Difference between revisions of "AY Honors/Geology/Answer Key"
From Pathfinder Wiki
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
==1. Give the geological meaning of the following words:== | ==1. Give the geological meaning of the following words:== | ||
| + | <gallery> | ||
| + | Image:Nile River and delta from orbit.jpg|Satellite image of the Nile '''River Delta''' | ||
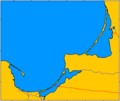
| + | Image:Baltic spits.png|The three narrow strips of land shown here are '''spits''' in the Baltic Sea | ||
| + | Image:DeadSeaSinkhole.jpg|'''Sinkholes''' near the Dead Sea | ||
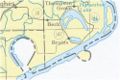
| + | Image:Oxbow lake.jpg|Map of an '''oxbow''' lake | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
;a. Delta: A delta is a landform where the mouth of a river flows into an ocean, sea, desert, estuary or lake. | ;a. Delta: A delta is a landform where the mouth of a river flows into an ocean, sea, desert, estuary or lake. | ||
;b. Sand spit: A spit a deposition landform found off coasts. A spit is a type of bar or beach that develops where a re-entrant occurs, such as at a cove, bay, ria, or river mouth. Spits are formed by the movement of sediment (typically sand) along a shore | ;b. Sand spit: A spit a deposition landform found off coasts. A spit is a type of bar or beach that develops where a re-entrant occurs, such as at a cove, bay, ria, or river mouth. Spits are formed by the movement of sediment (typically sand) along a shore | ||
| − | ;c. Sinkhole: | + | ;c. Sinkhole: A sinkhole is a natural depression or hole in the surface topography caused by the removal of soil or bedrock, often both, by water. Sinkholes may vary in size from less than a meter to several hundred meters in diameter and depth, and vary in form from soil-lined bowls to bedrock-edged chasms. They may be formed gradually or suddenly, and are found worldwide. |
| − | ;d. Oxbow lake: | + | ;d. Oxbow lake:n oxbow lake is a type of lake which is formed when a wide meander from a stream or a river is cut off to form a lake. They are called oxbow lakes due to the distinctive curved shape that results from this process. In Australia, an oxbow lake is called a billabong. |
| + | |||
;e. Moraine: | ;e. Moraine: | ||
;f. Cirque: | ;f. Cirque: | ||
Revision as of 01:02, 22 April 2007
1. Give the geological meaning of the following words:
- a. Delta
- A delta is a landform where the mouth of a river flows into an ocean, sea, desert, estuary or lake.
- b. Sand spit
- A spit a deposition landform found off coasts. A spit is a type of bar or beach that develops where a re-entrant occurs, such as at a cove, bay, ria, or river mouth. Spits are formed by the movement of sediment (typically sand) along a shore
- c. Sinkhole
- A sinkhole is a natural depression or hole in the surface topography caused by the removal of soil or bedrock, often both, by water. Sinkholes may vary in size from less than a meter to several hundred meters in diameter and depth, and vary in form from soil-lined bowls to bedrock-edged chasms. They may be formed gradually or suddenly, and are found worldwide.
- d. Oxbow lake
- n oxbow lake is a type of lake which is formed when a wide meander from a stream or a river is cut off to form a lake. They are called oxbow lakes due to the distinctive curved shape that results from this process. In Australia, an oxbow lake is called a billabong.
- e. Moraine
- f. Cirque
- g. Mesa
- h. Alluvial fan
- i. Anticline
- j. Syncline