Difference between revisions of "AY Honors/Small Mammal Pets/Answer Key"
(Pellets don't cause obiesity, and lots of care must be taken in feeding foods with moisture) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | {{Taxobox | |
| + | | color = pink | ||
| + | | name = Dwarf Winter White Russian Hamster | ||
| + | | image = Phodopus sungorus 2 - Colour corrected.jpg | ||
| + | | image_width = 250px | ||
| + | | regnum = [[Animal]]ia | ||
| + | | phylum = [[Chordate|Chordata]] | ||
| + | | classis = [[Mammal]]ia | ||
| + | | ordo = [[Rodent]]ia | ||
| + | | subordo = [[Myomorpha]] | ||
| + | | superfamilia = [[Muroidea]] | ||
| + | | familia = [[Cricetidae]] | ||
| + | | subfamilia = [[Cricetinae]] | ||
| + | | genus = ''[[Phodopus]]'' | ||
| + | | species = '''''P. sungorus''''' | ||
| + | | binomial = ''Phodopus sungorus'' | ||
| + | | binomial_authority = (Pallas, 1773) | ||
| + | | subdivision_ranks = Subspecies | ||
| + | | subdivision = | ||
| + | ''Phodopus sungorus sungorus'' | ||
| + | (see text) | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | '''Winter White Russian hamsters''' are a species of [[Hamster]] in the genus ''[[Phodopus]]''. They are typically half the size of the better-known [[Golden Hamster|Syrian hamster]], and therefore called dwarf hamsters along with all ''Phodopus'' species. Features include a typically thick dark grey dorsal stripe and furry feet. The tail is so short that it hardly shows when the hamster is sitting. As winter approaches and the days shorten, Winter Whites' dark fur greys until it is almost completely white (hence the name). In the wild, this adaptation helps them evade predators in the snow-covered steppes of winter. They live mainly in [[Siberia]] and are also found in [[Dzungaria]], [[Kazakhstan]], [[Mongolia]] and [[Manchuria]]. | ||
| − | + | It has been debated whether the Winter White hamster was a [[sub-species]] of the [[Campbell's dwarf hamster|Campbell's Dwarf Hamster]] (''Phodopus campbelli'') or not; however, recently it was decided that Winter Whites are of their own species, ''Phodopus sungorus''. | |
| − | + | The average lifespan of the Winter White Russian Dwarf Hamster is 1½ to 2 years, although they can live longer. | |
| − | [[Category: | + | ==Pet Ownership== |
| + | Winter Whites are often found on the [[pet]] market, in [[Europe]] and [[Asia]] more so than in [[North America]] and indeed are rarely found in pet stores in [[Canada]]. Care is similar to that of the [[Campbell's dwarf hamster|Campbell's Dwarf Hamster]]. Winter White hamsters generally make excellent pets; however, a larger [[Golden Hamster|Syrian Hamster]] would be more suitable for younger children, as they can be handled more clumsily. Winter White hamsters should not be fed food containing sources of [[monosaccharide]]s because of the risk of developing [[diabetes mellitus]]{{Fact|date=February 2007}}. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Winter Whites, in common with the [[Campbell's dwarf hamster|Campbell's Dwarf Hamster]] are sociable and will live together peacefully with others of their own species, but are best introduced at a young age and will require a sufficiently large cage to ensure they live together happily. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <gallery> | ||
| + | Image:Pearl Winter White Russian Dwarf Hamster - Front.jpg|Pearl Winter White - Front | ||
| + | Image:Pearl Winter White Russian Dwarf Hamster - Side.jpg|Pearl Winter White - Side | ||
| + | Image:Pearl Winter White Russian Dwarf Hamster - Rear.jpg|Pearl Winter White - Rear | ||
| + | Image:Pearl Winter White Russian Dwarf Hamster - Face.jpg|Pearl Winter White - Face | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Breeding== | ||
| + | |||
| + | In general, dwarf hamsters typically have more of a family structure than the [[Golden Hamster|Syrian Hamster]]. Conventional beliefs are that dwarf hamsters will happily live in mated pairs, with both male and female caring for the young. However, this may be a result of a frequent confusion of the Winter Whites and the Campbell's hamsters. Current research suggests biparental care in Campbell's hamsters (Phodopus campbelli) but not in Winter Whites (Phodopus sungorus).<ref>Research by Dr. Katherine Wynne-Edwards at Queen's University, Ontario, Canada</ref> Some report that same-sex pairs and larger groups do not always get along well and frequent fighting may occur and be a great distress for them, or even lead to death. :-) You can keep the males in with the females when she has her litter, as the male is known to help the female with gathering food ect. This also has concequences, he might mate with the female again, if he does seperate the two adults before the next litter is born! :-) | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Phases== | ||
| + | |||
| + | There are several phases (colorations) of Winter White hamsters: their normal (dark brownish-grey colouring) or sapphire (blue-grey colouring). A white pattern called pearl (white with coloured hairs) sometimes exists in either phase, producing the normal pearl or sapphire pearl forms. However, these colours may be difficult to find, and the range of colours is much narrower than in the case of the [[Campbell's dwarf hamster|Campbell's]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Winter White hamsters, also called Siberian hamsters, come from the steppes of Siberia and Kazakhstan and possess an adaptation not seen in [[Campbell's dwarf hamster|Campbells]]: they can moult into a white winter coat. This camouflages them against the snow and also gives them their name. This moulting is brought on by the amount of day light; if the hamster is kept in an environment with short duration of day light (< 12 hours of light/day) for more than 6 weeks, they will change into their winter coat (white guard hair with thick inner hair) with only a single black stripe going through the centre of the back. Such seasonal moulting is mediated through the nocturnal secretion of melatonin, the hormone secreted by the pineal gland. Short day lengths also triggers the regression of the gonads in both male and females, and thus Winter Whites become infertile. Because Winter White hamsters show such photoperiodic and seasonal changes in physiology and various behaviours, it is also used as a research model system for studying seasonality and photoperiodism. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <gallery> | ||
| + | Image:Phodopus_sungorus.jpg|Normal colouration. | ||
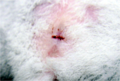
| + | Image:Winter White - Vaginal Spotting.png|Vaginal spotting on a 6-month-old Winter White. The anus is visible as a more puckered orifice halfway from the vaginal entrance to the base of the tail. | ||
| + | Image:Winter White - Vaginal Spotting - Zoom.png|More defined version of previous image. | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Campbell's/Winter White Hybrids == | ||
| + | |||
| + | Of the five species kept commonly as pets, only the [[Campbell's dwarf hamster|Campbells]] and Winter Whites are able to interbreed and produce live offspring (hybrids). Hybrids are most often unknowingly produced through incorrect identification of the two similar species of hamsters, and unfortunately the number of hybrids is increasing particularly within pet shops in many countries today where they are often mislabelled as being one or other of the pure species. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Although hybrids make suitable pets, the breeding of hybrids should be avoided as it can cause health and birthing problems, and also the widespread breeding and distribution of hybrids could threaten the existence of both pure species in captivity. Therefore, if intending to breed Russian hamsters it is important to ensure that both hamsters being bred are a pure form of, and of the same, species to avoid producing hybrids. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Footnotes== | ||
| + | {{reflist|2}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==External links== | ||
| + | |||
| + | *[http://www.petwebsite.com/hamsters/dwarf_winter_white_russian_hamsters.htm Pet Web Site (formerly The Complete Hamster Site) section on Dwarf Winter White Russian Hamsters] | ||
| + | *[http://www.petwebsite.com/hamsters/hybrid_hamsters.htm Pet Web Site (formerly The Complete Hamster Site) section on Hybrid Hamsters] | ||
| + | *[http://www.hamster-heaven.com Hamster Heaven] | ||
| + | *[http://www.xander.it/video.htm Xander.it] - Winter White video gallery | ||
| + | *[http://www.furrycritters.co.uk FurryCritters] | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Hamster}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Hamsters]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[cs:Křečík džungarský]] | ||
| + | [[de:Dsungarischer Zwerghamster]] | ||
| + | [[es:Phodopus sungorus]] | ||
| + | [[fr:Hamster russe]] | ||
| + | [[hr:Bijeli ruski hrčak]] | ||
| + | [[it:Phodopus sungorus]] | ||
| + | [[he:אוגר סיבירי]] | ||
| + | [[nl:Russische dwerghamster]] | ||
| + | [[ja:ジャンガリアンハムスター]] | ||
| + | [[ko:윈터 와이트 러시안 햄스터]] | ||
| + | [[pl:Chomik dżungarski]] | ||
| + | [[ru:Хомячок джунгарский]] | ||
| + | [[sl:Sibirski hrček]] | ||
| + | [[fi:Venäjänkääpiöhamsteri]] | ||
| + | [[zh:短尾侏儒倉鼠]] | ||
Revision as of 15:21, 17 June 2007
Template:Taxobox Winter White Russian hamsters are a species of Hamster in the genus Phodopus. They are typically half the size of the better-known Syrian hamster, and therefore called dwarf hamsters along with all Phodopus species. Features include a typically thick dark grey dorsal stripe and furry feet. The tail is so short that it hardly shows when the hamster is sitting. As winter approaches and the days shorten, Winter Whites' dark fur greys until it is almost completely white (hence the name). In the wild, this adaptation helps them evade predators in the snow-covered steppes of winter. They live mainly in Siberia and are also found in Dzungaria, Kazakhstan, Mongolia and Manchuria.
It has been debated whether the Winter White hamster was a sub-species of the Campbell's Dwarf Hamster (Phodopus campbelli) or not; however, recently it was decided that Winter Whites are of their own species, Phodopus sungorus.
The average lifespan of the Winter White Russian Dwarf Hamster is 1½ to 2 years, although they can live longer.
Pet Ownership
Winter Whites are often found on the pet market, in Europe and Asia more so than in North America and indeed are rarely found in pet stores in Canada. Care is similar to that of the Campbell's Dwarf Hamster. Winter White hamsters generally make excellent pets; however, a larger Syrian Hamster would be more suitable for younger children, as they can be handled more clumsily. Winter White hamsters should not be fed food containing sources of monosaccharides because of the risk of developing diabetes mellitusTemplate:Fact.
Winter Whites, in common with the Campbell's Dwarf Hamster are sociable and will live together peacefully with others of their own species, but are best introduced at a young age and will require a sufficiently large cage to ensure they live together happily.
Breeding
In general, dwarf hamsters typically have more of a family structure than the Syrian Hamster. Conventional beliefs are that dwarf hamsters will happily live in mated pairs, with both male and female caring for the young. However, this may be a result of a frequent confusion of the Winter Whites and the Campbell's hamsters. Current research suggests biparental care in Campbell's hamsters (Phodopus campbelli) but not in Winter Whites (Phodopus sungorus).& Some report that same-sex pairs and larger groups do not always get along well and frequent fighting may occur and be a great distress for them, or even lead to death. :-) You can keep the males in with the females when she has her litter, as the male is known to help the female with gathering food ect. This also has concequences, he might mate with the female again, if he does seperate the two adults before the next litter is born! :-)
Phases
There are several phases (colorations) of Winter White hamsters: their normal (dark brownish-grey colouring) or sapphire (blue-grey colouring). A white pattern called pearl (white with coloured hairs) sometimes exists in either phase, producing the normal pearl or sapphire pearl forms. However, these colours may be difficult to find, and the range of colours is much narrower than in the case of the Campbell's.
Winter White hamsters, also called Siberian hamsters, come from the steppes of Siberia and Kazakhstan and possess an adaptation not seen in Campbells: they can moult into a white winter coat. This camouflages them against the snow and also gives them their name. This moulting is brought on by the amount of day light; if the hamster is kept in an environment with short duration of day light (< 12 hours of light/day) for more than 6 weeks, they will change into their winter coat (white guard hair with thick inner hair) with only a single black stripe going through the centre of the back. Such seasonal moulting is mediated through the nocturnal secretion of melatonin, the hormone secreted by the pineal gland. Short day lengths also triggers the regression of the gonads in both male and females, and thus Winter Whites become infertile. Because Winter White hamsters show such photoperiodic and seasonal changes in physiology and various behaviours, it is also used as a research model system for studying seasonality and photoperiodism.
Campbell's/Winter White Hybrids
Of the five species kept commonly as pets, only the Campbells and Winter Whites are able to interbreed and produce live offspring (hybrids). Hybrids are most often unknowingly produced through incorrect identification of the two similar species of hamsters, and unfortunately the number of hybrids is increasing particularly within pet shops in many countries today where they are often mislabelled as being one or other of the pure species.
Although hybrids make suitable pets, the breeding of hybrids should be avoided as it can cause health and birthing problems, and also the widespread breeding and distribution of hybrids could threaten the existence of both pure species in captivity. Therefore, if intending to breed Russian hamsters it is important to ensure that both hamsters being bred are a pure form of, and of the same, species to avoid producing hybrids.
Footnotes
- ↑ Research by Dr. Katherine Wynne-Edwards at Queen's University, Ontario, Canada
External links
- Pet Web Site (formerly The Complete Hamster Site) section on Dwarf Winter White Russian Hamsters
- Pet Web Site (formerly The Complete Hamster Site) section on Hybrid Hamsters
- Hamster Heaven
- Xander.it - Winter White video gallery
- FurryCritters
cs:Křečík džungarský de:Dsungarischer Zwerghamster es:Phodopus sungorus fr:Hamster russe hr:Bijeli ruski hrčak it:Phodopus sungorus he:אוגר סיבירי nl:Russische dwerghamster ja:ジャンガリアンハムスター ko:윈터 와이트 러시안 햄스터 pl:Chomik dżungarski ru:Хомячок джунгарский sl:Sibirski hrček fi:Venäjänkääpiöhamsteri zh:短尾侏儒倉鼠