Difference between revisions of "AY Honors/Rainforests/Answer Key"
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
==3. Explain what causes so much rain to fall in rainforest biome areas.== <!--T:5--> | ==3. Explain what causes so much rain to fall in rainforest biome areas.== <!--T:5--> | ||
| + | [[File:Atmospheric circulation.svg|thumb|450px|Atmospheric circulation diagram.]] | ||
| + | The equator is heated by direct sunlight. As air rises, the water vapor cools and condenses and falls as rain causing the tropical rainforest. This is why tropical rainforests are mostly found along the equator (see the pattern labeled "Hadley cells" in the diagram). The drier air moves north and south of the equator and falls, causing deserts to form. Similar convection currents occur at 60 degrees north and south causing the temperate rain forest. This is why temperate rainforests are mostly found between the poles and the equator (see the pattern labeled "Ferrel cells" in the diagram) | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Steigungsregen.jpg|thumb|450px|Mountains disrupt the normal precipitation patterns.]] | ||
| + | Irregularities in the general pattern described above can be caused by mountains and coastlines. Here, the air cools as it rises, allowing water to condense and fall as rain. | ||
| + | {{clear}} | ||
==4. Draw a diagram showing the vertical layers of plants in a tropical rainforest. Label them.== <!--T:6--> | ==4. Draw a diagram showing the vertical layers of plants in a tropical rainforest. Label them.== <!--T:6--> | ||
Revision as of 00:57, 28 January 2017
1. Describe a rainforest.
Rainforests are forest communities, which receive heavy rainfall and are home to half of all terrestrial animal and plant species (including two thirds of all flowering plants). The amount of sun in the layers of plants is important to determine what is able to grow.
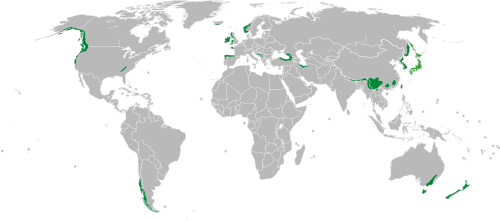
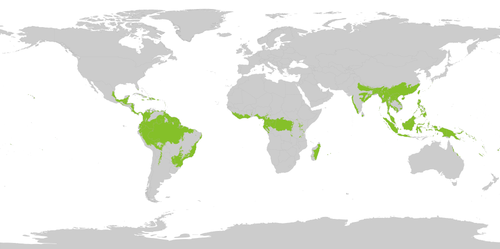
2. State the two main kinds of rainforests and describe how they are different. Diagram on a map locations of these two main kinds of rainforests identifying these types.
- NOTE
- For hands-on Pathfinders, have them mark the average depth of rain on the wall for each kind of forest and then stick their hand in a bowl of water that is 45 degrees and 80 degrees to feel the difference in average temperature of each climate.
Temperate rainforests (Tropical dry forest)
Temperate rainforests receive 55 inches of rain each year with about 6 months of a dryer season. Average temperatures of 39-54F. Leaves often fall off during the dry season. Canopy covers 70 percent of the sky. They are found between polar and equatorial regions.
Tropical rainforest (Tropical wet forest)
Tropical rainforests receive 78 inches or much more rain each year with average temperatures between 77-84F year round. Vertically layered forest because of competition for light in the thick forest. Trees usually do not lose their leaves. Found mostly in the equatorial regions
3. Explain what causes so much rain to fall in rainforest biome areas.
The equator is heated by direct sunlight. As air rises, the water vapor cools and condenses and falls as rain causing the tropical rainforest. This is why tropical rainforests are mostly found along the equator (see the pattern labeled "Hadley cells" in the diagram). The drier air moves north and south of the equator and falls, causing deserts to form. Similar convection currents occur at 60 degrees north and south causing the temperate rain forest. This is why temperate rainforests are mostly found between the poles and the equator (see the pattern labeled "Ferrel cells" in the diagram)
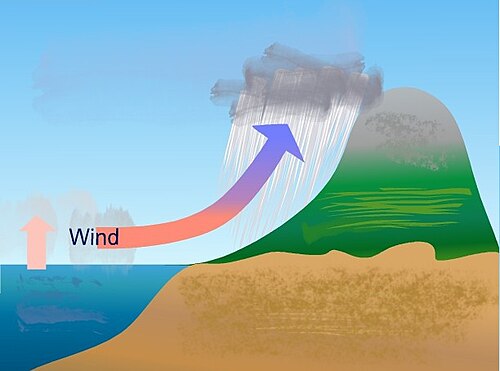
Irregularities in the general pattern described above can be caused by mountains and coastlines. Here, the air cools as it rises, allowing water to condense and fall as rain.
4. Draw a diagram showing the vertical layers of plants in a tropical rainforest. Label them.
5. Describe, draw, or use a hands-on demonstration to show how rainforests regenerate (replace lost or injured living organisms).
6. Be able to identify five birds that live in the tropical rainforest.
7. Be able to identify ten animals that live in the tropical rainforest.
8. List the predominant vegetation in rainforests.
9. What is an epiphyte? Be able to identify from pictures three plant examples.
10. Learn about one invasive species that affects the rainforest.
11. What are some renewable resources that rainforests provide for humans?
12. List at least three ways that rainforests can be protected.
14. Do at least three of the following activities:
a. Visit an exhibit or conservatory of rainforest trees and/or plants.
b. Make a collection of at least three types of epiphytes.
c. Visit a zoo where there are animals typical of the rainforest biome.
Adventist Youth Honors Answer Book/Zoo Visit
d. Watch a video about the rainforest, or plants or animals that live there.
<HTML5video type="youtube" width="400" autoplay="false">beTLIa5EVe4</HTML5video>