The printable version is no longer supported and may have rendering errors. Please update your browser bookmarks and please use the default browser print function instead.
Shock is a medical condition where the delivery of oxygen and nutrients is insufficient to meet the body's needs. The main carrier of oxygen and nutrients in the body is the blood, so anytime there is a loss of blood, there is a risk of shock. Shock is a life-threatening emergency.
First aid treatment of shock includes:
- Immediate reassurance and comforting the victim if conscious.
- If alone, go for help. If not, send someone to go for help and someone stay with the victim.
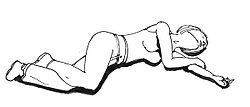
- Ensure that the airway is clear and check for breathing. Place the victim in the recovery position if possible.
- Attempt to stop any obvious bleeding.
- Cover the victim with a blanket or jacket, but not too thick or it may cause a dangerous drop in blood pressure.
- Do not give a drink. Moisten lips if requested.
- Prepare for cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR).
- Give as much information as possible when the ambulance arrives.