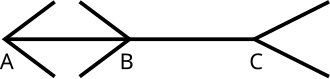
Requisitos para la especialidad JA de Vista
1. Completar lo siguiente:
- a. Realizar esta actividad.
Esté con los ojos vendados. Deje que alguien coloque un artículo entre 15 y 20 metros de usted. Ahora busque el artículo. Registre en cuánto tiempo encontró el artículo. Ahora, vuélvase a vendar los ojos. Deje que alguien coloque el artículo en otro lugar pero dentro de la misma distancia que antes. Quítese la venda de los ojos. Busque el artículo. Registre en cuánto tiempo encontró el artículo.
- b.
Mirar el video: https://youtu.be/syaQgmxb5i0. Ahora responder las siguientes preguntas:
- ¿Para qué se utiliza el sentido de la vista?
- ¿Cuán importante es?
- c. ¿Qué tan grande es el ojo humano?
2. Anatomía del ojo. Etiquetar las partes.
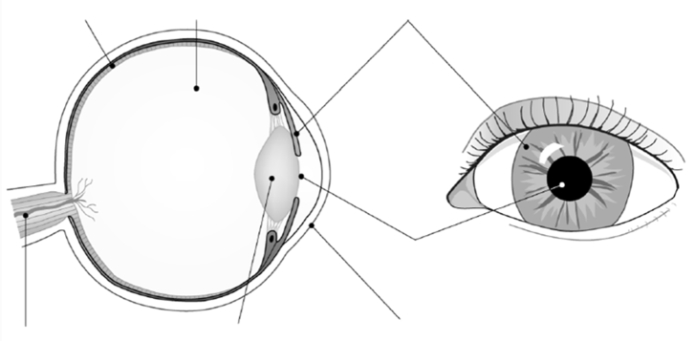
Eye Function Drag
Haga clic en el enlace proporcionado arriba y haga el ejercicio sobre las funciones de las partes del ojo. Cuando termine, verifique su respuesta. Luego, el sistema marcará su trabajo. Imprima y pegue su trabajo.
3. ¿Cómo funciona un cristalino? Completar la siguiente oración usando las palabras del cuadro.
Tenemos cristalinos en cada uno de nuestros _______________. Este es un lente ______________. La función de estos cristalinos es ______________ la ________________ para que podamos _____________________. El punto en el que se cruzan los rayos se llama foco o el ____________________. La luz es ________________________ a medida que entra y vuelve a salir.
| ojos | refractada | luz | punto focal | |||
| enfocar | ver | convexo |
4. Mirar el video:
- a.
A continuación se muestran los pasos de cómo ven los seres humanos. Organizarlos en orden cronológico colocando números (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6) en la columna «posición» para reflejar el orden correcto en el que deberían estar.
| Posición | Pasos |
| Cuando miras un objeto, la luz reflejada por el objeto atraviesa la pupila de tu ojo. | |
| Tu cerebro ordena la imagen para que la veas correctamente. | |
| La córnea y el lente enfocan la luz en la retina. | |
| Se forma una imagen invertida en la retina. La retina está formada por células sensibles a la luz llamadas fotorreceptores. | |
| El iris, un músculo que controla el tamaño de la pupila, permite que entre la cantidad correcta de luz en el ojo. | |
| Cuando la imagen se forma en los fotorreceptores en la retina, las reacciones químicas producen un impulso eléctrico que viaja por el «nervio óptico» hasta el cerebro. |
- b.
Rellenar el espacio en blanco: Un médico que se especializa en examinar, diagnosticar y tratar los ojos y las enfermedades oculares se llama un ____________________.
- c.
El examen de agudeza visual, el examen de campo visual y el examen de tonometría son exámenes que realiza un oftalmólogo en el ojo. Igualar el nombre del término con su significado:
| Examen de agudeza visual | ????? | Una persona lee una tabla optométrica para medir qué tan bien ve a distintas distancias. |
| Examen de campo visual | ????? | Este examen determina la presión del líquido dentro del ojo para evaluar la presencia de glaucoma. |
| Examen de tonometría | ????? | Los oftalmólogos utilizan este examen para medir la visión lateral o periférica. |
- d. Cuáles son los papeles de:
- i. Bastones
- ii. Conos
5. ¿Cómo se compara la vista de los seres humanos con la de otras criaturas? Comparar con tres de los siguientes animales: águilas, búhos, camarones mantis, ciervos, cabras, caballos, alces, ovejas, cabras.
6. Completar lo siguiente:
- a. Comparar las características clave del ojo y una cámara al completar la tabla.
| Característica en una cámara | Característica en un ojo | Uso |
| Pupila | ||
| Lente | ||
| Disparador | ||
| Retina | Recibe luz |
- b.
Write a paragraph below to compare how the eye and the camera work. Cover the following factors in your answer:
- i.
Similarities: What features do they have in common? What does each convert the light energy into when it is processed? Which way up does the image form in both?
- ii.
Differences: How does the lens change in each to produce an image? How do the types of image made by each compare? How are the images captured and kept?
With reference to the eye chart explain:
- a.
20/20 vision
- b.
20/70 vision
8.
What is visual impairment?
9.
Define these eye problems and state their "cures".
- a.
Glaucoma
- b.
Cataracts
- c.
Strabismus
- d.
"Sore eyes"/conjunctivitis
- e.
Colour blindness
10.
Fill in the blanks: (Watch the video - https://youtu.be/ypF037wlYZg)
- a.
________________ is the bending of light when it passes through a transparent medium such as glass, lens or water.
- b.
The refractive errors are _______________, ___________________, ____________ and _______________.
- c.
_________________is also known as near-sightedness. People with this have eyes that are a little longer than normal, measuring from the front of the eyeball to the back. Therefore, light focuses in front of the retina instead of on it.
- d.
___________________ is also known as farsightedness. People with this have trouble focusing on things close up because their eyes are too "short" from front to back. Therefore, light focuses behind the retina instead of on it, causing blurry vision.
- e.
_____________________ is a condition in which your eye isn’t completely round. Therefore, light gets bent more in one direction than another. That means only part of an object is in focus so things at a distance may look blurry and wavy.
- f.
_________________ is the normal loss of near focusing ability that occurs with age. Most people begin to notice the effects of presbyopia sometime after age 40, when they start having trouble seeing small print clearly.
- g.
Read Genesis 48:10. Which of the refractive errors did Israel have?
- h.
State if the following statement below is true or false: “All the refractive errors can be corrected by wearing the right glasses or contact lens.”
11.
Eye care:
- a.
How should I clean my eyes?
- b.
Write one sentence on how we can strain our eyes.
- c.
How should we rest them?
- d.
Matthew has been using a computer continuously for 4 hours! Now he is complaining of eye strain. Give Matthew three pieces of advice to help him relax his eyes.
- e.
Explain the 20-20-20 rule of eye relaxation.
- f.
What do I do if I cannot see very well?
12.
Give two meanings to the expression “The eyes are a window to the soul.”
13.
What are the effects of exposing ourselves to watching:
- a.
Violence/pornography (mention three)
- b.
Video games: Give three advantages and disadvantages
- c.
Social media: Give three advantages and disadvantages
14.
Explain 1 Samuel 16:7.
15.
Explain “fixing our eyes on Jesus.” (Hebrews 12:2)
16.
Mention four ways that life can be made easier for the visually impaired.
17.
Optical illusion:
- a.
Fill in the blanks using the word bank in the box below the passage.
_____________ Illusions can use colour, ______________ and patterns to create ___________ that can be deceptive or misleading to our _____________. The information gathered by the eye is processed by the brain, creating a perception that in reality, does not match the true image. Perception refers to the interpretation of what we take in through our _____________. Optical illusions occur because our brain is trying to _______________ what we see and make sense of the world around us. Optical illusions simply trick our brains into seeing things which may or may not be _____________.
| images | eyes | brains | optical | real | light | interpret |
- b.
Provide the answers to the optical illusions below.
- Müller-Lyer Illusion
- Take a very close look at the 2 line segments. Do you think one line is longer than the other?
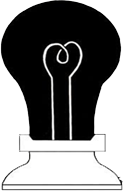
- Lightbulb Illusion
- Stare closely at this lightbulb for 25 seconds. Then immediately stare at a white wall or sheet of paper. What do you see?
- Shepard's Elephant Illusion
- How many legs do I have?
- Teach or Learn
- In this illusion you can see the word Teach and its reflection. Can you read the reflection too? What does it say?
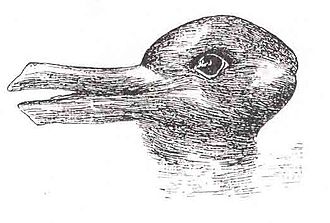
- Animal Illusion
- How many animals do you see in the image?
18.
Watch the video on how to do an origami eye. Make an origami eye.