus Arctos (Brown Bear) {{H:title|169 pounds force|751N}}, and the Canis lupus (gray wolf) {{H:title|133 pounds force|593N}}. Because the canine teeth are so sharp in carnivora, these forces can result in enough pressure to break bones. | The skull of carnivora often has a ridge that runs along the top from front to back. This ridge is where the powerful muscles that work the jaw is attached to provide the maximum force. The Panthera leo (lion) has a jaw force of {{H:title|397.4 pounds force|1768N}}, Pathera tigris (Tiger) {{H:title|342.8 pounds force|1525N}}, Ursus Arctos (Brown Bear) {{H:title|169 pounds force|751N}}, and the Canis lupus (gray wolf) {{H:title|133 pounds force|593N}}. Because the canine teeth are so sharp in carnivora, these forces can result in enough pressure to break bones. | ||
| + | <!--T:34--> | ||
{| border ="0" | {| border ="0" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 122: | Line 150: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | ===e. Pinnipedia=== | + | ===e. Pinnipedia=== <!--T:35--> |
| + | <!--T:36--> | ||
This is no longer considered an order in its own right. Rather, it is now considered a superfamily of Carnivora | This is no longer considered an order in its own right. Rather, it is now considered a superfamily of Carnivora | ||
| − | ===f. Rodentia=== | + | ===f. Rodentia=== <!--T:37--> |
Rodents have two incisors in the upper as well as in the lower jaw which grow continuously and must be kept worn down by gnawing; this is the origin of the name, from the Latin rodere, to gnaw, and dens, dentis, tooth. These teeth are used for cutting wood, biting through the skin of fruit, or for defense. The teeth have enamel on the outside and exposed dentine on the inside, so they self-sharpen during gnawing. Rodents lack canines, and have a space between their incisors and premolars. Nearly all rodents feed on plants, seeds in particular, but there are a few exceptions which eat insects or even fish. | Rodents have two incisors in the upper as well as in the lower jaw which grow continuously and must be kept worn down by gnawing; this is the origin of the name, from the Latin rodere, to gnaw, and dens, dentis, tooth. These teeth are used for cutting wood, biting through the skin of fruit, or for defense. The teeth have enamel on the outside and exposed dentine on the inside, so they self-sharpen during gnawing. Rodents lack canines, and have a space between their incisors and premolars. Nearly all rodents feed on plants, seeds in particular, but there are a few exceptions which eat insects or even fish. | ||
| + | <!--T:38--> | ||
{| border ="0" | {| border ="0" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 137: | Line 167: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | ===g. Lagomorpha=== | + | ===g. Lagomorpha=== <!--T:39--> |
Lagomorphs differ from rodents in that: | Lagomorphs differ from rodents in that: | ||
* they have four incisors in the upper jaw (not two as in rodents); | * they have four incisors in the upper jaw (not two as in rodents); | ||
| Line 143: | Line 173: | ||
* they will redigest first-time droppings to obtain the most from their plant diet. | * they will redigest first-time droppings to obtain the most from their plant diet. | ||
| + | <!--T:40--> | ||
They resemble rodents, however, in that their teeth grow throughout their life, thus necessitating constant chewing to keep them from growing too long. | They resemble rodents, however, in that their teeth grow throughout their life, thus necessitating constant chewing to keep them from growing too long. | ||
| + | <!--T:41--> | ||
{| border ="0" | {| border ="0" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 153: | Line 185: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | ===h. Artiodactyla=== | + | ===h. Artiodactyla=== <!--T:42--> |
The Artiodactyla are mammals with hooves and which bear most of their weight on an even number of toes. They are sometimes called the ''even-toed ungulates'' (ungulates are hooved animals). | The Artiodactyla are mammals with hooves and which bear most of their weight on an even number of toes. They are sometimes called the ''even-toed ungulates'' (ungulates are hooved animals). | ||
| + | <!--T:43--> | ||
{| border ="0" | {| border ="0" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[Image:Lightmatter_unidentified_pig-like_animal.jpg|thumb|200px|''Potamochoerus porcus'' (Red River Hog)]] <b> [[File:Bactrian Camel Tennoji.jpg|thumb|200px|''Camelus bactrianus'' (Bactrian Camel)]] <br> [[Image:Giraffe_standing.jpg|thumb|200px|''Giraffa camelopardalis'' (Giraffe)]] <br> [[Image:Sable_bull.jpg|thumb|200px|''Hippotragus niger'' (Sable Antelope)]] <br> [[Image:Lleyn_sheep.jpg|thumb|200px|''Ovis aries'' (Domestic sheep)]] | | [[Image:Lightmatter_unidentified_pig-like_animal.jpg|thumb|200px|''Potamochoerus porcus'' (Red River Hog)]] <b> [[File:Bactrian Camel Tennoji.jpg|thumb|200px|''Camelus bactrianus'' (Bactrian Camel)]] <br> [[Image:Giraffe_standing.jpg|thumb|200px|''Giraffa camelopardalis'' (Giraffe)]] <br> [[Image:Sable_bull.jpg|thumb|200px|''Hippotragus niger'' (Sable Antelope)]] <br> [[Image:Lleyn_sheep.jpg|thumb|200px|''Ovis aries'' (Domestic sheep)]] | ||
| + | <!--T:44--> | ||
| [[Image:Hippo_pod_edit.jpg|thumb|200px|''Hippopotamus amphibius'' (Hippopotamus)]] <br> [[Image:Moschustier.jpg|thumb|200px| ''Moschus moschiferus'' (Siberian musk deer)]] <br> [[Image:Okapi2.jpg|thumb|200px|''Okapia johnstoni'' (Okapi) ]] <br> [[Image:Budorcas_taxicolor01.jpg|thumb|200px|''Budorcas taxicolor'' (Takin)]] <br> | | [[Image:Hippo_pod_edit.jpg|thumb|200px|''Hippopotamus amphibius'' (Hippopotamus)]] <br> [[Image:Moschustier.jpg|thumb|200px| ''Moschus moschiferus'' (Siberian musk deer)]] <br> [[Image:Okapi2.jpg|thumb|200px|''Okapia johnstoni'' (Okapi) ]] <br> [[Image:Budorcas_taxicolor01.jpg|thumb|200px|''Budorcas taxicolor'' (Takin)]] <br> | ||
| [[Image:Collared_peccary02_-_melbourne_zoo.jpg|thumb|200px|''Tayassu tajacu'' (Collared Peccary)]] <br> [[Image:White-tailed_deer.jpg|200px|thumb|''Odocoileus virginianus'' (White-tailed Deer)]] [[Image:Pronghorn_antelope.jpg|thumb|200px| ''Antilocapra americana'' (Pronghorn)]] <br> [[Image:American_bison_k5680-1.jpg|thumb|200px|''Bison bison'' (Bison)]] <br> [[Image:Blackbuck_male_female.jpg|thumb|200px|''Antilope cervicapra'' (Blackbuck)]] <br> [[Image:Ovibos_moschatus.jpg|thumb|200px|''Ovibos moschatus'' (Muskox)]] | | [[Image:Collared_peccary02_-_melbourne_zoo.jpg|thumb|200px|''Tayassu tajacu'' (Collared Peccary)]] <br> [[Image:White-tailed_deer.jpg|200px|thumb|''Odocoileus virginianus'' (White-tailed Deer)]] [[Image:Pronghorn_antelope.jpg|thumb|200px| ''Antilocapra americana'' (Pronghorn)]] <br> [[Image:American_bison_k5680-1.jpg|thumb|200px|''Bison bison'' (Bison)]] <br> [[Image:Blackbuck_male_female.jpg|thumb|200px|''Antilope cervicapra'' (Blackbuck)]] <br> [[Image:Ovibos_moschatus.jpg|thumb|200px|''Ovibos moschatus'' (Muskox)]] | ||
| Line 165: | Line 199: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | ===i. Sirenia=== | + | ===i. Sirenia=== <!--T:45--> |
| + | <!--T:46--> | ||
These slow moving herbivores are named after the Sirens of the Homerian legend of Odysseus. | These slow moving herbivores are named after the Sirens of the Homerian legend of Odysseus. | ||
| + | <!--T:47--> | ||
{| border ="0" | {| border ="0" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 176: | Line 212: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | ===j. Cetacea=== | + | ===j. Cetacea=== <!--T:48--> |
| + | <!--T:49--> | ||
This group includes whales, porpoises and dolphins. The word cetus means large sea animal, and is the name of a constellation also known as the whale. These mammals are truly aquatic, and many are quite massive, incapable of walking on land. | This group includes whales, porpoises and dolphins. The word cetus means large sea animal, and is the name of a constellation also known as the whale. These mammals are truly aquatic, and many are quite massive, incapable of walking on land. | ||
| + | <!--T:50--> | ||
See questions 6 and 7 below. | See questions 6 and 7 below. | ||
| + | <!--T:51--> | ||
{| border ="0" | {| border ="0" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 190: | Line 229: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | ==4. List four beneficial mammals and tell how they are beneficial.== | + | ==4. List four beneficial mammals and tell how they are beneficial.== <!--T:52--> |
::Bats eat flying insects | ::Bats eat flying insects | ||
| + | <!--T:53--> | ||
::Dogs provide assistance to the blind and comfort to the sick. | ::Dogs provide assistance to the blind and comfort to the sick. | ||
| + | <!--T:54--> | ||
::Cats keep down the rodent population | ::Cats keep down the rodent population | ||
| + | <!--T:55--> | ||
::Hyena is a scavenger and helps keep the environment clean and free of disease | ::Hyena is a scavenger and helps keep the environment clean and free of disease | ||
| + | <!--T:56--> | ||
::Bears carry the nutrients of the salmon they eat into the forest. This actually completes the mineral cycle. Minerals start in the forest and are carried by the rains into the streams, then rivers, and finally into the ocean. The salmon take the minerals from the ocean environment and carry them back to the streams and rivers where they are eaten by the bears. The bears carry these minerals back to the forest when they defecate or die. If this cycle was not complete the forest would eventually not have enough of the nutrients needed to be healthy. | ::Bears carry the nutrients of the salmon they eat into the forest. This actually completes the mineral cycle. Minerals start in the forest and are carried by the rains into the streams, then rivers, and finally into the ocean. The salmon take the minerals from the ocean environment and carry them back to the streams and rivers where they are eaten by the bears. The bears carry these minerals back to the forest when they defecate or die. If this cycle was not complete the forest would eventually not have enough of the nutrients needed to be healthy. | ||
| + | <!--T:57--> | ||
::When wolves were put back into the ecosystem of Yellowstone, we learned how important one animal is in helping form a healthy ecosystem. Without wolves, the Elk could eat and drink without fear, and they had eaten most of the willow along the river. There were very few beaver left. When the wolves came back into the environment, the elk were afraid of certain areas where a wolf might hide and this allowed the willows to grow back. Now there is a growing beaver population. | ::When wolves were put back into the ecosystem of Yellowstone, we learned how important one animal is in helping form a healthy ecosystem. Without wolves, the Elk could eat and drink without fear, and they had eaten most of the willow along the river. There were very few beaver left. When the wolves came back into the environment, the elk were afraid of certain areas where a wolf might hide and this allowed the willows to grow back. Now there is a growing beaver population. | ||
| + | <!--T:58--> | ||
::Any others that the Pathfinder can think of. Accept all reasonable answers. | ::Any others that the Pathfinder can think of. Accept all reasonable answers. | ||
| − | ==5. List four things mammals do that are harmful.== | + | ==5. List four things mammals do that are harmful.== <!--T:59--> |
::Skunks can make a neighborhood smell quite bad | ::Skunks can make a neighborhood smell quite bad | ||
::Tigers, lions, bears, wolves and many other carnivorous mammals have killed and sometimes eaten people. They also prey on livestock. | ::Tigers, lions, bears, wolves and many other carnivorous mammals have killed and sometimes eaten people. They also prey on livestock. | ||
| Line 220: | Line 265: | ||
Accept all reasonable answers. | Accept all reasonable answers. | ||
| − | ==6. List four mammals that are completely aquatic and designate their natural range.== | + | ==6. List four mammals that are completely aquatic and designate their natural range.== <!--T:60--> |
:Salt Water Mammals | :Salt Water Mammals | ||
::1. Whales | ::1. Whales | ||
| Line 253: | Line 298: | ||
::::[[Image:Dalls_Porpoise_Back.jpg|240px]] [[Image:Cetacea_range_map_Dall%27s_Porpoise.PNG|240px]] | ::::[[Image:Dalls_Porpoise_Back.jpg|240px]] [[Image:Cetacea_range_map_Dall%27s_Porpoise.PNG|240px]] | ||
| + | <!--T:61--> | ||
:Fresh Water Mammals | :Fresh Water Mammals | ||
::1. ''Inia geoffrensis'' (Amazon or Pink Dolphin) lives in the Amazon River and Orinoco River systems. | ::1. ''Inia geoffrensis'' (Amazon or Pink Dolphin) lives in the Amazon River and Orinoco River systems. | ||
| Line 259: | Line 305: | ||
::::[[File:Schnabeldelphin-drawing.jpg|240px]] [[File:Cetacea_range_map_South_Asian_river_dolphin.png |240px]] | ::::[[File:Schnabeldelphin-drawing.jpg|240px]] [[File:Cetacea_range_map_South_Asian_river_dolphin.png |240px]] | ||
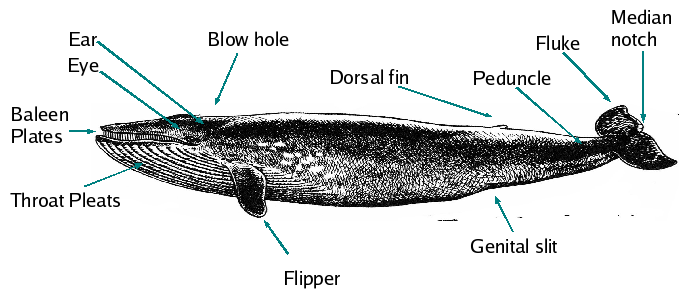
| − | ==7. Name the largest mammal in the world and tell where it lives, how it feeds, and what it eats.== | + | ==7. Name the largest mammal in the world and tell where it lives, how it feeds, and what it eats.== <!--T:62--> |
| + | <!--T:63--> | ||
The ''Balaenoptera musculus'' (Blue Whale) is the largest animal on the planet. Specimens have been recorded over {{H:title|98 feet|30 meters}} in length and are estimated to weigh more than {{H:title|99 tons|90 tonnes}}. These whales have been seen in every ocean of the world and feed by filtering the water through the giant balleen plates in their mouth. Adult whales can eat up to {{H:title|4.4 tons|4 tonnes}} krill (euphausiids) and copepods each day and the calves can drink up to {{H:title|106 Gallons|400 litres}}/day. | The ''Balaenoptera musculus'' (Blue Whale) is the largest animal on the planet. Specimens have been recorded over {{H:title|98 feet|30 meters}} in length and are estimated to weigh more than {{H:title|99 tons|90 tonnes}}. These whales have been seen in every ocean of the world and feed by filtering the water through the giant balleen plates in their mouth. Adult whales can eat up to {{H:title|4.4 tons|4 tonnes}} krill (euphausiids) and copepods each day and the calves can drink up to {{H:title|106 Gallons|400 litres}}/day. | ||
| + | <!--T:64--> | ||
::[[Image:Baleen_parts.png]] | ::[[Image:Baleen_parts.png]] | ||
| + | <!--T:65--> | ||
These amazing creatures were hunted by man to the brink of extinction. Over 378,000 were killed to provide oil and whale meat. The population of ''B. musculus'' (Blue Whales) is now only about 1% of the total 100 years ago. | These amazing creatures were hunted by man to the brink of extinction. Over 378,000 were killed to provide oil and whale meat. The population of ''B. musculus'' (Blue Whales) is now only about 1% of the total 100 years ago. | ||
| − | ==8. List eight species of wild mammals that are in your region. Spend at least 5 hours searching for wild mammals in their natural habitat.== | + | ==8. List eight species of wild mammals that are in your region. Spend at least 5 hours searching for wild mammals in their natural habitat.== <!--T:66--> |
| + | <!--T:67--> | ||
http://www.enature.com/home/ is a good place to find wild animals in your area. You can search by zip code for mammals, and also any other animals and plants, so it's a useful resource for any Nature honor. | http://www.enature.com/home/ is a good place to find wild animals in your area. You can search by zip code for mammals, and also any other animals and plants, so it's a useful resource for any Nature honor. | ||
| − | ==9. Write or tell a story about "Wild Mammals I Have Observed".== | + | ==9. Write or tell a story about "Wild Mammals I Have Observed".== <!--T:68--> |
| + | <!--T:69--> | ||
A good opportunity for a story would obviously be the 5 hour search in the last requirement, if you can't think of another story about wild mammals that you have observed. | A good opportunity for a story would obviously be the 5 hour search in the last requirement, if you can't think of another story about wild mammals that you have observed. | ||
| − | ==References== | + | ==References== <!--T:70--> |
*http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cetacea | *http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cetacea | ||
*http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bats | *http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bats | ||
Revision as of 22:44, 24 November 2014
Template:Honor desc Template:Honor Master Template:Honor Master
1. What Bible verse gives the day mammals were created?
Genesis 1:24,25, 31
24And God said, "Let the land produce living creatures according to their kinds: livestock, creatures that move along the ground, and wild animals, each according to its kind." And it was so.
25God made the wild animals according to their kinds, the livestock according to their kinds, and all the creatures that move along the ground according to their kinds. And God saw that it was good.
26Then God said, "Let us make man in our image, in our likeness, and let them rule over the fish of the sea and the birds of the air, over the livestock, over all the earth, and over all the creatures that move along the ground."
27So God created man in his own image, in the image of God he created him; male and female he created them.
28God blessed them and said to them, "Be fruitful and increase in number; fill the earth and subdue it. Rule over the fish of the sea and the birds of the air and over every living creature that moves on the ground."
29Then God said, "I give you every seed-bearing plant on the face of the whole earth and every tree that has fruit with seed in it. They will be yours for food.
30And to all the beasts of the earth and all the birds of the air and all the creatures that move on the ground—everything that has the breath of life in it—I give every green plant for food." And it was so.
31God saw all that he had made, and it was very good. And there was evening, and there was morning—the sixth day.
2. List four characteristics of a mammal.
- 1. Endothermic (Warm-blooded)
- 2. Hair or Fur
- 3. Mammary (milk producing) glands
- 4. Sebaceous (fat-secreting) glands
- 5. Heterodont Dentition (Different shapes of teeth in their mouths)
3. Give one or more identifying characteristics of each of the following orders of mammals, and name one or more species of mammals found in each order:
a. Marsupialia
Marsupials have a pouch that protects the young as they are developing. The infant is born at very early stage of development and crawls out of the womb and across the mothers belly to the pouch where the baby finds a nipple that it attaches to as it continues to grow.
| |
b. Insectivora
Insectivora means literally insect eater and that is the main connecting feature of the animals in this order. Many of the animals that were once a part of this order have been moved to other orders based on DNA analysis. The order Insectivora has been replaced by the orders Erinaceomorpha and Soricomorpha.
c. Chiroptera
- The order of flying mammals commonly called "bats".
Bats are mammals. Though sometimes called "flying rodents", "flying mice," or even mistaken for invertebrate bugs and birds, bats are neither rodents nor arthropods. There are two suborders of bats:
- Megabat Megachiroptera (megabats)
- Microbat Microchiroptera (microbats/echolocating bats)
Despite the name, not all megabats are larger than microbats. The major distinction between the two suborders is based on other factors:
- Microbats use Animal echolocation, whereas megabats do not (except for Rousettus and relatives, which do).
- Microbats lack the claw at the second toe of the forelimb.
- The ears of microbats do not form a closed ring, but the edges are separated from each other at the base of the ear.
- Microbats lack underfur; they have only guard hairs or are naked.
Megabats eat fruit, nectar or pollen while microbats eat insects, blood (small quantities of blood of animals), small mammals, and fish, relying on animal echolocation for navigation and finding prey.
| |
d. Carnivora
Carnivora are meat eaters, and have canine teeth that are especially adapted for this behavior. They tend to have good eye sight, a good sense of smell and a well developed brain, all working together to improve their hunting ability.
The order carnivora is not the only order that has carnivores or hunters. Many other orders have creatures that hunt their prey. For example marsupialia contains the Sarcophilus harrisii (Tasmanian Devil) and the now extinct Thylacinus cynocephalus (Tasmanian wolf). Insectivora species hunt, but they primarily hunt and eat insects or worms. Bats hunt insects, and the Vampire bat stalks many mammals to drink blood as they sleep.
It should also be said that there are a number of species included in the order carnivora that are not carnivores. Ailuruss (Pandas) are a good example as they primarily eat bamboo, using their canines to rip the hard bamboo apart. Many or the ursas (bears) will have a diet higher in berries than meat.
The skull of carnivora often has a ridge that runs along the top from front to back. This ridge is where the powerful muscles that work the jaw is attached to provide the maximum force. The Panthera leo (lion) has a jaw force of 1768N, Pathera tigris (Tiger) 1525N, Ursus Arctos (Brown Bear) 751N, and the Canis lupus (gray wolf) 593N. Because the canine teeth are so sharp in carnivora, these forces can result in enough pressure to break bones.
| |
|
|
e. Pinnipedia
This is no longer considered an order in its own right. Rather, it is now considered a superfamily of Carnivora
f. Rodentia
Rodents have two incisors in the upper as well as in the lower jaw which grow continuously and must be kept worn down by gnawing; this is the origin of the name, from the Latin rodere, to gnaw, and dens, dentis, tooth. These teeth are used for cutting wood, biting through the skin of fruit, or for defense. The teeth have enamel on the outside and exposed dentine on the inside, so they self-sharpen during gnawing. Rodents lack canines, and have a space between their incisors and premolars. Nearly all rodents feed on plants, seeds in particular, but there are a few exceptions which eat insects or even fish.
| |
|
|
g. Lagomorpha
Lagomorphs differ from rodents in that:
- they have four incisors in the upper jaw (not two as in rodents);
- they will only eat vegetation (unlike rodents, who will eat meat and vegetation)
- they will redigest first-time droppings to obtain the most from their plant diet.
They resemble rodents, however, in that their teeth grow throughout their life, thus necessitating constant chewing to keep them from growing too long.
| |
|
|
h. Artiodactyla
The Artiodactyla are mammals with hooves and which bear most of their weight on an even number of toes. They are sometimes called the even-toed ungulates (ungulates are hooved animals).
| |
|
|
i. Sirenia
These slow moving herbivores are named after the Sirens of the Homerian legend of Odysseus.
j. Cetacea
This group includes whales, porpoises and dolphins. The word cetus means large sea animal, and is the name of a constellation also known as the whale. These mammals are truly aquatic, and many are quite massive, incapable of walking on land.
See questions 6 and 7 below.
File:Narwhals breach.jpg Monodon monoceros (Narwhal) |
4. List four beneficial mammals and tell how they are beneficial.
- Bats eat flying insects
- Dogs provide assistance to the blind and comfort to the sick.
- Cats keep down the rodent population
- Hyena is a scavenger and helps keep the environment clean and free of disease
- Bears carry the nutrients of the salmon they eat into the forest. This actually completes the mineral cycle. Minerals start in the forest and are carried by the rains into the streams, then rivers, and finally into the ocean. The salmon take the minerals from the ocean environment and carry them back to the streams and rivers where they are eaten by the bears. The bears carry these minerals back to the forest when they defecate or die. If this cycle was not complete the forest would eventually not have enough of the nutrients needed to be healthy.
- When wolves were put back into the ecosystem of Yellowstone, we learned how important one animal is in helping form a healthy ecosystem. Without wolves, the Elk could eat and drink without fear, and they had eaten most of the willow along the river. There were very few beaver left. When the wolves came back into the environment, the elk were afraid of certain areas where a wolf might hide and this allowed the willows to grow back. Now there is a growing beaver population.
- Any others that the Pathfinder can think of. Accept all reasonable answers.
5. List four things mammals do that are harmful.
- Skunks can make a neighborhood smell quite bad
- Tigers, lions, bears, wolves and many other carnivorous mammals have killed and sometimes eaten people. They also prey on livestock.
- Groundhogs, prairie dogs, gophers, moles and many other burrowing animals can create tripping hazards for humans, horses and other mammals
- Elephants can do quite a bit of damage to gardens and yards
- Mice can eat a large amount of grain and reproduce so rapidly that large quantities of food can disappear quite quickly.
- Rats can carry disease such as bubonic plague
- Deer can carry a disease known as chronic wasting disease
- Beavers can back up streams and flood areas as well as cut down trees that are part of an orchard or yard
- Many mammals can carry rabies or distemper and pass these diseases to humans or pets
- Coyotes in urban settings can eat pets or spread garbage
- Deer, moose and other large mammals are involved in thousands of car accidents every year. Sometimes these accidents include human fatalities.
- Humans are the most dangerous destructive mammals of all.
Accept all reasonable answers.
6. List four mammals that are completely aquatic and designate their natural range.
- Salt Water Mammals
- 1. Whales
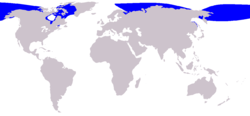
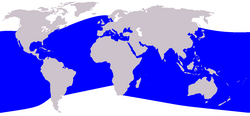
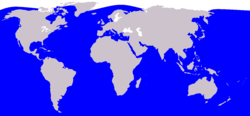
- a. Balaenoptera musculus (Blue Whale) lives near the surface of the ocean and can be found in every ocean of the world.
- b. Delphinapterus leucas (Beluga Whale) lives in Arctic and Sub-Arctic waters. Some will migrate to warmer waters in the summer and even swim up northern rivers into brackish (partly-salty) waters to hunt.
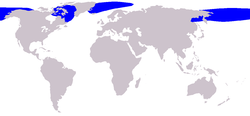
- c. Balaena mysticetu (Bowhead Whale) lives solely in the Arctic near the surface of the ocean.
- d. Megaptera novaeangliae (Humpback Whale) lives in all the oceans in the world except the polar seas. They live mostly in shallow water.
- 2. Dolphins
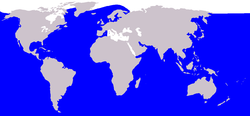
- a. Tursiops truncatus (Bottlenose Dolphins) live in warm and temperate seas and oceans all over the world.
- b. Orcinus orca (Orcas or Killer Whales) live in all the oceans and many of the seas in the world. (Even though this aquatic mammal has the name of "whale" it is in the dolphin (Delphinidae) family)
- c. Stenella longirostris (Spinner Dolphin):
- 1.Eastern Spinner Dolphin (S. l. orientalis), found in the tropical eastern Pacific.
- 2.Central American or Costa Rican Spinner Dolphin (S. l. centroamericana), also found in the tropical eastern Pacific.
- 3.Gray's or Hawaiian Spinner Dolphin (S. l. longirostris), found in the central Pacific around Hawaii but represents a mixed bag of broadly similar subtypes found throughout the world.
- 4.Dwarf Spinner Dolphin (S. l. roseiventris), first found in the Gulf of Thailand.

- d. Lagenorhynchus obliquidens (Pacific White Sided Dolphin) lives in the Pacific Ocean
- 3. Porpoise
- a. Neophocaena phocaenoides (Finless Porpoise) lives in the shallow coastal waters of Asia especially around India, China, Indonesia and Japan. A unique fresh water population is found in the Yangtze River. At the western end, their range includes the length of the western coast of India and continues up into the Persian Gulf.
- b. Phocoena phocaena (Harbour Porpoise) is widespread in cooler coastal waters in the Northern Hemisphere, largely in areas with a mean temperature of about 15°C. In the Atlantic, Harbour Porpoises may be present in a concave band of water running from the coast of western Africa round to the eastern seaboard of the United States, including the coasts of Spain, France, the United Kingdom, Ireland, Norway, Iceland, Greenland and Newfoundland.
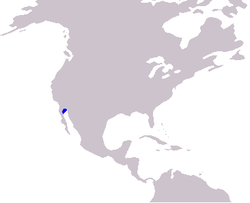
- c. Phocoena sinus (Vaquita) is a very endangered species that lives only in the Sea of Cortez, the northern part of the Gulf of California.
- d. Phocoenoides dalli (Dall's Porpoise) ranges across the north Pacific Ocean from southern California to southern Japan (including the Sea of Japan in the south up to the Bering Sea in the north).
- 1. Whales
- Fresh Water Mammals
7. Name the largest mammal in the world and tell where it lives, how it feeds, and what it eats.
The Balaenoptera musculus (Blue Whale) is the largest animal on the planet. Specimens have been recorded over 30 meters in length and are estimated to weigh more than 90 tonnes. These whales have been seen in every ocean of the world and feed by filtering the water through the giant balleen plates in their mouth. Adult whales can eat up to 4 tonnes krill (euphausiids) and copepods each day and the calves can drink up to 400 litres/day.
These amazing creatures were hunted by man to the brink of extinction. Over 378,000 were killed to provide oil and whale meat. The population of B. musculus (Blue Whales) is now only about 1% of the total 100 years ago.
8. List eight species of wild mammals that are in your region. Spend at least 5 hours searching for wild mammals in their natural habitat.
http://www.enature.com/home/ is a good place to find wild animals in your area. You can search by zip code for mammals, and also any other animals and plants, so it's a useful resource for any Nature honor.
9. Write or tell a story about "Wild Mammals I Have Observed".
A good opportunity for a story would obviously be the 5 hour search in the last requirement, if you can't think of another story about wild mammals that you have observed.