Difference between revisions of "AY Honors/Sharks/Answer Key"
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
==3. Identify from pictures or personal observation 10 species of sharks.== | ==3. Identify from pictures or personal observation 10 species of sharks.== | ||
{{:Adventist Youth Honors Answer Book/Species Account/Sphyrna mokarran}} | {{:Adventist Youth Honors Answer Book/Species Account/Sphyrna mokarran}} | ||
| + | |||
{{:Adventist Youth Honors Answer Book/Species Account/Negaprion brevirostris}} | {{:Adventist Youth Honors Answer Book/Species Account/Negaprion brevirostris}} | ||
| + | |||
{{:Adventist Youth Honors Answer Book/Species Account/Isurus oxyrinchus}} | {{:Adventist Youth Honors Answer Book/Species Account/Isurus oxyrinchus}} | ||
| + | |||
{{:Adventist Youth Honors Answer Book/Species Account/Carcharhinus limbatus}} | {{:Adventist Youth Honors Answer Book/Species Account/Carcharhinus limbatus}} | ||
| + | |||
{{:Adventist Youth Honors Answer Book/Species Account/Carcharhinus brachyurus}} | {{:Adventist Youth Honors Answer Book/Species Account/Carcharhinus brachyurus}} | ||
| + | |||
{{:Adventist Youth Honors Answer Book/Species Account/Carcharhinus longimanus}} | {{:Adventist Youth Honors Answer Book/Species Account/Carcharhinus longimanus}} | ||
| + | |||
{{:Adventist Youth Honors Answer Book/Species Account/Carcharhinus leucas}} | {{:Adventist Youth Honors Answer Book/Species Account/Carcharhinus leucas}} | ||
| + | |||
{{:Adventist Youth Honors Answer Book/Species Account/Carcharodon carcharias}} | {{:Adventist Youth Honors Answer Book/Species Account/Carcharodon carcharias}} | ||
| + | |||
{{:Adventist Youth Honors Answer Book/Species Account/Prionace glauca}} | {{:Adventist Youth Honors Answer Book/Species Account/Prionace glauca}} | ||
| + | |||
{{:Adventist Youth Honors Answer Book/Species Account/Galeocerdo cuvier}} | {{:Adventist Youth Honors Answer Book/Species Account/Galeocerdo cuvier}} | ||
Revision as of 01:42, 14 April 2013
Template:AY patch unavailable Template:Honor header
1. On what day of Creation Week were sharks created?
Sharks were created on the fifth day:
Then God said, “Let the waters swarm with fish and other life. Let the skies be filled with birds of every kind.” So God created great sea creatures and every living thing that scurries and swarms in the water, and every sort of bird—each producing offspring of the same kind. And God saw that it was good. Then God blessed them, saying, “Be fruitful and multiply. Let the fish fill the seas, and let the birds multiply on the earth.” And evening passed and morning came, marking the fifth day.
2. What is the study of sharks called?
The study of the subclass of cartilaginous fish including sharks, rays, and skates is called Elasmobranchology. These fish are collectively called the elasmobranchii.
3. Identify from pictures or personal observation 10 species of sharks.
Adventist Youth Honors Answer Book/Species Account/Sphyrna mokarran
Adventist Youth Honors Answer Book/Species Account/Negaprion brevirostris
Adventist Youth Honors Answer Book/Species Account/Isurus oxyrinchus
Adventist Youth Honors Answer Book/Species Account/Carcharhinus limbatus
Adventist Youth Honors Answer Book/Species Account/Carcharhinus brachyurus
Adventist Youth Honors Answer Book/Species Account/Carcharhinus longimanus
Adventist Youth Honors Answer Book/Species Account/Carcharhinus leucas
Adventist Youth Honors Answer Book/Species Account/Carcharodon carcharias
Adventist Youth Honors Answer Book/Species Account/Prionace glauca
Adventist Youth Honors Answer Book/Species Account/Galeocerdo cuvier
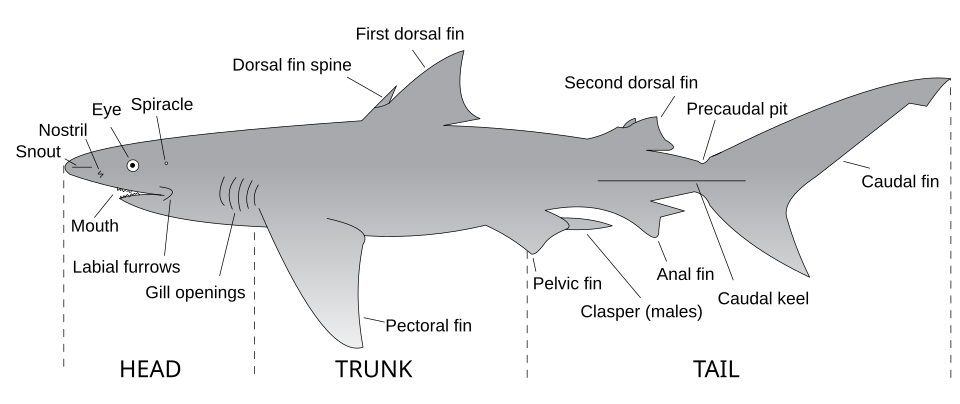
4. Draw a shark and identify the following shark parts:
- a. 1st Dorsal fin
- b. 2nd Dorsal fin
- c. Pectoral fin
- d. Pelvic fin
- e. Anal fin
- f. Caudal fin
- g. Gill openings
- h. Spine
- i. Eye
- j. Snout
- k. Nostril
- l. Mouth
5. Explain the shark sensory system: Smell, Sight, Taste, Hearing, Touch, Electroreception
Smell, sight, taste, hearing, touch, and electroreception are the six sensory systems sharks are equipped with allowing them to successfully exploit the environment they live in by locating prey, avoiding danger and finding a mate.
Smell
Sharks possess a pair of nostrils (also referred to as nares), just under the edge of their snout. The nares are completely separate from the mouth and throat and do not aid in respiration. Instead they are used purely for olfaction. Each nare is divided into two channels by a nasal flap. The water enters one channel (incurrent aperture) and passes over an area called the olfactory lamellae which contain neuro-sensory cells. These then send chemosensory information via the olfactory bulb to the large olfactory lobe in the shark's forebrain. The olfactory lamellae are a series of folds on the surface of the olfactory sac; these folds increase the surface area and provide the shark with a greater opportunity of detecting smells. After passing through the olfactory sac the water is then channeled out through the recurrent aperture.
If the shark detects a smell which it wants to investigate (odor from prey or pheromones from a potential mate), it will swim in the direction of the scent moving its head back and forth (similar to its natural swimming motion), this motion will allow it to detect the direction of the smell by following the most concentrated signal. These movements can become exaggerated into larger “S” shapes if the shark loses the signal or if the signal is too wide to use for accurate navigation.
Sight
In the majority of shark species, the eyes are well developed, complex structures containing rod (highly sensitive to light intensity) and in some species cone cells (may allow sharks to see in color). They can control the amount of light entering the eye by dilating or contracting their pupils. Focusing is controlled by the rectus muscles which pull the lens closer to or further away from the retina. When used in conjunction with the oblique muscles, movement of the entire eye is achieved.
Most sharks have excellent vision in dim light conditions; this is due to the retina containing millions of rod cells together with a structure called the tapetum lucidum. This is a layer found behind the retina which reflects light back onto the retina, amplifying the image. Pigmented cells cover the tapetum reducing reflections and protecting the retina in bright light.
Sharks have an upper and lower eyelid but these usually do not meet and therefore do not provide a full cover for the eye. Some sharks, such as the tiger shark, have a “third eyelid” known as the nictitating membrane. This rolls up from the base of the eye to completely cover the eyeball. The use of this nicitating membrane is demonstrated regularly in shark documentaries, and most notably when the shark is attacking its prey. Species like the white shark which do not have the nicitating membrane often employ a different strategy to safeguard the eye; they roll the eye into the back of the socket exposing a hardened pad at the rear of the eyeball. The existence of such strategies designed to protect the eye, highlight the importance of sight as a sensory function to the shark.
Some sharks, such as the blue shark, have a light sensitive “third eye”. Indicated by a lighter colored spot called the pineal window on the top of the sharks head directly above the pineal gland. Athough speculative, it is suggested that the shark may use this to aid navigation.
Taste
As a shark bites into an object (prey or otherwise), chemicals are released and attach themselves to gustatory sensory cells present in the shark's mouth and throat. These gustatory cells then send messages to structures (the thalamus and the hypothalamus) located in the shark's forebrain. The shark will then either accept or reject the object it has bitten.
Hearing
The shark ear is located in the frontal skull (chrondocranium) and is completely internal with only a tiny opening on the shark's head - not the spiracle which is involved in respiration. The ear detects sound with frequencies ranging from <20 to about 800 Hertz (humans detect sound between 20 and 20,000 Hertz). Most sharks show an attraction to infrasound (<20Hz). This is most likely due to the low frequency sounds emitted by struggling prey. The shark ear is also used for balance and orientation (by utilizing the fluid-filled semi-circular canals, with the movement of the fluid activating sensory hair cells) and pressure detection (by direct activation of the hair cells within the canals allowing sensory signals to be relayed to the brain via the auditory nerve).
Touch
A shark can feel a certain amount of direct contact due to free nerve endings embedded in the skin, mouth, jaws and even teeth. They can also sense things internally due to the presence of proprioceptors (microscopic sensory cells) found throughout the muscles, joints, digestive system and blood vessels. Sharks have a heightened sense of indirect touch via water displacement around the shark's body. This is accomplished by the movement of sensory hair cells which are present in the neuromasts that make up the lateral line system. This system is comprised of a series of canals or channels usually visible to the naked eye as a series of pores or lines, these run from the head all the way to the upper lobe of the tail.
Electroreception
The Ampullae of Lorenzini are specialized pores consisting of a small chamber (the ampulla) and a sub-dermal canal which projects outward to the surface of the skin. The ampulla contains hundreds of sensory hair cells. The wall of the canal contains a double layer of connective tissue fibers and epithelial cells, which are tightly joined together to form a high electrical resistance between the inner and outer wall of the canal. The canal and ampulla themselves are filled with a high potassium, low resistance gel that forms an electrical core conductor with a resistance equaling that of seawater.
Fish carry an electrical charge different to that of seawater and so a weak voltage is created (by the movement of positive and negative particles moving back and forth shifting electrons in an attempt to become stable). Because the salt in the water contains both sodium and chlorine ions which can move freely in the water the electricity itself is transported, and this is what the ampullae of lorenzini is able to detect.
6. Name the largest member of the shark family and its maximum adult size.
The Whale Shark grows from 41 to 46 feet (12.5 to 14 meters) long.
7. Name the most aggressive member of the shark family.
The great white shark is arguably the world's largest known extant macropredatory fish, and is one of the primary predators of marine mammals. It is also known to prey upon a variety of other marine animals, including fish and seabirds. It is ranked first in having the most attacks on humans.
8. Name the predators of the Great White Shark.
The Great white sharks are apex predators, which means they sit at the very top of the food chain. They patrol the ocean and regulate a healthy marine ecosystem. A great white shark's only predators are:
- Humans
- Other Great White Sharks
- Orca Whales
9. Explain the shark breeding habits.
Biologists have tagged and release thousands of sharks to determine their breeding habits. Their findings reveal that most non migrating shark species return to the same shallow breading grounds every year. After they reach maturity (10 to 14 years) they return to their birth grounds to select a mate. After a ten to twelve months gestation period, a female shark can have a litter of up to eighteen little sharks. After their birth, most species abandon their young and they are left to fend for themselves. The young sharks remain in the shallow waters for two or three years, until they are large enough to defend themselves from bigger predators. Then they head out into the open seas, and the cycle begins again.
10. How do sharks give birth?
Different species of shark give birth in different ways. Some lay eggs, some hatch eggs inside the mother, and others give birth to live young.
11. Discuss with a group the following
a. How to be safe when you are in a shark's natural environment
b. Misconceptions of sharks
c. Dangers of sharks
12. Do two of the following activities:
a. Take a trip to a local aquarium and learn about the shark daily feeding schedule and habits.
Look for your local aquarium on the net and make sure they have sharks. This option will almost certainly be the most rewarding for your Pathfinders, but it will also require the most work on your part to get it organized. Try to contact the aquarium before setting off on your trip so that you can make arrangements to meet with a staff member there. They are usually very willing to help you, and will be delighted to provide you with information regarding the daily feeding schedule. Note that some zoos have aquariums too, so if a zoo is more convenient than an aquarium, you might want to investigate this possibility.
These honors also have aquarium visits in the requirements, so consider tackling several honors together:
b. Watch a documentary about sharks and identify how sharks hurt and benefit humans.
Watching shark documentaries is tons of fun! Here are several to get to started.
Inside Nature's Giants - Great White Shark [Full Documentary]
National Geographic HD Alaskan Killer Shark
c. Visit a natural history museum and observe how sharks are displayed within their ecosystem.
Look for the nearest Natural History Museum on the internet.