Difference between revisions of "AY Honors/Home Nursing/Answer Key"
(/* 5. What is a communicable disease? How is it transmitted? What precautions should be followed to guard against communicable diseases? List safety measures to be observed when caring for a person wi) |
m (1 revision from w:Infection control) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | '''Infection control and health care epidemiology''' | |
| + | is the discipline concerned with preventing the spread of infections within the health-care setting. | ||
| + | As such, it is a practical (rather than an academic) sub-discipline of [[epidemiology]]. | ||
| + | It is an essential (though often underrecognized and undersupported) part of the infrastructure of health care. | ||
| + | Infection control and hospital epidemiology are akin to [[public health]] practice, practiced within the confines of a particular health-care delivery system rather than directed at society as a whole. | ||
| − | + | Infection control concerns itself both with prevention (hand hygiene/hand washing, cleaning/disinfection/sterilization, vaccination, surveillance) and with investigation and management of demonstrated or suspected spread of infection within a particular health-care setting (e.g. outbreak investigation). It is on this basis that the common title being adopted within health care is '''"Infection Prevention & Control". | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ==Infection control in healthcare facilities== | |
| + | ===Hand hygiene=== | ||
| + | Independent studies by [[Ignaz Semmelweis]] in [[1847]] in [[Vienna]] and [[Oliver Wendell Holmes, Sr.|Oliver Wendell Holmes]] in [[1843]] in [[Boston]] established a link between the hands of health care workers and the spread of [[Nosocomial infection|hospital-acquired]] disease.<ref>[http://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/rr5116a1.htm CDC Guideline for Hand Hygiene in Health-Care Settings]</ref> The [[Centers for Disease Control and Prevention|Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)]] has stated that “It is well-documented that the most important measure for preventing the spread of pathogens is effective handwashing.” <ref>[http://www.cdc.gov/nceh/vsp/cruiselines/hand_hygiene_general.htm CDC General information on Hand Hygiene]</ref> In the United States, [[Hand washing#Medical hand washing|hand washing]] is mandatory in most health care settings and required by many different state and local regulations as well as good sense http://www.safechemdirect.co.uk] | ||
| − | + | In the United States, [[Occupational Safety and Health Administration|Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA)]] standards<ref>[http://www.osha.gov/pls/oshaweb/owadisp.show_document?p_table=STANDARDS&p_id=10051 OSHA Bloodborne Pathogens Regulations 1910.1030]</ref> require that employers must provide readily accessible hand washing facilities, and must ensure that employees wash hands and any other skin with soap and water or flush mucous membranes with water as soon as feasible after contact with blood or other potentially infectious materials (OPIM). | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | ===Cleaning, disinfection and sterilization=== | ||
| − | + | Cleaning, [[disinfection]] and [[sterilization (microbiology)|sterilization]]... | |
| − | + | {{Expand-section|date=June 2008}} | |
| − | + | Sterilization is a process intended to kill all microorganisms and is the highest level of microbial kill that is possible. Sterilizers may be heat only, steam, or liquid chemical. <ref> (Miller, Chris H.. Infection Control and Management of Hazardous Materials for the Dental Team, 3rd Edition. Mosby Elsevier Health Science, 2005. chpt 11).</ref> | |
| − | + | Effectivenss of the sterilizer (oftern called an autoclave") is determined in three ways. <ref> (Miller, Chris H.. Infection Control and Management of Hazardous Materials for the Dental Team, 3rd Edition. Mosby Elsevier Health Science, 2005. chpt 11).</ref> | |
| − | + | First by the mechanical indicators and gauges on the machine itself, second the heat sensitive inicators or tape on the sterilzing bag turn color, and thirdly and most importantly is the biological test. With the biological test, a highly heat and chemical resistant microorganism (often the bacterial endospore) is selected as the standard challenge. If the process kills this microorganism, the sterilizer is considered to be effective. It should be noted that in order to be effective, instruments must be cleaned, otherwise the debris may form a protective barrier, shielding the microbes from the lethal process. Similarly care must be taken after sterilization to ensure sterile instruments do not become contaminated prior to use.<ref> (Miller, Chris H.. Infection Control and Management of Hazardous Materials for the Dental Team, 3rd Edition. Mosby Elsevier Health Science, 2005. chpt 11).</ref> | |
| − | + | Disinfection refers to the use of liquid chemicals on surfaces and at room temperature to kill disease causing microorganisms. Disinfection is a less effective process than sterilization because it does not kill bacterial endospores. <ref> (Miller, Chris H.. Infection Control and Management of Hazardous Materials for the Dental Team, 3rd Edition. Mosby Elsevier Health Science, 2005. chpt 11).</ref> | |
| − | |||
| − | + | ===Personal protective equipment=== | |
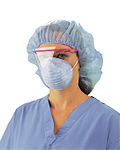
| − | + | [[Image:Disp-med-ppe.jpg|thumb|120px|Disposable PPE]] | |
| − | + | [[Personal protective equipment|Personal protective equipment (PPE)]] is specialized clothing or equipment worn by a worker for protection against a hazard. The hazard in a health care setting is exposure to blood, saliva, or other bodily fluids or aerosols that may carry infectious materials such as [[Hepatitis C]], [[HIV]], or other blood borne or bodily fluid [[pathogen]]. PPE prevents contact with a potentially infectious material by creating a physical barrier between the potential infectious material and the healthcare worker. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | In the United States, the [[Occupational Safety and Health Administration|Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA)]] requires the use of [[Personal protective equipment|Personal protective equipment (PPE)]] by workers to guard against blood borne pathogens if there is a reasonably anticipated exposure to blood or other potentially infectious materials. <ref>[http://www.osha.gov/pls/oshaweb/owadisp.show_document?p_table=STANDARDS&p_id=10051#1910.1030(d)(2)(i) OSHA Bloodborne Pathogens Regulations 1910.1030(d)(2)(i)]</ref> | |
| − | + | Components of [[Personal protective equipment|Personal protective equipment (PPE)]] include [[Medical gloves|gloves]], [[Hospital gown|gowns]], bonnets, shoe covers, [[face shield]]s, [[CPR mask]]s, [[goggles]], [[surgical mask]]s, and respirators. How many components are used and how the components are used is often determined by regulations or the infection control protocol of the facility in question. Many or most of these items are [[disposable]] to avoid carrying infectious materials from one patient to another patient and to avoid difficult or costly [[disinfection]]. In the United States, [[Occupational Safety and Health Administration|OSHA]] requires the immediate removal and disinfection or disposal of worker's PPE prior to leaving the work area where exposure to infectious material took place.<ref>[http://www.osha.gov/pls/oshaweb/owadisp.show_document?p_table=STANDARDS&p_id=10051#1910.1030(d)(3)(vii) OSHA 1910.1030(d)(3)(vii)]</ref> | |
| − | + | ===Vaccination of health care workers=== | |
| + | Health care workers may be exposed to certain infections in the course of their work. [[Vaccine]]s are available to provide some protection to workers in a healthcare setting. Depending on regulation, recommendation, the specific work function, or personal preference, healthcare workers or first responders may receive vaccinations for [[Hepatitis B#Prevention|hepatitis B]]; [[Influenza vaccine| influenza]]; [[MMR vaccine|measles, mumps and rubella]]; [[TDaP|Tetanus, diphtheria, pertussis]]; [[Neisseria meningitidis#Vaccines|N. meningitidis]]; and [[Varicella vaccine|varicella]]. In general, [[vaccine]]s do not guarantee complete protection from disease, and there is [[Vaccine#Potential for adverse side effects in general|potential]] for adverse effects from receiving the vaccine. <ref>[http://www.cdc.gov/node.do/id/0900f3ec8005df1f CDC Vaccine Site]</ref> | ||
| − | + | ===Post exposure prophylaxis=== | |
| + | In some cases where vaccines do not exist Post Exposure prophylaxis is another method of protecting the health care worker exposed to a life threatening infectious disease. For example, the viral particles for HIV-AIDS can be precipited out of the blood through the use of an antibody injection if given within 4 hours of a significant exposure. | ||
| − | + | ===Surveillance for emerging infections=== | |
| + | Surveillance is the act of infection investigation using the CDC definitions. Determining an infection requires an ICP to review a patient's chart and see if the patient had the signs and symptom of an infection. Surveillance definition cover infections of the bloodstream, Urinary tract, pneumonia, and sugical sites. | ||
| − | + | Surveillance traditionally involved significant manual data assessment and entry in order to assess preventative actions such as isolation of patients with an infectious disease. Increasingly, integrated computerised software solutions are becoming available, such as [http://www.rl-solutions.com/infection-control/infection-monitorpro.html Infection Monitor Pro]. Such products actively assess incoming risk messages from microbiology and other online sources. By reducing the need for data entry, this software significantly reduces the data workload of Infection Control Practitioners (ICP), freeing them to concentrate on clinical surveillance. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | As approximately [http://www.cdc.gov/ncidod/eid/vol4no3/weinstein.htm one third of healthcare acquired infections are preventable] , surveillance and preventative activities are increasingly a priority for hospital staff. In the United States, a study on the Efficacy of Nosocomial Infection Control Project (SENIC) by the CDC found that hospitals reduced their nosocomial infection rates by approximately 32 per cent by focusing on surveillance activities and prevention efforts. | |
| − | + | ==Outbreak investigation== | |
| + | When an unusual cluster of illness is noted, infection control teams undertake an investigation to determine whether there is a true outbreak, a pseudo-outbreak (a result of contamination within the diagnostic testing process), or just random fluctuation in the frequency of illness. If a true outbreak is discovered, infection control practitioners try to determine what permitted the outbreak to occur, and to rearrange the conditions to prevent ongoing propagation of the infection. Often, breaches in good practice are responsible, although sometimes other factors (such as construction) may be the source of the problem. | ||
| − | + | ==Training in infection control and health care epidemiology== | |
| + | Practitioners can come from several different educational streams. Many begin as nurses, some as medical technologists (particularly in clinical microbiology), and some as physicians (typically infectious disease specialists). Specialized training in infection control and health care epidemiology are offered by the professional organizations described below. Physicians who desire to become infection control practitioners often are trained in the context of an infectious disease fellowship. | ||
| − | + | In the United States, [http://www.cbic.org Certification Board of Infection Control and Epidemiology] is a private company that certifies infection control practitioners based on their educational background and professional experience, in conjunction with testing their knowledge base with standardized exams. The credential awarded is CIC, Certification in Infection Control and Epidemiology. One must have 2 years of Infection Control experience in order to sit for the boards. Certification must be renewed every five years. | |
| − | + | A [http://www.shea-online.org/about/shea_courses.cfm course] in hospital epidemiology (infection control in the hospital setting) is offered jointly each year by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | http://www.apic.org/ offers a training course for practitioners called EPI 101 and 102. | |
| − | + | == Footnotes == | |
| + | {{reflist}} | ||
| − | + | == See also == | |
| − | == | + | * [[Infectious disease]] |
| − | + | * [[body substance isolation]] | |
| + | * [[Nosocomial infection]] | ||
| + | * [[Public health]] | ||
| − | + | ==External links== | |
| − | + | * [http://www.apic.org Association for Professionals in Infection Control and Epidemiology] is primarily composed of infection prevention and control professionals with nursing or medical technology backgrounds | |
| − | + | * [http://shea-online.org The Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America] is more heavily weighted towards practitioners who are physicians or doctoral-level epidemiologists. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[Category:Epidemiology]] | |
| − | + | [[ja:感染管理]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | [[ | ||
Revision as of 03:42, 30 July 2008
Infection control and health care epidemiology is the discipline concerned with preventing the spread of infections within the health-care setting. As such, it is a practical (rather than an academic) sub-discipline of epidemiology. It is an essential (though often underrecognized and undersupported) part of the infrastructure of health care. Infection control and hospital epidemiology are akin to public health practice, practiced within the confines of a particular health-care delivery system rather than directed at society as a whole.
Infection control concerns itself both with prevention (hand hygiene/hand washing, cleaning/disinfection/sterilization, vaccination, surveillance) and with investigation and management of demonstrated or suspected spread of infection within a particular health-care setting (e.g. outbreak investigation). It is on this basis that the common title being adopted within health care is "Infection Prevention & Control".
Infection control in healthcare facilities
Hand hygiene
Independent studies by Ignaz Semmelweis in 1847 in Vienna and Oliver Wendell Holmes in 1843 in Boston established a link between the hands of health care workers and the spread of hospital-acquired disease.& The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has stated that “It is well-documented that the most important measure for preventing the spread of pathogens is effective handwashing.” & In the United States, hand washing is mandatory in most health care settings and required by many different state and local regulations as well as good sense http://www.safechemdirect.co.uk]
In the United States, Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) standards& require that employers must provide readily accessible hand washing facilities, and must ensure that employees wash hands and any other skin with soap and water or flush mucous membranes with water as soon as feasible after contact with blood or other potentially infectious materials (OPIM).
Cleaning, disinfection and sterilization
Cleaning, disinfection and sterilization... Template:Expand-section
Sterilization is a process intended to kill all microorganisms and is the highest level of microbial kill that is possible. Sterilizers may be heat only, steam, or liquid chemical. & Effectivenss of the sterilizer (oftern called an autoclave") is determined in three ways. & First by the mechanical indicators and gauges on the machine itself, second the heat sensitive inicators or tape on the sterilzing bag turn color, and thirdly and most importantly is the biological test. With the biological test, a highly heat and chemical resistant microorganism (often the bacterial endospore) is selected as the standard challenge. If the process kills this microorganism, the sterilizer is considered to be effective. It should be noted that in order to be effective, instruments must be cleaned, otherwise the debris may form a protective barrier, shielding the microbes from the lethal process. Similarly care must be taken after sterilization to ensure sterile instruments do not become contaminated prior to use.&
Disinfection refers to the use of liquid chemicals on surfaces and at room temperature to kill disease causing microorganisms. Disinfection is a less effective process than sterilization because it does not kill bacterial endospores. &
Personal protective equipment
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is specialized clothing or equipment worn by a worker for protection against a hazard. The hazard in a health care setting is exposure to blood, saliva, or other bodily fluids or aerosols that may carry infectious materials such as Hepatitis C, HIV, or other blood borne or bodily fluid pathogen. PPE prevents contact with a potentially infectious material by creating a physical barrier between the potential infectious material and the healthcare worker.
In the United States, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) requires the use of Personal protective equipment (PPE) by workers to guard against blood borne pathogens if there is a reasonably anticipated exposure to blood or other potentially infectious materials. &
Components of Personal protective equipment (PPE) include gloves, gowns, bonnets, shoe covers, face shields, CPR masks, goggles, surgical masks, and respirators. How many components are used and how the components are used is often determined by regulations or the infection control protocol of the facility in question. Many or most of these items are disposable to avoid carrying infectious materials from one patient to another patient and to avoid difficult or costly disinfection. In the United States, OSHA requires the immediate removal and disinfection or disposal of worker's PPE prior to leaving the work area where exposure to infectious material took place.&
Vaccination of health care workers
Health care workers may be exposed to certain infections in the course of their work. Vaccines are available to provide some protection to workers in a healthcare setting. Depending on regulation, recommendation, the specific work function, or personal preference, healthcare workers or first responders may receive vaccinations for hepatitis B; influenza; measles, mumps and rubella; Tetanus, diphtheria, pertussis; N. meningitidis; and varicella. In general, vaccines do not guarantee complete protection from disease, and there is potential for adverse effects from receiving the vaccine. &
Post exposure prophylaxis
In some cases where vaccines do not exist Post Exposure prophylaxis is another method of protecting the health care worker exposed to a life threatening infectious disease. For example, the viral particles for HIV-AIDS can be precipited out of the blood through the use of an antibody injection if given within 4 hours of a significant exposure.
Surveillance for emerging infections
Surveillance is the act of infection investigation using the CDC definitions. Determining an infection requires an ICP to review a patient's chart and see if the patient had the signs and symptom of an infection. Surveillance definition cover infections of the bloodstream, Urinary tract, pneumonia, and sugical sites.
Surveillance traditionally involved significant manual data assessment and entry in order to assess preventative actions such as isolation of patients with an infectious disease. Increasingly, integrated computerised software solutions are becoming available, such as Infection Monitor Pro. Such products actively assess incoming risk messages from microbiology and other online sources. By reducing the need for data entry, this software significantly reduces the data workload of Infection Control Practitioners (ICP), freeing them to concentrate on clinical surveillance.
As approximately one third of healthcare acquired infections are preventable , surveillance and preventative activities are increasingly a priority for hospital staff. In the United States, a study on the Efficacy of Nosocomial Infection Control Project (SENIC) by the CDC found that hospitals reduced their nosocomial infection rates by approximately 32 per cent by focusing on surveillance activities and prevention efforts.
Outbreak investigation
When an unusual cluster of illness is noted, infection control teams undertake an investigation to determine whether there is a true outbreak, a pseudo-outbreak (a result of contamination within the diagnostic testing process), or just random fluctuation in the frequency of illness. If a true outbreak is discovered, infection control practitioners try to determine what permitted the outbreak to occur, and to rearrange the conditions to prevent ongoing propagation of the infection. Often, breaches in good practice are responsible, although sometimes other factors (such as construction) may be the source of the problem.
Training in infection control and health care epidemiology
Practitioners can come from several different educational streams. Many begin as nurses, some as medical technologists (particularly in clinical microbiology), and some as physicians (typically infectious disease specialists). Specialized training in infection control and health care epidemiology are offered by the professional organizations described below. Physicians who desire to become infection control practitioners often are trained in the context of an infectious disease fellowship.
In the United States, Certification Board of Infection Control and Epidemiology is a private company that certifies infection control practitioners based on their educational background and professional experience, in conjunction with testing their knowledge base with standardized exams. The credential awarded is CIC, Certification in Infection Control and Epidemiology. One must have 2 years of Infection Control experience in order to sit for the boards. Certification must be renewed every five years.
A course in hospital epidemiology (infection control in the hospital setting) is offered jointly each year by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America.
http://www.apic.org/ offers a training course for practitioners called EPI 101 and 102.
Footnotes
- ↑ CDC Guideline for Hand Hygiene in Health-Care Settings
- ↑ CDC General information on Hand Hygiene
- ↑ OSHA Bloodborne Pathogens Regulations 1910.1030
- ↑ (Miller, Chris H.. Infection Control and Management of Hazardous Materials for the Dental Team, 3rd Edition. Mosby Elsevier Health Science, 2005. chpt 11).
- ↑ (Miller, Chris H.. Infection Control and Management of Hazardous Materials for the Dental Team, 3rd Edition. Mosby Elsevier Health Science, 2005. chpt 11).
- ↑ (Miller, Chris H.. Infection Control and Management of Hazardous Materials for the Dental Team, 3rd Edition. Mosby Elsevier Health Science, 2005. chpt 11).
- ↑ (Miller, Chris H.. Infection Control and Management of Hazardous Materials for the Dental Team, 3rd Edition. Mosby Elsevier Health Science, 2005. chpt 11).
- ↑ OSHA Bloodborne Pathogens Regulations 1910.1030(d)(2)(i)
- ↑ OSHA 1910.1030(d)(3)(vii)
- ↑ CDC Vaccine Site
See also
External links
- Association for Professionals in Infection Control and Epidemiology is primarily composed of infection prevention and control professionals with nursing or medical technology backgrounds
- The Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America is more heavily weighted towards practitioners who are physicians or doctoral-level epidemiologists.