Difference between revisions of "AY Honors/Seeds/Answer Key"
(Marked this version for translation) |
(move IAConnection to Overview page) |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
|insignia=Seeds_Honor.png | |insignia=Seeds_Honor.png | ||
}}<!--{{Honor_Master|honor=Seeds|master=Naturalist|group=Flora}}--> | }}<!--{{Honor_Master|honor=Seeds|master=Naturalist|group=Flora}}--> | ||
| − | |||
<!--T:34--> | <!--T:34--> | ||
Revision as of 02:47, 28 February 2021
1
The main purpose of a seed is to grow a new plant, thus propagating the species.
2
Then God said, "I give you every seed-bearing plant on the face of the whole earth and every tree that has fruit with seed in it. They will be yours for food. Genesis 1:29
3
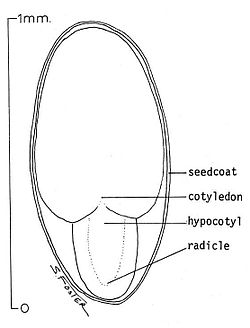
- Seed Coat - The seed coat is the covering which encloses the seed (small embryonic plant, usually with some stored food).
- Cotyledon - This is a significant part of the embryo within the seed of a plant. Upon germination, the cotyledon becomes the embryonic first leaves of a seedling.
- Embryo - A seed embryo includes the cotyledon which becomes the plant's first leaves, the epicotyl (not shown), which becomes the shoot above the leaves, the hypocotyl which becomes the plant's stem, and the radicle which becomes the plant's root.
4
Gravity
The effect of gravity on the dispersal of seeds and spores is straightforward. Heavier seeds will tend to drop downward from the parent plant, and not by themselves travel very far. Spores, being much lighter, are more influenced by physical movements in the environment, especially those of wind and water, and therefore less strictly subject to the simple motion of gravity (see examples below). Gravity may be sufficient agent for plants growing on steep slopes, but upslope movement of a population can be a problem. The naked seeds of gymnosperms are largely dependent upon gravity for dispersal. Most conifers are long-lived large shrubs or tall trees, thus taking full advantage of gravitational dispersal and allowing for gradual upslope movement of a population. Dispersal of seeds "strictly" by gravity should not overlook storm effects: seeds from a deteriorating cone growing high on a tall, narrow tree will get spread widely during a wind storm (see "Wind" below).
Encasing seeds in a rounded fruit promotes gravity driven movement away from the parent.
- Pine trees
- Spruce trees
- Fir trees
- Junipers
- Cedars
- Hemlocks
Mechanical dispersal
Numerous species have mechanical means to overcome the tendency of a seed to drop close to its parent. Seedpods are often shaped so that the seeds are flung away from the parent plant with considerable force as the seedpod matures
Examples of fruit with mechanical dispersal mechanisms:
- Yellow wood sorrel and Touch-me-not – as the seed dries, becomes sensitive to disturbance, ejecting tiny seeds in an explosive discharge. Touch-me-not is named for this behavior.
- Maple trees - the seeds of the Maple tree are those little "helicopters" that children love to play with. As the seeds falls, the wings cause it to rotate, slowing its descent, and thus allowing a breeze to carry it farther from the parent. When the seed strikes the ground, it bores into the soil.
Wind
For non-aquatic, terrestrial plants, the wind is an obvious supplier of energy for movement, and many plants clearly take advantage of this fact. This type of seed dispersal is not efficient, but very effective. Perhaps most familiar are the feather-light fiber parachutes with attached achenes that are produced by a number of species of flowers, a well-known example being the dandelion (see right).
- Milkweed
- Thistles
- Dandelions
Water
Plants that grow in water (aquatic and obligate wetland species) are likely to utilize water to disperse their seeds. For example, all mangroves disperse their offspring by water. In one mechanism, the seedling separates from the fruit, leaving its cotyledons behind, and—floating horizontally on the water surface—is carried away by tidal or river flow. After a month or two, the propagated seed turns vertical in the water. Once it "feels" bottom or strands, roots start to develop and leaves appear at the upper end.
A mechanism commonly seen in coastal plants are those that promote flotation of the fruit, allowing the seed to be carried away on the tide or ocean currents. Examples would be:
- The coconut produces a large, dry, fiber-filled fruit capable of a long survival adrift at sea.
- Alexandrian laurel or kamani produces a globose fruit that is almost cork-like.
Animals
A significant aspect of plant-animal cooperation involves plants designed to take advantage of animal abilities to move. Some fruit have prickly burrs or spikes that attach themselves to a passing animal's fur or feathers so that the animal will carry them away. Some seeds are contained within a soft fruit that "invites" animals to consume it. These seeds have a tough protective outer-coating so that while the fruit is digested, the seeds will pass through their host's digestive tract intact, and grow wherever they fall. Some seeds are appealing to rodents (such as squirrels) who hoard them in hidden caches, often beneath the surface of the soil, in order to avoid starving during the winter and early spring. Those seeds that are left uneaten have the chance to germinate and grow into a new plant.
Some animals that disperse may also eat the seed.
- Beggarlice
- Cockle burr
- Apple
- Banana
- Strawberry
- Oak (acorns)
5
This list does not include the dozens of seeds used as spices or oil (see below), nor does it include seeds which are incidentally eaten as part of a fruit (strawberry, banana). However, you should accept such answers if they are given.
- Almond
- Barley
- Brazil nut
- Cashew
- Chestnut
- Chickpea (garbanzo)
- Cocoa
- Coconut
- Corn
- Cowpea
- Filbert
- Green bean
- Lentil
- Lima bean
- Macadamia
- Millet
- Mustard
- Navy bean
- Oat
- Pea
- Peanut
- Pecan
- Pine nut
- Pinto bean
- Pistachio
- Pomegranate
- Pumpkin
- Rice
- Rye
- Sesame
- Soybean
- Sunflower
- Walnut
- Wheat
- White bean
6
- Coconut
- Corn
- Cottonseed
- Canola oil (a variety of rapeseed oil)
- Olive
- Palm
- Peanut
- Safflower
- Sesame
- Soybean
- Sunflower
- Rice Bran
7
- Anise
- Caraway
- Cardamom
- Cocoa
- Coriander
- Cumin
- Dill
- Fennel
- Nutmeg
- Mustard
- Vanilla
8
Requirements for seed germination
Seed germination depends on many factors, both internal and external. The most important external factors include: water, oxygen, temperature, and the correct soil conditions. Every variety of seed requires a different set of variables for successful germination. This depends greatly on the individual seed variety and is closely linked to the ecological conditions in the plants' natural habitat.
Water
Germination requires moist conditions. Mature seeds are usually very dry and need to take up significant amounts of water before they can "come back to life." The uptake of water into seeds leads to a marked swelling. The pressure caused by water aids in cracking the seed coat for germination. When seeds are formed, most plants store large amounts of food, such as starch, proteins, or oils, for the embryo inside the seed. When the seed absorbs water, it breaks down these stored food resources and allows the seedling to germinate and grow until it reaches the light. Once the seedling starts growing, it requires a continuous supply of water and nutrients.
Oxygen
Most seeds respond best when water levels are enough to moisten the seeds but not soak them, and when oxygen is readily available. Once the seed coat is cracked, the germinating seedling requires oxygen. If the soil is waterlogged, it might cut off the necessary oxygen supply and prevent the seed from germinating.
Temperature and light
Seeds germinate over a wide range of temperatures, with many preferring temperatures slightly higher than room-temperature. Often, seeds have a set temperature range for sprouting and will not sprout above or below a certain temperature. In addition, some seeds may require exposure to light or to cold temperature to break dormancy before they can germinate. As long as the seed is in its dormant state, it will not germinate even if conditions are favorable. For example, seeds requiring the cold of winter are inhibited from germinating if they never experience frost. Some seeds will only germinate when temperatures reach hundreds of degrees, as during a forest fire. Without fire, they are unable to crack their seed coats. Many seeds in forest settings will not germinate until an opening in the canopy allows then to receive sufficient light for the growing seedling.
Stratification
Seeds must be mature and environmental factors must be favorable before germination can take place. When a mature seed is placed under favorable conditions and fails to germinate, it is said to be dormant. Some seeds will not germinate (begin to grow) until they have been dormant for a while. The length of time plant seeds remain dormant can be reduced or eliminated by a simple seed treatment called stratification. Seeds should be planted promptly after stratification.
Stratification mimics natural processes that weaken the seed coat before germination. In nature, some seeds require particular conditions to germinate, such as the heat of a fire (e.g., many Australian native plants), or soaking in a body of water for a long period of time. Others have to be passed through an animal's digestive tract to weaken the seed coat and enable germination.
9
References
- Wikipedia articles