Especialidades JA/Bactérias/Respostas
Nível de Habilidade
2
Ano
2012
Version
13.02.2026
Autoridade de Aprovação
Divisão Sul Americana
1
2
3
4
5
Different types of bacteria have different environmental requirements for reproduction, but in general bacteria usually need warm locations with plenty of their particular nutrients readily available.
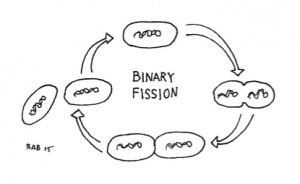
Most bacteria reproduce through binary fusion, a form of asexual reproduction. In this process, the bacteria creates a duplicate set of genetic material, the genetic material moves to each end of the bacteria, and the cell then squeezes in half, creating two effectively identical bacteria cells.
There are also a few variations of asexual reproduction in different groups of bacteria.
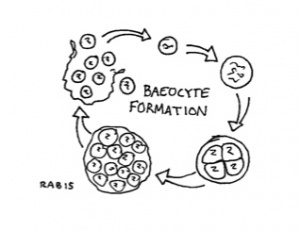
Some Cyanobacteria produce Baeocytes, enlarged bacterial cells that have rapid multiple division internally before breaking open and spewing out numerous new bacteria.
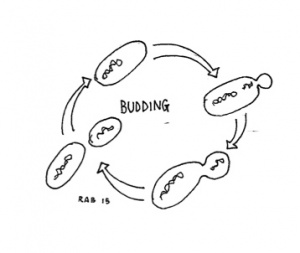
Certain bacteria may reproduce through budding, a process where a small bud forms on a parent bacteria, genetic material is transferred to the bud, and then it separates.
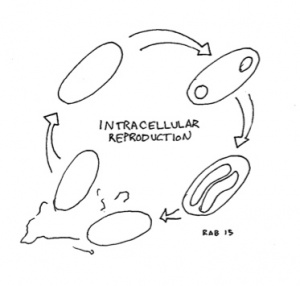
Some bacteria, including some of the Firmicutes bacteria, create two complete daughter cells inside the parent, then the parent breaks open and dies, releasing the two new bacteria cells.
Given that bacterial reproduction is primarily through forms of fission (division), there is no change in genetic material aside from mutation. However, Bacteria do have other ways to transfer genetic material, though not quite analogous to sexual reproduction.
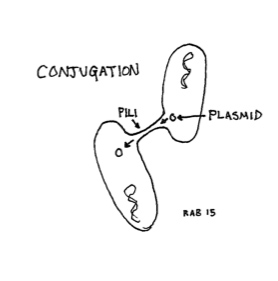
Conjugation: Bacteria transfer genes (usually on plasmids) via their pili.
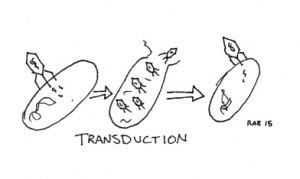
Transduction: A bacteriophage (a virus that uses bacteria as a host) may pick up some pieces of genetic material from a previous host and incidentally transfer it into a new bacterial host.
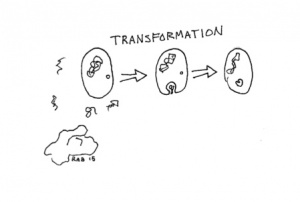
Transformation: Bacteria may pick up fragments of genetic material from their environment, usually left by dead bacteria.
6
Bacteria may be Autotrophs (roughly meaning self-food) or Heterotrophs (roughly meaning different-food). Autotrophs are capable of acquiring carbon from inorganic sources (usually in the form of Carbon Dioxide), Heterotrophs must consume some organic materials (sugars, fats, starches, etc) for the uptake of carbon.
Categories of Autotrophs:
Photoautotrophs (light-self-feed) are capable of photosynthesis, using sunlight as part of the process to take up nutrients from their environment. Some may be able to draw on sulfur compounds, or acidic hydrogen compounds. Among the photoautotrophs are the green and the purple photosynthetic bacteria, neither of which produce oxygen as a byproduct, and the cyanobacteria, the so-called blue-green bacteria (though some taxonomists place these in their own category separate from other bacteria).
Chemoautotrophs (chemical-self-feed) are those that can produce their own organic compounds, but do not necessarily need sunlight as a precursor. Some of the bacteria at the base of the food chain near deep sea hydrothermal vents are chemoautotrophs. Different chemoautotrophs utilize different “foods,” including iron, ammonia, nitrite, sulfur and hydrogen gas. Some of the most important are those that can convert nitrite (NH3) into a form of nitrogen that plants can absorb. This process is called nitrification, or more commonly nitrogen fixing. Some bacteria capable of fixing nitrogen are considered chemolithotrophs, able to effectively live on rock as a substrate.
Categories of Heterotrophs:
Saprophytes (dead-feed) are the bacteria that break down organic matter into simpler molecules. These are the decomposers, as well as many of the beneficial bacteria in the guts of animals (including people). Some are capable of breaking down cellulose or other plant-based materials that human digestive systems cannot.
Parasitic bacteria are those that draw nutrients directly from a host. Rickettsia and Chlamydia, two disease-causing bacteria, must live inside animal cells, and are examples of parasitic bacteria.
Respiration:
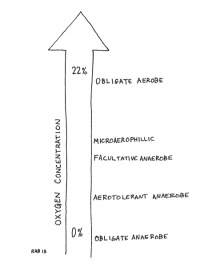
Bacteria, whether autotrophs or heterotrophs, may be either Aerobic (requiring oxygen as part of their respiration) or anaerobic (either not requiring oxygen, or being unable to grow in the presence of atmospheric oxygen). Bacteria that require oxygen for their metabolic functions are called obligate aerobes, while those that cannot live in the presence of oxygen are called obligate anaerobes. Between them there are different gradations of oxygen tolerance. Microaerophyllic bacteria live best in low-oxygen environments. Facultative anaerobes are capable of living without oxygen, but thrive in the presence of oxygen. And aerotolerant anaerobes are those that live best without oxygen, but are generally unaffected negatively by the presence of oxygen.
7
There are many harmful bacteria, impacting humans, animals and plants. As question 10 discusses illnesses caused by bacteria, more attention can be given in this question to bacteria that are “harmful” in other ways.
Some examples of harmful bacteria include:
Bacillus anthracis (Anthrax) - often found in soil, the spores can lead to death in cattle if ingested.
Clostridium botulinum (Botulism) - A bacteria that produces a neurotoxin as a byproduct of its metabolic process - it is often a cause of food poisoning.
Streptococcus sp. (Strep) - A bacteria that is usually always present in small amounts in humans, when the immune system is weakened (through surgery, through cold or fatigue, or for other reasons), there can be rapid growth and damage, potentially leading to strep throat, pneumonia or other illnesses.
8
9
10
Cholera (Vibrio cholera) - Transferred through water contaminated with bodily fluids.
Prevention: In areas where cholera may be prevalent, wash hands thoroughly, avoid fresh fruit or vegetables unless you can peel them yourself, only eat cooked food, do not drink the local water.
Tetanus (Clostridium tetani) - Transferred through contamination into wounds.
Prevention: Vaccination (note that tetanus vaccinations need updated relatively frequently compared to many other types of vaccinations) Also, be careful around rusty and dirty objects that can cause puncture wounds or cuts. Wash wounds thoroughly and apply a surface antiseptic. Leave deeper wounds open to drain (seek medical attention as appropriate).
Tuberculosis (Mycobacterium tuberculosis) - Transferred through droplets in coughs and sneezes.
Prevention: Use caution in areas where tuberculosis is common. Wear face masks, wash hands, do not touch hands to face or mouth, try to avoid enclosed spaces with those that may be infected, work in open, well ventilated areas.
Lyme Disease (Borrelia burgdorferi) - Transferred through the bite of certain ticks.
Prevention: Avoid or use caution in areas that may be infested with ticks (tall grasses, thick undergrowth, etc). Wear long pants and long sleeves, tuck pant legs into boots or socks, use insect repellents with DEET, check frequently for ticks, remove ticks carefully, apply surface antiseptic.
11