Difference between revisions of "AY Honors/Airplane Modeling/Answer Key"
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
Many kits are available for building that will meet this requirement. | Many kits are available for building that will meet this requirement. | ||
| − | === | + | === [http://www.sigmfg.com/ SIG Manufacturing] is a major supplier. === |
To help you navigate, SIG uses the following shorthand on their website. | To help you navigate, SIG uses the following shorthand on their website. | ||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
This model is more challenging to build than the AMA Cub, or Thermal Dart. The wing includes airfoil shape, and diherdral angle for stability. This model would be better suited for either older modellers or modellers with some experience already. A nice rubber band powered free flight model. | This model is more challenging to build than the AMA Cub, or Thermal Dart. The wing includes airfoil shape, and diherdral angle for stability. This model would be better suited for either older modellers or modellers with some experience already. A nice rubber band powered free flight model. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === [http://www.guillow.com/ Guillow's] is also a major supplier. === | ||
| + | |||
| + | Some possible models from Guillow's include: | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== [http://www.guillow.com/kitimages/300/prod_det_4201.jpg Cadet] ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | A simple to build rubber band powered model. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== [http://www.guillow.com/kitimages/300/prod_det_4301.jpg Cloud Buster] ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Similar to the SIG Cub. This model has airfoil wing, and dihedral angle as well. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== [http://www.guillow.com/kitimages/300/prod_det_4401.jpg Fly Boy] ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | This model involves more skill and work with it's built up (3D) fuselage. Still a fairly simple model, this kit will involve a larger time commitment, and a bit more skill. An experienced modeller to help instruct would be an asset for this kit. | ||
== Build a balsa wood glider from a kit and observe its flying characteristics as related to variable positions of the wings. == | == Build a balsa wood glider from a kit and observe its flying characteristics as related to variable positions of the wings. == | ||
| − | === | + | === [http://www.sigmfg.com/ SIG Manufacturing] is a major supplier. === |
See the shorthand help above to navigate their site. | See the shorthand help above to navigate their site. | ||
| − | + | A possible glider model from SIG is: | |
==== [http://www.sigmfg.com/images/yy1SIGFF14.jpg Flip] ==== | ==== [http://www.sigmfg.com/images/yy1SIGFF14.jpg Flip] ==== | ||
| Line 44: | Line 60: | ||
This model is a nice free flight glider kit. It does not technically meet the needs of this requirement since the plans call for the wing to be in a fixed location. This does not allow the modeller to observe its flying characteristics as related to variable positions of the wings. With a bit of spare balsa and some simple modifications, this glider can be built with movable wings. | This model is a nice free flight glider kit. It does not technically meet the needs of this requirement since the plans call for the wing to be in a fixed location. This does not allow the modeller to observe its flying characteristics as related to variable positions of the wings. With a bit of spare balsa and some simple modifications, this glider can be built with movable wings. | ||
| − | + | === [http://www.guillow.com/ Guillow's] is also a major supplier. === | |
| + | |||
| + | Almost all of their toy balsa gliders would qualify for this requirement since they all have the ability to adjust the wings forward or back. Some possible models include: | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== [http://www.guillow.com/kitimages/300/prod_det_26.jpg Eagle] ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Very basic balsa glider. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== [http://www.guillow.com/kitimages/300/prod_det_30.jpg Jetfire] ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Similar to Eagle, with a wider wingspan and dihedral angle. | ||
=== Do It Yourself "Penny Glider" plans. === | === Do It Yourself "Penny Glider" plans. === | ||
| Line 140: | Line 166: | ||
== Make and successfully fly two different styles of airplanes using sheets of paper between eight (20.3 cm) and fourteen (35.6 cm) inches in width and length. == | == Make and successfully fly two different styles of airplanes using sheets of paper between eight (20.3 cm) and fourteen (35.6 cm) inches in width and length. == | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://fatlion.com/science/paperairplanes.html Paper Plane] with airfoil wings is a fun paper airplane to build. It requires more than simply folding a piece of paper up, and can be used to teach the concept of Bernoulli's Principle. | ||
== Define, locate, and explain the usage of the following basic items: == | == Define, locate, and explain the usage of the following basic items: == | ||
| Line 156: | Line 184: | ||
;Fuselage: | ;Fuselage: | ||
| − | |||
The elongated body or frame of an airplane, any kind of frame or body. The central body of an airplane that is designed to accommodate the crew and passengers (or cargo). | The elongated body or frame of an airplane, any kind of frame or body. The central body of an airplane that is designed to accommodate the crew and passengers (or cargo). | ||
;Wing: | ;Wing: | ||
| − | |||
Any surface used primarily for supporting an airplane inflight by forward motion. | Any surface used primarily for supporting an airplane inflight by forward motion. | ||
;Aileron: | ;Aileron: | ||
| − | |||
Ailerons are movable control surfaces that are present on the trailing edge of both the right and left wings of a plane. Each surface moves in opposite directions enabling a plane to roll right or left. For a plane to roll to the left, the left wing aileron moves upwards while the aileron on the right wing moves downwards. | Ailerons are movable control surfaces that are present on the trailing edge of both the right and left wings of a plane. Each surface moves in opposite directions enabling a plane to roll right or left. For a plane to roll to the left, the left wing aileron moves upwards while the aileron on the right wing moves downwards. | ||
;Rudder: | ;Rudder: | ||
| − | |||
This is the term used to describe the part of the tail that moves back and forth. This movement causes the tail of a plane to move which then turns the plane. | This is the term used to describe the part of the tail that moves back and forth. This movement causes the tail of a plane to move which then turns the plane. | ||
;Horizontal stabilizer: | ;Horizontal stabilizer: | ||
| − | |||
The horizontal "mini wing" at the tail section of the airplane. The elevator is attached to the horizontal stabilizer with hinges. | The horizontal "mini wing" at the tail section of the airplane. The elevator is attached to the horizontal stabilizer with hinges. | ||
;Strut: | ;Strut: | ||
| − | |||
A diagnal brace going from the fuselage to the bottom of the wing consisting of a bar or rod used to support the wing on the airplane. | A diagnal brace going from the fuselage to the bottom of the wing consisting of a bar or rod used to support the wing on the airplane. | ||
;Cockpit: | ;Cockpit: | ||
| − | |||
Compartment where the pilot sits while flying the aircraft. | Compartment where the pilot sits while flying the aircraft. | ||
;Engine: | ;Engine: | ||
| − | |||
The source of power to turn the propellor or turbines and generate thrust. Can be an internal cumbustion engine, jet engine, or in the case of an airplane model a rubber band engine. | The source of power to turn the propellor or turbines and generate thrust. Can be an internal cumbustion engine, jet engine, or in the case of an airplane model a rubber band engine. | ||
;Landing gear: | ;Landing gear: | ||
| − | |||
An undercarriage that supports the weight of the plane when it is on the ground. | An undercarriage that supports the weight of the plane when it is on the ground. | ||
;Propeller: | ;Propeller: | ||
| − | |||
The mechanical device attached to the engine that rotates to push against air and create thrust. | The mechanical device attached to the engine that rotates to push against air and create thrust. | ||
; Dihedral: | ; Dihedral: | ||
| − | |||
Dihedral is where the right and left wing tips are higher than the fuselage. More dihedral generally means that a plane will be more stable in the air, but will be more difficult to turn. Most planes require a bit of dihedral to fly well. | Dihedral is where the right and left wing tips are higher than the fuselage. More dihedral generally means that a plane will be more stable in the air, but will be more difficult to turn. Most planes require a bit of dihedral to fly well. | ||
; Elevator: | ; Elevator: | ||
| − | |||
Elevator is the term used to describe a plane's horizontal control surface on the tail. This surface enables a plane to pitch upwards or downwards. When an elevator surface moves upwards, the tail moves downwards (the nose of the plane then points up) and vice-versa. Without an elevator, it is hard to control the altitude of a plane as you can't control the rise and fall of the nose of the plane. | Elevator is the term used to describe a plane's horizontal control surface on the tail. This surface enables a plane to pitch upwards or downwards. When an elevator surface moves upwards, the tail moves downwards (the nose of the plane then points up) and vice-versa. Without an elevator, it is hard to control the altitude of a plane as you can't control the rise and fall of the nose of the plane. | ||
; Thrust: | ; Thrust: | ||
| − | |||
The mechanical force generated by the engine to move the airplane through the air. | The mechanical force generated by the engine to move the airplane through the air. | ||
;Vertical stabilizer: | ;Vertical stabilizer: | ||
| − | |||
The vertical fin which is part of the tail assembly of the airplane. The rudder is attached to the vertical stabilizer with a hinge. | The vertical fin which is part of the tail assembly of the airplane. The rudder is attached to the vertical stabilizer with a hinge. | ||
; V-Tail: | ; V-Tail: | ||
| − | |||
V-Tail aircraft are planes that have only 2 stabilization surfaces (in the shape of a V) instead of a conventional horizontal and vertical stabilizers. In a V-Tail aircraft, the 2 control surfaces of the V-Tail work together to give elevator and rudder responses. | V-Tail aircraft are planes that have only 2 stabilization surfaces (in the shape of a V) instead of a conventional horizontal and vertical stabilizers. In a V-Tail aircraft, the 2 control surfaces of the V-Tail work together to give elevator and rudder responses. | ||
Revision as of 15:39, 7 August 2006
Build and successfully fly an airplane from a kit made of balsa wood and tissue paper, and rubber band or gas powered.
Many kits are available for building that will meet this requirement.
SIG Manufacturing is a major supplier.
To help you navigate, SIG uses the following shorthand on their website.
F/F = Free flight C/L = Control line R/C = Remote control
BIY = Build it yourself ARF = Almost ready to fly RTF = Ready to Fly
Some possible models from SIG include:
AMA Cub
This model has been also called "Delta Dart" and has been sold by SIG for beginner modellers since 1968. Designed by Frank Ehling, these can be built by even younger modellers with little or no experience. Rubber band powered, the wing covering paper is pre-printed with markings to show where to glue the wood pieces. Kit includes everything you need except some glue. Likely the most cost effective model for club purposes as well.
Ask your local hobby shop if they stock this model, or order from SIG.
Thermal Dart
Basically a larger version of the AMA Cub.
SIG Parasol
Easy to build like a cub, this model looks a little more like a scale airplane.
SIG Cub
This model is more challenging to build than the AMA Cub, or Thermal Dart. The wing includes airfoil shape, and diherdral angle for stability. This model would be better suited for either older modellers or modellers with some experience already. A nice rubber band powered free flight model.
Guillow's is also a major supplier.
Some possible models from Guillow's include:
Cadet
A simple to build rubber band powered model.
Cloud Buster
Similar to the SIG Cub. This model has airfoil wing, and dihedral angle as well.
Fly Boy
This model involves more skill and work with it's built up (3D) fuselage. Still a fairly simple model, this kit will involve a larger time commitment, and a bit more skill. An experienced modeller to help instruct would be an asset for this kit.
SIG Manufacturing is a major supplier.
See the shorthand help above to navigate their site.
A possible glider model from SIG is:
Flip
This model is a nice free flight glider kit. It does not technically meet the needs of this requirement since the plans call for the wing to be in a fixed location. This does not allow the modeller to observe its flying characteristics as related to variable positions of the wings. With a bit of spare balsa and some simple modifications, this glider can be built with movable wings.
Guillow's is also a major supplier.
Almost all of their toy balsa gliders would qualify for this requirement since they all have the ability to adjust the wings forward or back. Some possible models include:
Eagle
Very basic balsa glider.
Jetfire
Similar to Eagle, with a wider wingspan and dihedral angle.
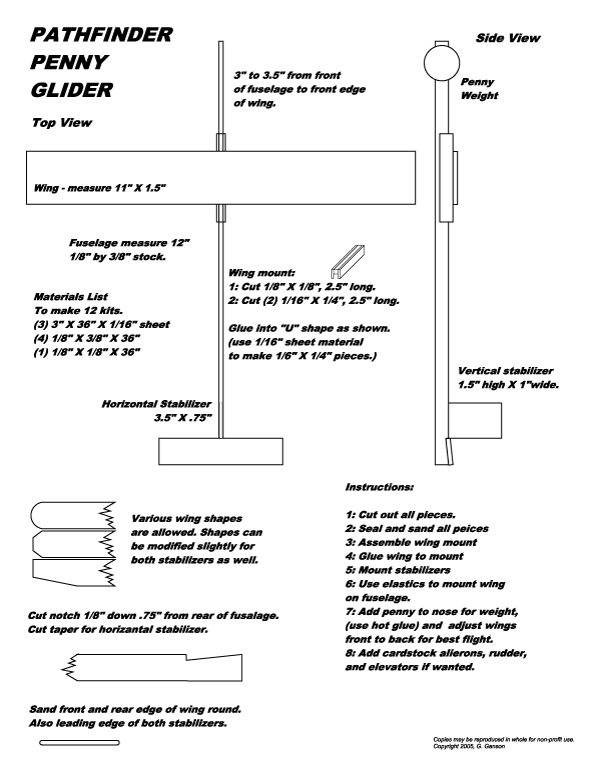
Do It Yourself "Penny Glider" plans.
Due to an ordering mixup with our glider kit supplier, our club was forced to get creative to meet the glider requirement in this Airplane Modeling honor. The end result was that I designed a glider that could be made from stock pieces of balsa. The glider flew well for the students that made them, and the plans made for very cost effective kits. I found the most efficient way to use balsa sheets is to make 12 glider kits. I am publishing the plans here in the hope that other youth groups can make good use of them.
Stock pieces required.
One set of the following pieces will create twelve glider kits.
- (3) 3" X 36" X 1/16" sheet
- (4) 1/8" X 3/8" X 36"
- (1) 1/8" X 1/8" X 36"
Other required supplies.
Wood glue / Hobby knifes
Ruler (Metal is best)
Water based sanding sealer - (I used Varathane Crystal Clear Waterborne thinned 50% with water)
150 grit sandpaper
Pencil / Hobby paint brushes
12 Pennies
Hot glue gun and glue
One copy of plan page printed for each student.
Make the kits in advance
Cut the pieces from the stock to the sizes shown in the plan. Use a hobby knife and steel ruler.
Fuselage - Cut the ⅛” x ⅜” stock into 12” long sections to make 12 fuselages.
Wings - Cut 6 pieces 11” x 1½” from 2 of the 1/16” sheets to make 12 wings.
Wing Mounts - Cut ⅛” x ⅛” stock into 12 - 2½ ” sections.
Wing Mounts – Cut 24 - ¼” x 2½ ” parts for wing mounts from 1/16" sheet balsa.
Horizontal Stabilizer – Cut 12 - 3½” x 3/4” peritoneal stabilizers from 1/16" sheet balsa.
Vertical Stabilizer - Cut 12 - 1½” x 1” vertical stabilizers from 1/16" sheet balsa.
(ensure grain runs the long direction on all 1/16" sheet balsa pieces)
Optionally cut the tapered notches in the fuselage for the horizontal stabilizer, or leave this step for the students depending on level of students ability with hobby knifes.
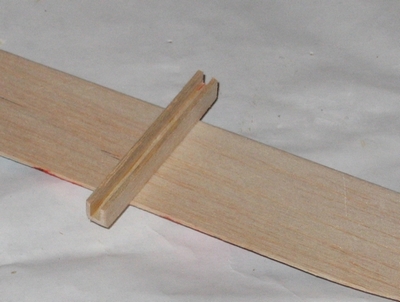
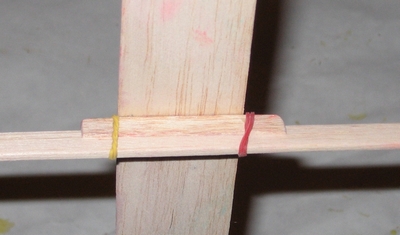
Each kit will contain one wing, one fuselage, one horizontal stabilizer, one vertical stabilizer, and the wing mounting pieces. One single kit is pictured below.
Have the students follow steps 1 through 8 to build the kits.
Instructions:
- Cut out all pieces.
- Seal and sand all peices
- Assemble wing mount
- Glue wing to mount
- Mount stabilizers
- Use elastics to mount wing on fuselage
- Add penny to nose for weight, (use hot glue) and adjust wings front to back for best flight.
- Add cardstock alierons, rudder, and elevators if wanted.
The following pictures are provided for reference.
Wing and wing mount:
Stabilizers glued to fuselage:
Wing mounting with elastic bands:
Finished Glider:
Plan Page.
Make and successfully fly two different styles of airplanes using sheets of paper between eight (20.3 cm) and fourteen (35.6 cm) inches in width and length.
Paper Plane with airfoil wings is a fun paper airplane to build. It requires more than simply folding a piece of paper up, and can be used to teach the concept of Bernoulli's Principle.
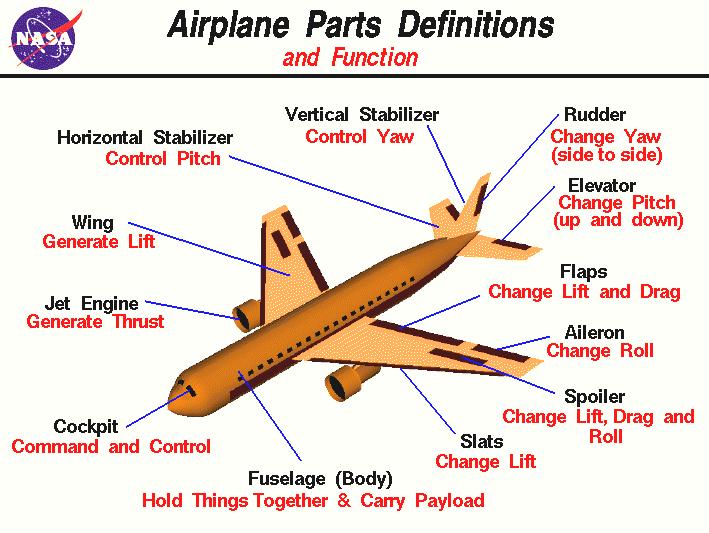
Define, locate, and explain the usage of the following basic items:
- Fuselage
- Wing
- Aileron
- Rudder
- Horizontal stabilizer
- Strut
- Cockpit
- Engine
- Landing Gear
- Propeller
- Fuselage
The elongated body or frame of an airplane, any kind of frame or body. The central body of an airplane that is designed to accommodate the crew and passengers (or cargo).
- Wing
Any surface used primarily for supporting an airplane inflight by forward motion.
- Aileron
Ailerons are movable control surfaces that are present on the trailing edge of both the right and left wings of a plane. Each surface moves in opposite directions enabling a plane to roll right or left. For a plane to roll to the left, the left wing aileron moves upwards while the aileron on the right wing moves downwards.
- Rudder
This is the term used to describe the part of the tail that moves back and forth. This movement causes the tail of a plane to move which then turns the plane.
- Horizontal stabilizer
The horizontal "mini wing" at the tail section of the airplane. The elevator is attached to the horizontal stabilizer with hinges.
- Strut
A diagnal brace going from the fuselage to the bottom of the wing consisting of a bar or rod used to support the wing on the airplane.
- Cockpit
Compartment where the pilot sits while flying the aircraft.
- Engine
The source of power to turn the propellor or turbines and generate thrust. Can be an internal cumbustion engine, jet engine, or in the case of an airplane model a rubber band engine.
- Landing gear
An undercarriage that supports the weight of the plane when it is on the ground.
- Propeller
The mechanical device attached to the engine that rotates to push against air and create thrust.
- Dihedral
Dihedral is where the right and left wing tips are higher than the fuselage. More dihedral generally means that a plane will be more stable in the air, but will be more difficult to turn. Most planes require a bit of dihedral to fly well.
- Elevator
Elevator is the term used to describe a plane's horizontal control surface on the tail. This surface enables a plane to pitch upwards or downwards. When an elevator surface moves upwards, the tail moves downwards (the nose of the plane then points up) and vice-versa. Without an elevator, it is hard to control the altitude of a plane as you can't control the rise and fall of the nose of the plane.
- Thrust
The mechanical force generated by the engine to move the airplane through the air.
- Vertical stabilizer
The vertical fin which is part of the tail assembly of the airplane. The rudder is attached to the vertical stabilizer with a hinge.
- V-Tail
V-Tail aircraft are planes that have only 2 stabilization surfaces (in the shape of a V) instead of a conventional horizontal and vertical stabilizers. In a V-Tail aircraft, the 2 control surfaces of the V-Tail work together to give elevator and rudder responses.