Difference between revisions of "AY Honors/Metal Craft/Answer Key"
| Line 59: | Line 59: | ||
===d. Metal file === | ===d. Metal file === | ||
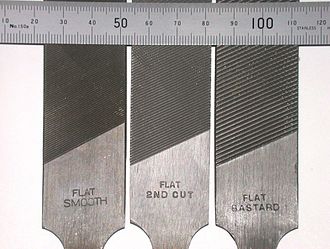
| + | [[Image:FilesFlat-Smooth-2ndCut-Bastard.jpg|thumb|Files with progressively coarser teeth (left toright)]] | ||
| + | [[Image:NeedleFiles.jpg|thumb|left|Needle files]] | ||
| + | Files have forward-facing cutting teeth, and cuts most effectively when pushed over the workpiece. Drawfiling involves laying the file sideways on the work, and carefully pushing or pulling it across the work. This catches the teeth of the file sideways instead of head on, and a very fine shaving action is produced. There are also varying strokes that produce a combination of the straight ahead stroke and the drawfiling stroke, and very fine work can be attained in this fashion. Using a combination of strokes, and progressively finer files, a skilled operator can attain a surface that is perfectly flat and near mirror finish. The grooves in a file may became clogged during use, causing the file to lose its cutting ability and trapped shavings can scratch the work surface. A file card can be used to clean the file. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Files should always be used with a handle, otherwise the naked tang can injure the operator. | ||
| + | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
[[Category:Adventist Youth Honors Answer Book|{{SUBPAGENAME}}]] | [[Category:Adventist Youth Honors Answer Book|{{SUBPAGENAME}}]] | ||
Revision as of 03:41, 1 February 2008
1. Name the various metals that can be used in metal craft.
Metals suitable for use in metal craft include:
- Tin
- Aluminum
- Copper
- Galvanized steel (duct work)
- Brass (an alloy of copper and zinc)
- Bronze (an alloy of copper and tin)
- Silver and gold (especially in foil form)
2. Complete one project using metal foil tooling. Complete the project by antiquing and framing.
Metal foil tooling is done by placing a piece of foil on top of a soft but firm surface and then making impressions with a stylus. The work surface can be a piece of scrap linoleum, leather, or crafting foam. The stylus is often a small wooden stick with a point on it, but you can also use a ballpoint pen or a pencil. A dowel about the same diameter as a pencil can be sharpened with a pencil sharpener to make an effective stylus.
The metal crafter can place a drawing on top of the foil and trace it with the stylus, or draw the design free hand. Once the image has been impressed in the foil, it can be placed in a frame. You can use something as elaborate as a picture frame, or as simple as craft sticks glued together.
Low cost kits are available with all the necessary materials at craft stores, hobby shops, and online retailers.
3. Complete one project using metal punch.
A punch is a hard metal rod with a shaped tip at one end and a blunt butt end at the other that is usually struck by a hammer. A variety of punches are used in engineering, but often the purpose is to form an impression of the tip on a workpiece. You can also use a nail set, a pick, or even a nail (though a nail will make squarish holes) instead of a punch.
Draw out your design on a piece of paper. It should be a simple line drawing with no shading. Then draw dots on the lines indicating where you will punch a hole. Fasten the drawing to a piece of sheet metal with tape. The sheet metal can be copper, tin, or aluminum (such as flashing), all of which are generally available at home improvement centers and hardware stores.
Place a piece of scrap plywood on your work surface to protect it, and then place a piece of scrap linoleum on top of that. Your piece of sheet metal goes on top of the linoleum.
Carefully place the tip of the punch on one of the dots in your drawing and strike the butt end of the punch sharply with a hammer. It should take only one blow. Then move the punch to the next dot and repeat until you have punch a hole (or merely made an indention) on every dot in your drawing. Remove the paper and admire your work.
Punched panels are often used to decorate the doors of a pie safe.
4. Complete one project using drilling, riveting, and bending of metal such as a simple candle holder.
5. Demonstrate properly the use of the following:
a. Tin Snips
Tin snips are tools used to cut thin sheet metal. They use the same principles as common scissors, but are able to handle thicker and harder material. There are three different types of tin snips; straight cutting, left cutting, and right cutting. Straight cutting in a straight line, left cutting snips (usually red) will cut in a curve to the left, and right cutting snips (usually green) will cut in a curve to the right.
In practical use the red snips pictured will be used in the right hand, for straight or curving cuts, with the base material to the right being cut neatly and the left hand will be pulling away a spiraling offcut. The green snips work in the opposite fashion in the left hand, with the waste being on the right.
b. Pop rivet
Pop rivets are made from flared aluminum tubes and a stem (or mandrel) through the center. The stem has a small ball at the end which has a diameter great than that of tube. The rivet assembly is inserted into a hole drilled through the parts to be joined and a specially pop riveting tool is used to draw the mandrel into the rivet. The ball at the end of the mandrel expands the end of the rivet and the mandrel snaps.
The rivet is placed in a pre-drilled hole and is set by pulling the mandrel head into the rivet body, expanding the rivet body and causing it to flare against the reverse side. As the head of the mandrel reaches the face of the blind side material, the pulling force is resisted, and at a predetermined force, the mandrel will snap at the break point of the mandrel.
To set a pop rivet, insert the stem into the nozzle of the riveting tool, then place the rivet's tube into a pre-drilled hole. Position the river such that the flared portion is held firmly against the surface of piece to be riveted, and squeeze the handles together. You should be able to squeeze them until the rivet "pops", or the handles have traveled their full distance. If that happens, release the handle and squeeze again. The tool will grip the stem in a different place. You may need to repeat this a few times until the rivet pops. After it pops, release the handle, and let the stem slide out of the tool's nozzle. A successful rivet joint depends on maintaining contact between the rivet's flared face and the material being riveted.
c. Electric drill
An electric drill is used for boring holes in materials - in the case of metal crafting, that material would be the metal being worked. Typically, one would use a twist bit made of high carbon steel, high speed steel, or cobalt steel for drilling holes in metal. Low carbon steel bits are not suited to drilling holes in metal, as they quickly lose their cutting edges. Drills and bits are typically only used for boring small-diameter holes in metal.
To drill a hole in metal, first use a centering punch to make a small indentation in the metal so the bit does not wander. Then clamp the piece of metal securely to a piece of scrap wood. When the bit penetrates to the other side, it will have a tendency to grab the piece and spin it around at high speed. This can be dangerous, especially if it catches a finger, and thus, it is very wise to clamp it securely so that the piece stays put. Once it is clamped, put on a pair of safety goggles and then place the tip of the bit in the indentation made with the centering punch and hold it perpendicular to the piece (that is, if the piece is perfectly horizontal, the bit will be perfectly vertical). If the bit is not perpendicular (straight in), it will have a greater tendency to wander.
Gently squeeze the trigger on the drill - as more pressure is applied to the trigger, the drill will turn the bit faster and faster. If the bit wanders off the mark, stop and recenter it. If it does it again, get out the center punch and knock a deeper indentation in the piece.
As you squeeze the trigger, gently press downward on the drill, but don't overdo it. If you press too hard, you risk breaking the bit (yes, it happens, and that's why safety goggles are important). Continue to hold the bit perpendicular to the piece. When the bit breaks through the other side of the piece, you need to have the bit rotating at a high speed, and you should not let up for a few seconds. If you stop too soon, the hole will not be circular. It is best to drill part way into the scrap wood supporting the piece, as the side flutes on the bit will cut the sides of the hole, and this will help you make a round hole. With the bit still turning, pull the bit out of the hole (it's easier to do when the bit is rotating).
d. Metal file
Files have forward-facing cutting teeth, and cuts most effectively when pushed over the workpiece. Drawfiling involves laying the file sideways on the work, and carefully pushing or pulling it across the work. This catches the teeth of the file sideways instead of head on, and a very fine shaving action is produced. There are also varying strokes that produce a combination of the straight ahead stroke and the drawfiling stroke, and very fine work can be attained in this fashion. Using a combination of strokes, and progressively finer files, a skilled operator can attain a surface that is perfectly flat and near mirror finish. The grooves in a file may became clogged during use, causing the file to lose its cutting ability and trapped shavings can scratch the work surface. A file card can be used to clean the file.
Files should always be used with a handle, otherwise the naked tang can injure the operator.