AY Honor Flags of Australia - Advanced Answer Key
Skill Level
2
Year
2015
Version
11.01.2026
Approval authority
Australian Union
1
2
| The National Colonial Flag Captains Bingle and Nicholson are credited with the first attempt to design a “national” flag for Australia circa 1823. It featured four stars of the Southern Cross on a red cross, with the Union Jack in the canton, on a white field.
| |
| The Anti-Transportation League Flag The Anti-Transportation League (1851) was one of the earliest expressions of the concept of federation and the understanding that the voices of the separate colonies would be heard more clearly if the colonies acted in unison.
When transportation ended in 1853, the league disbanded and its flag did not fly again. The flag had a dark blue field with the Union Jack in the canton and five stars arranged in the pattern of the Southern Cross. The five stars represented Tasmania, Victoria, New South Wales, South Australia and New Zealand. A white border ran around three sides, but not against the hoist. | |
| The Murray River Flag An unofficial flag, the Murray River flag was flown on some paddle steamers that were part of the Murray River trade of the 1850’s. It features the Southern Cross and Stripes, this flag’s design was influenced by earlier flags such as the national colonial flag and the New South Wales merchant flag of the 1830s.
| |
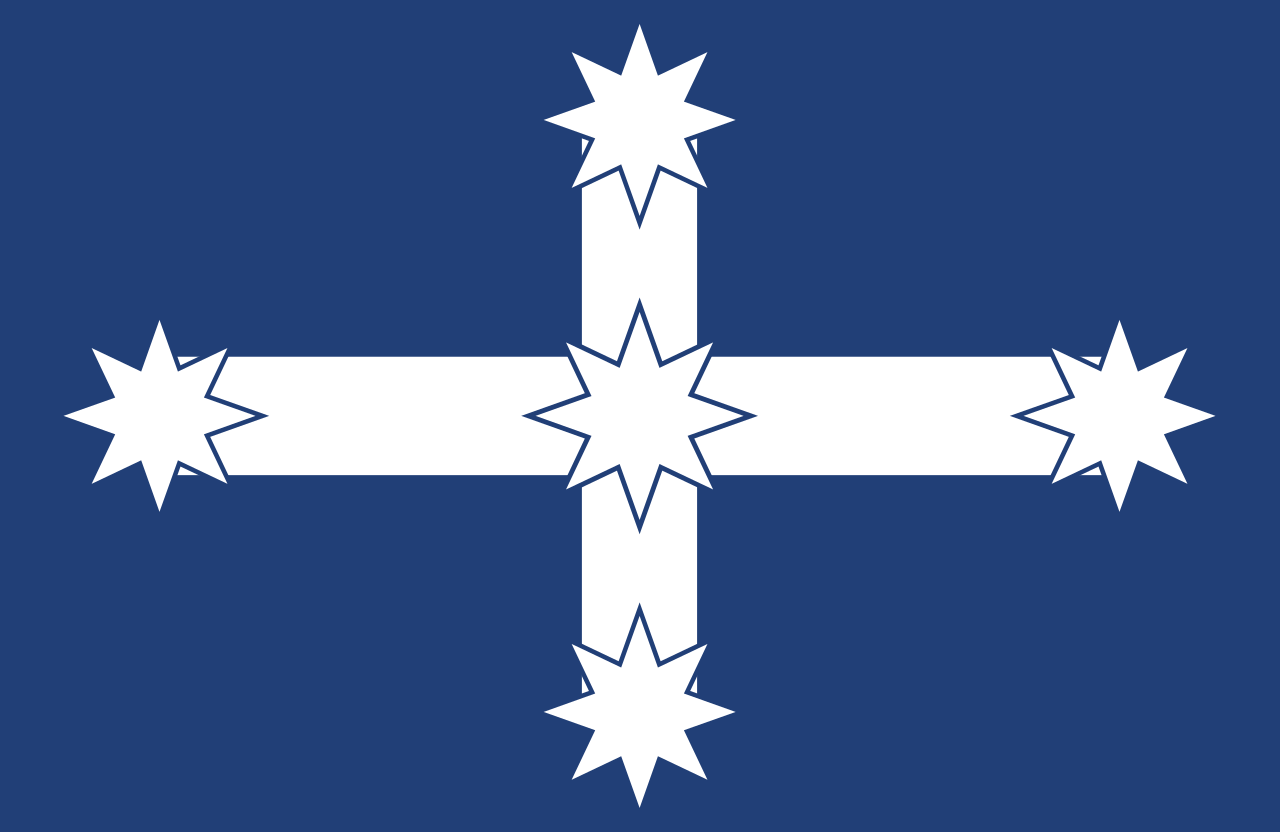
| The Eureka Flag This flag was flown by miners during the battle at the Eureka Stockade near Ballarat, Victoria in 1854. They were protesting the high cost of gold mining licenses and other grievances. It expressed a sense of identity growing out of the colonial period. It continues to be used as a symbol of nationalism, having been revived by a wide range of activists. It features a blue field with a white cross linking five white stars, one in the centre and one at each end of the cross.
| |
| The Australian Federation Flag This flag was the chief symbol of the political movement, in the 1880’s and 1890’s, towards federation of the six Australian colonies. It was used to promote national consciousness and the need for federation; in so doing they made it a very popular banner. So much so that it was still being seen as late as the 1920’s. It featured the stars of the Southern Cross in white placed on a blue cross on a white field with the Union Jack in the canton.
|
3
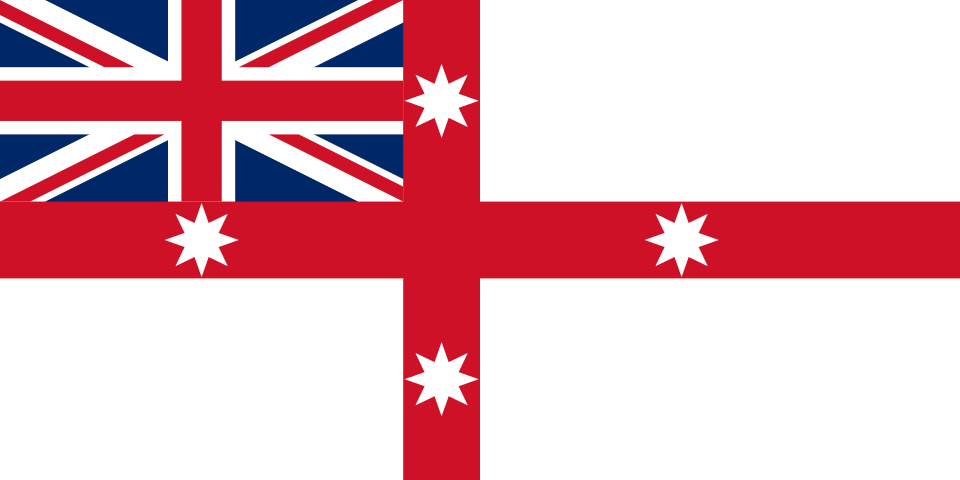
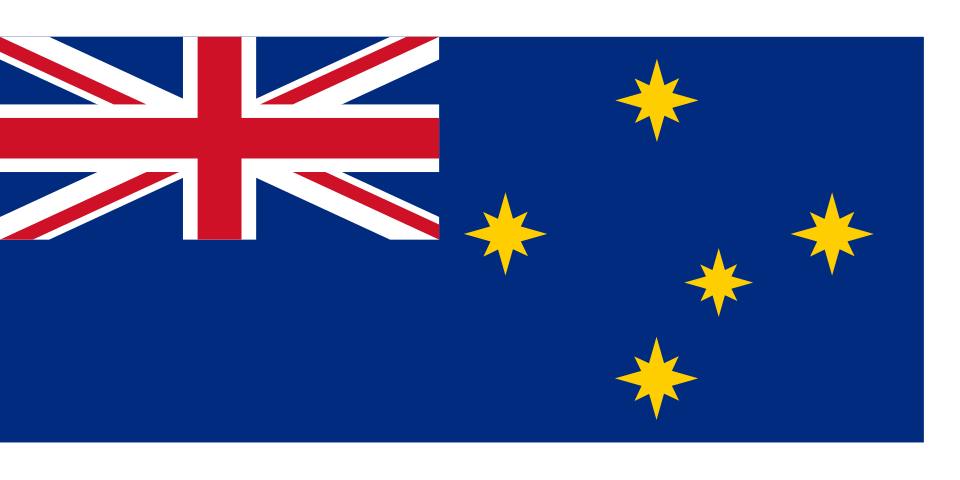
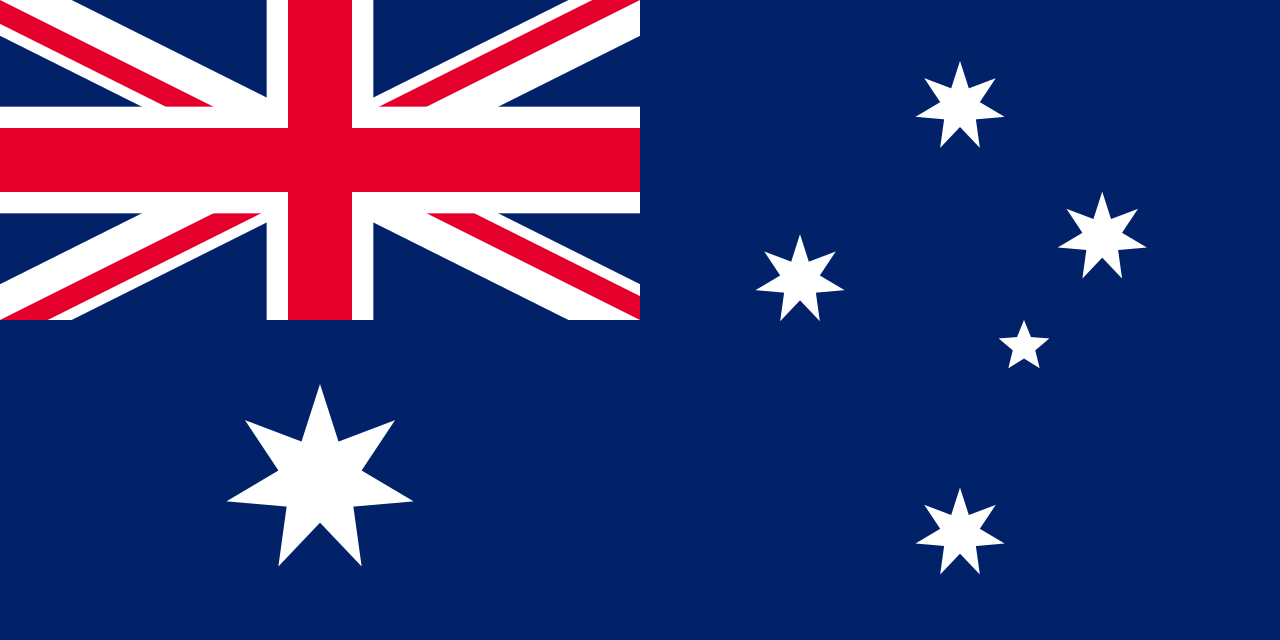
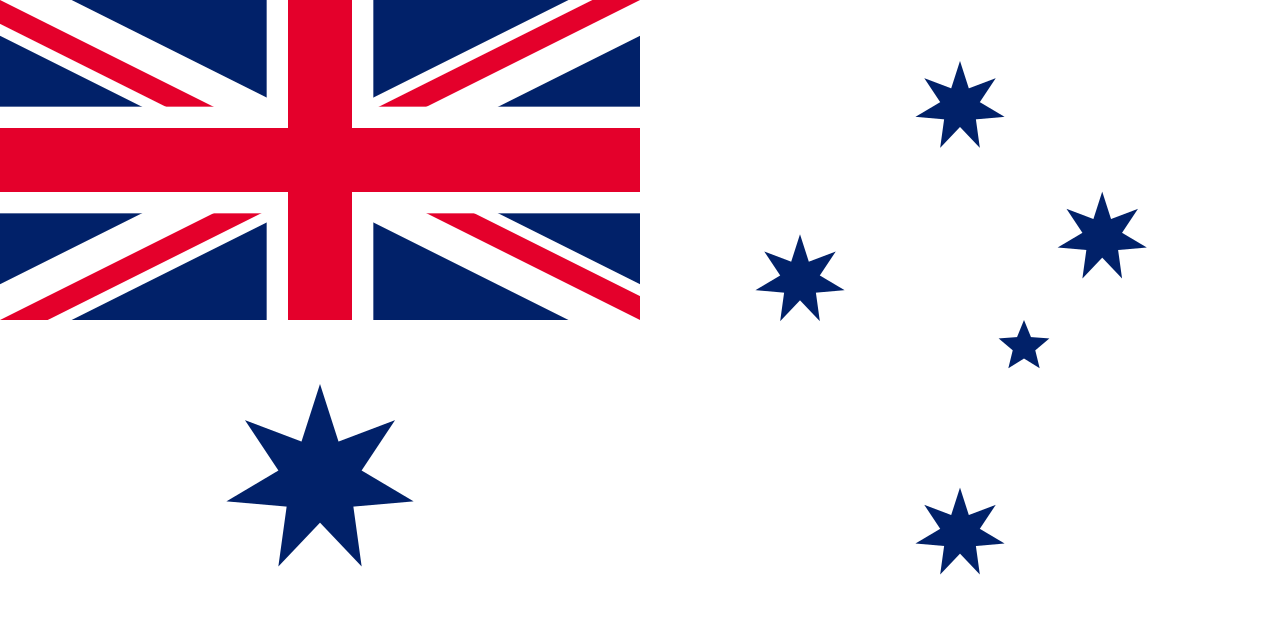
Under the Flags Act, 1953, the Australian Blue Ensign was given official recognition as the Australian National Flag. This is the correct flag for citizens and business enterprises to fly on land. The Australian Red Ensign was reaffirmed as the proper “colours” for Australian registered ships in the Shipping Registration Act, 1981. It should be flown by merchantmen, yachts and small craft. It should never be flown over land.
| The Australian Army The Australian Army has no separate ensign but is the protector of the Australian National Flag by which it is represented.
| |
| The Royal Australian Navy The distinctive Australian White Ensign was adopted in 1967. From its formation in 1911, until 1967, the White Ensign of the Royal Navy was used. The White Ensign is reserved exclusively for use by the Royal Australian Navy on its ships and over its shore establishments.
| |
| The Royal Australian Navy The distinctive Australian White Ensign was adopted in 1967. From its formation in 1911, until 1967, the White Ensign of the Royal Navy was used. The White Ensign is reserved exclusively for use by the Royal Australian Navy on its ships and over its shore establishments.
| |
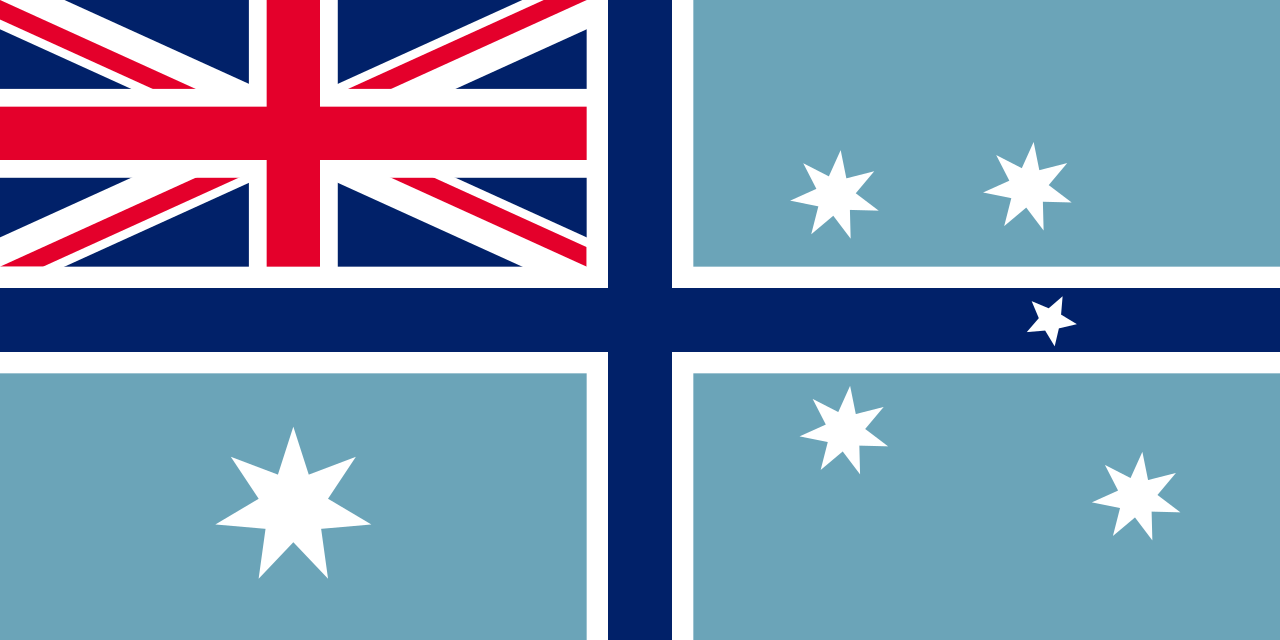
| The Royal Australian Airforce In 1948, the distinctive light blue ensign was approved for use by the Royal Australian Air Force and it was adopted in 1948. This ensign incorporated the Southern Cross and Commonwealth Star and it replaced the Royal Air Force Ensign that had been in use since 1922. In 1981 the leaping kangaroo was placed at the centre of the ensign’s roundel.
| |
| The Tri-Service Flag The tri-service flag represents the three services of the Australian defence force: the red stripe represents the Australian Army, the dark blue stripe represents the Royal Australian Navy and the light blue stripe represents the Royal Australian Air Force. The defence force emblem, as a charge is placed in the centre of the flag, also represents the three services: the crossed swords for the army, the anchor for the navy and the eagle for the air force. The Commonwealth Star and boomerang represent Australia.
| |
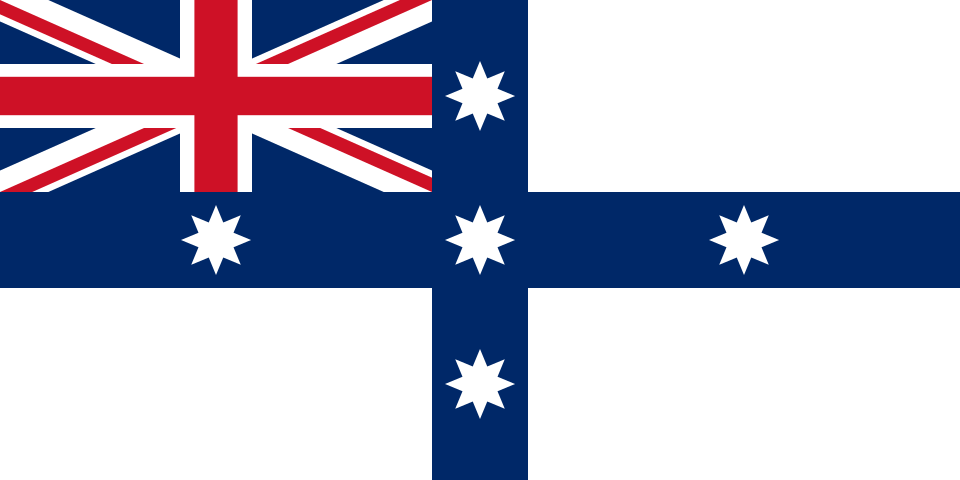
| The Civil Air Ensign of Australia Dating from 1935, the civil air ensign represents the Commonwealth government organisation responsible for civil aviation. It can be seen flying from civil aviation buildings, aircraft, boats and airports. When adopted the stars were yellow and were changed to white in 1947 to improve recognition of the flag when viewed from a distance.
|
4
| Her Majesty the Queen’s Personal Flag for Australia HM Queen Elizabeth II has a special flag that is flown to acknowledge her role as Queen of Australia. Approval was given for the design in September 1962 and it was first flown during the visit of 1963.
It consists of the Commonwealth Coat of Arms, on which is placed a large Commonwealth Star overlapping the centre. The Queen’s initial with the Royal Crown (St Edward’s) within a chaplet (i.e. garland) of roses, are emblazoned on the star. The Queen’s Personal Flag is a royal standard and is used in the same way as the Royal Standard is used in the United Kingdom. When flown on or outside a building, no other flag should be flown with it. | |
| The Governor-General’s Flag In 1930 King George V approved a special flag for the Governor-General in each Dominion of the Empire. This was to reflect the change in status from representatives of the British authorities to the personal representatives of the sovereign. The Australian version was first used in 1936.
It features the Royal Crest, consisting of the crown of St Edward beneath a crowned lion. Beneath the crest is a golden scroll inscribed with the words “Commonwealth of Australia”, all placed on a dark blue field. |
The governor of each Australian State has a personal flag, generally the State flag with the addition of a crown above the State Badge, as shown below.
The two exceptions to the general rule being the flags of the Governors of Victoria and Queensland. The Victorian flag has a golden field while the Queensland flag is the Union Flag with the State badge placed as a charge on its centre.
The Administrator of the Northern Territory flies the Australian National Flag.
5
As there are protocols and rules relative to the national flag and the values for which it stands to be observed and followed by those living under the protection of the nation for their continued prosperity and happiness, so in the Christian life there are protocols to be observed and rules to be followed by those wanting the protection, blessing and guidance of God.
As the national flag is to be respected as the embodiment of the nation and should never touch the ground, floor or water, so the Bible is to be respected as the Word of God and must never be handled with disrespect.
As the national flag is to take precedence over all other flags so the allegiance to God is paramount in all matters of integrity, accountability, diligence, perseverance and discipline.
As the national flag is held so close to people’s hearts that they will risk their lives for it, so the Christian will be faithful, unto death if required, in their advocating of the values expressed in the Bible.
As when the Queen’s Personal Standard is flown on or outside a building, no other flag is to be flown with it, so the Christian will not allow any other philosophy or belief system to detract from the display of the Gospel of the Bible in their life.
As the populace is encouraged to fly the national flag on days of significance in the history of the nation as a sign of commitment to the ideals represented by the flag, so the Christian is encouraged to display their commitment to the Law of God and their determination to abide by its precepts in their daily lives.
6
On days of national commemoration, the Australian National Flag and other flags should be flown on public buildings. Private citizens are also encouraged to fly the Australian National Flag on such days provided they have the facilities to do so in a dignified manner.
Days of National Commemoration
- January 1 – Anniversary of the establishment of the Commonwealth of Australia.
- January 26 – Australia Day.
- February 6 – Anniversary of the accession of the Sovereign.
- March, second Monday – Commonwealth Day.
- April 21 – Anniversary of the birthday of the Sovereign.
- April 25 – ANZAC Day. Flags to be flown at half-mast until noon and at the peak until the usual for the closure of business.
- May 9 – Anniversary of the inauguration of Canberra as the seat of government of the Commonwealth (ACT Only).
- June 2 – Anniversary of the Coronation of the Sovereign.
- June 10 – Anniversary of the birthday of the Consort of the Sovereign.
- June, second Monday – Official birthday of the Sovereign, except WA & Qld, where it is observed in September & October respectively.
- September 3 – Australian National Flag Day.
- September, last Monday - Official birthday of the Sovereign - WA.
- October, first Monday - Official birthday of the Sovereign – Qld.
- October 24 – United Nations Day. The United Nations flag, if available, should be flown all day. If only one flagpole is available, the United Nations should be flown, even if that flagpole is usually reserved for the Australian National flag. If two flagpoles are available, the United Nations flag should be flown in the pre-eminent position.
- November 11 – Remembrance Day. Flags should be flown at the peak from 8.00am to 10.30am, at half-mast until 11.03am, and at the peak until the usual time for the closure of business.
7
Prepare a timeline for the history of flags in Australia since 1800.
- January1, 1801 – Union Jack (in current form) used in Australia as national flag.
- February 28, 1851 – Australian Anti-Transportation flag unfurled.
- November 29, 1854 – Eureka flag raised.
- August 1869 – Badge of NSW flag authorised. Using the red cross of St George on a white field (later addition of gold lion of England and four eight pointed stars of the Southern Cross).
- January 3, 1870 – Western Australian flag adopted (later change to direction of swan).
- February 4, 1870 – Victorian flag adopted. Using the Southern Cross on the fly (later addition of Imperial crown, which itself was replaced by the crown of St Edward).
- September 25, 1876 – Tasmanian flag adopted (later detail of lion changed).
- November 20, 1876 – Queensland flag proclaimed (later change to crown).
- January 1, 1901 – Federation proclaimed. Australian colonies unite to form the Commonwealth of Australia.
- September 3, 1901 – First time the Australian National Flag flown. Winning design of public competition announced by Prime Minister Barton.
- February 20, 1903 – King Edward VII gives approval for the design for the Australian National Flag (Commonwealth Blue Ensign) and one for the flag of the merchant navy (Commonwealth Red Ensign). The points of the Southern Cross stars are simplified to four seven-pointed and one fivepointed star.
- January 13, 1904 – South Australian flag proclaimed.
- February 23, 1908 – Australian National Flag. Modified to current form, with seven-pointed Commonwealth Star.
- March 23, 1934 – Dimensions of national flag specified in Commonwealth Gazette.
- During 1935 – Civil air ensign adopted (stars later changed from gold to white).
- July 16, 1936 – Australia Governor-General’s flag adopted.
- March 15, 1941 – Prime Minister Menzies issues a press statement. The statement encourages the Australian public to fly Commonwealth Blue Ensign on land. Australian merchant ships are to continue to fly the Australian Red Ensign.
- February 24, 1947 – Prime Minister Chifley issues a statement. The statement supports the earlier statement of Menzies and encourages more general use of the Commonwealth Blue Ensign.
- October 20, 1947 – United Nations flag adopted.
- During 1949 – Royal Australian Air Force adopts its own ensign. This ensign was approved by King George VI in 1948. Later in 1982, the ensign is amended with the addition of a kangaroo to the roundel.
- December 4, 1950 – Government decides to formally proclaim the Commonwealth Blue Ensign as the Australian National Flag.
- During 1951 – King George VI approves the Government’s recommendation that the Commonwealth Blue Ensign be adopted as the Australian National Flag.
- December 3, 1953 – Flags Bill passed by Commonwealth Parliament.
- April 14, 1954 – Flags Act 1953 takes effect. This Act declares the Commonwealth Blue Ensign as the Australian National flag.
- September 20, 1962 – Queen’s personal flag for Australia approved.
- March 1, 1967 – Australian White Ensign adopted as flag of Royal Australian Navy.
- July 12, 1971 – Aboriginal flag first raised.
- July 1, 1978 – Northern Territory adopted.
- January 11, 1980 – Norfolk Island flag adopted.
- March 25, 1981 – Shipping Registration Act 1981. This Act confirms the use of the Australian Red Ensign as the flag for use by Australian registered merchant ships. – Prime Minister Menzies issues a press statement. The statement encouragesthe Australian public to fly Commonwealth Blue Ensign on land. Australian merchant ships are to continue to fly the Australian Red Ensign.
- February 24, 1947 – Prime Minister Chifley issues a statement. The statement supports the earlier statement of Menzies and encourages more general use of the Commonwealth Blue Ensign.
- October 20, 1947 – United Nations flag adopted.
- During 1949 – Royal Australian Air Force adopts its own ensign. This ensign was approved by King George VI in 1948. Later in 1982, the ensign is amended with the addition of a kangaroo to the roundel.
- December 4, 1950 – Government decides to formally proclaim the Commonwealth Blue Ensign as the Australian National Flag.
- During 1951 – King George VI approves the Government’s recommendation that the Commonwealth Blue Ensign be adopted as the Australian National Flag.
- December 3, 1953 – Flags Bill passed by Commonwealth Parliament.
- April 14, 1954 – Flags Act 1953 takes effect. This Act declares the Commonwealth Blue Ensign as the Australian National flag.
- September 20, 1962 – Queen’s personal flag for Australia approved.
- March 1, 1967 – Australian White Ensign adopted as flag of Royal Australian Navy.
- July 12, 1971 – Aboriginal flag first raised.
- July 1, 1978 – Northern Territory adopted.
- January 11, 1980 – Norfolk Island flag adopted.
- March 25, 1981 – Shipping Registration Act 1981. This Act confirms the use of the Australian Red Ensign as the flag for use by Australian registered merchant ships.