AY Honors/Animal Tracking/Answer Key
1. Know ten kinds of tracks, including two kinds of bird tracks. Make plaster casts of five.
To do this, you will need to bring dry plaster of Paris, water, a mixing container, a mixing stick (a paint stirrer will do nicely), and something to make rings out of. Plaster of Paris can be bought either dry, or ready-mixed. It is probably better to get the dry type so that you can mix it on site. It will need to be soupy to make a detailed cast. When you find a suitable track, place a ring around it. The ring can be made from almost anything - a large tin can with the bottom cut out, a paper cup with the bottom removed, a strip of poster board 4 cm![]() wide and taped together at the ends to form a circle, etc. Make sure the ring is larger than the track, and note that some tracks are 15 cm
wide and taped together at the ends to form a circle, etc. Make sure the ring is larger than the track, and note that some tracks are 15 cm![]() long or more. What a pity it would be to find a huge bear or moose track and not have a large enough ring to cast it! You can also make the cast without a ring, but it is much better if you use one. Once the ring is in place, mix just enough plaster and water to fill the ring up to 2.5 cm
long or more. What a pity it would be to find a huge bear or moose track and not have a large enough ring to cast it! You can also make the cast without a ring, but it is much better if you use one. Once the ring is in place, mix just enough plaster and water to fill the ring up to 2.5 cm![]() deep. It sets quickly, so you will not want to mix up too much at a time. Mix water with the dry plaster and stir it until it is smooth. It should be about the same consistency as pancake batter or apple sauce. Pour it into the ring. Once this is done, you can set out in search of more tracks, or you can wait until the plaster sets. If you set out for more, be sure to come back to collect your cast.
deep. It sets quickly, so you will not want to mix up too much at a time. Mix water with the dry plaster and stir it until it is smooth. It should be about the same consistency as pancake batter or apple sauce. Pour it into the ring. Once this is done, you can set out in search of more tracks, or you can wait until the plaster sets. If you set out for more, be sure to come back to collect your cast.
One good way to complete this requirement is by heading to a river right after flooding has receded. There will likely be plenty of easily identifiable kinds of tracks, and the smooth mud makes for excellent casting.
Snow is difficult to cast because it is not nearly as firm as mud. Furthermore, plaster generates heat when it is mixed, and this can easily melt the snow surrounding the track.
Mammals
Raccoon
Raccoon (Procyon lotor)
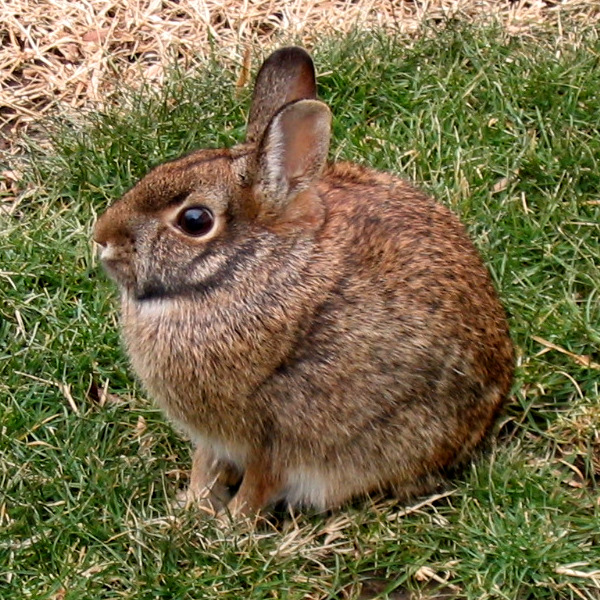
Rabbits and Hares
Rabbits and Hares (Lagomorpha)
Deer
Deer, various species (Odocoileus spp.)
Moose
Moose (Alces alces)
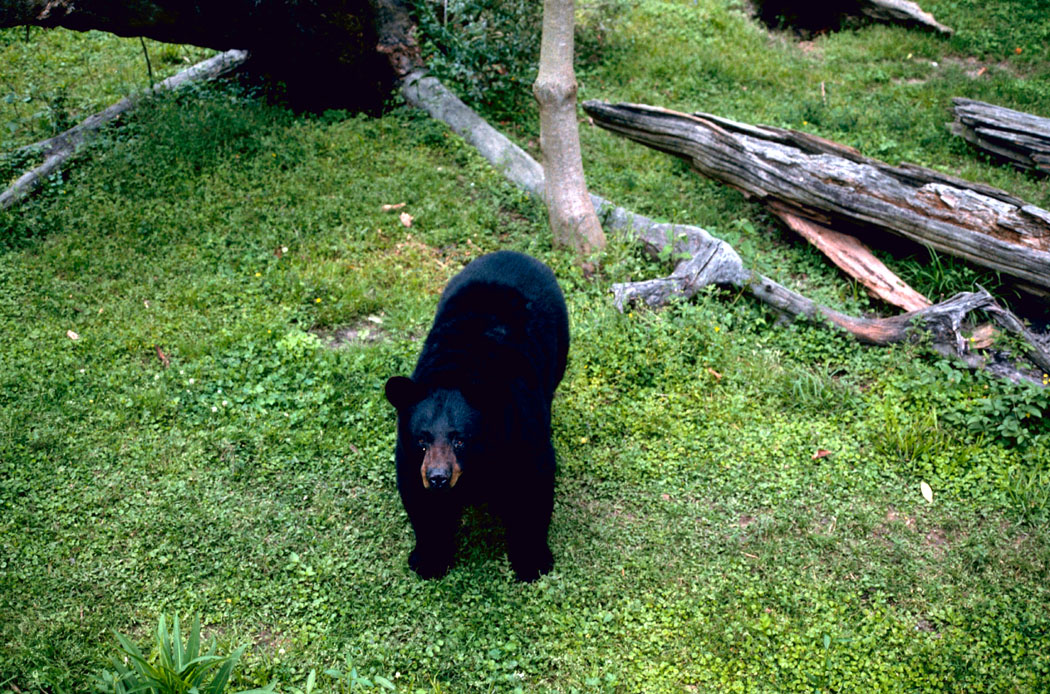
Bear
Bear, various species (Ursus spp.)
Beaver
Beaver (Castor canadensis)
Muskrat
Canines
Dogs, wolves, coyotes (Canidae)
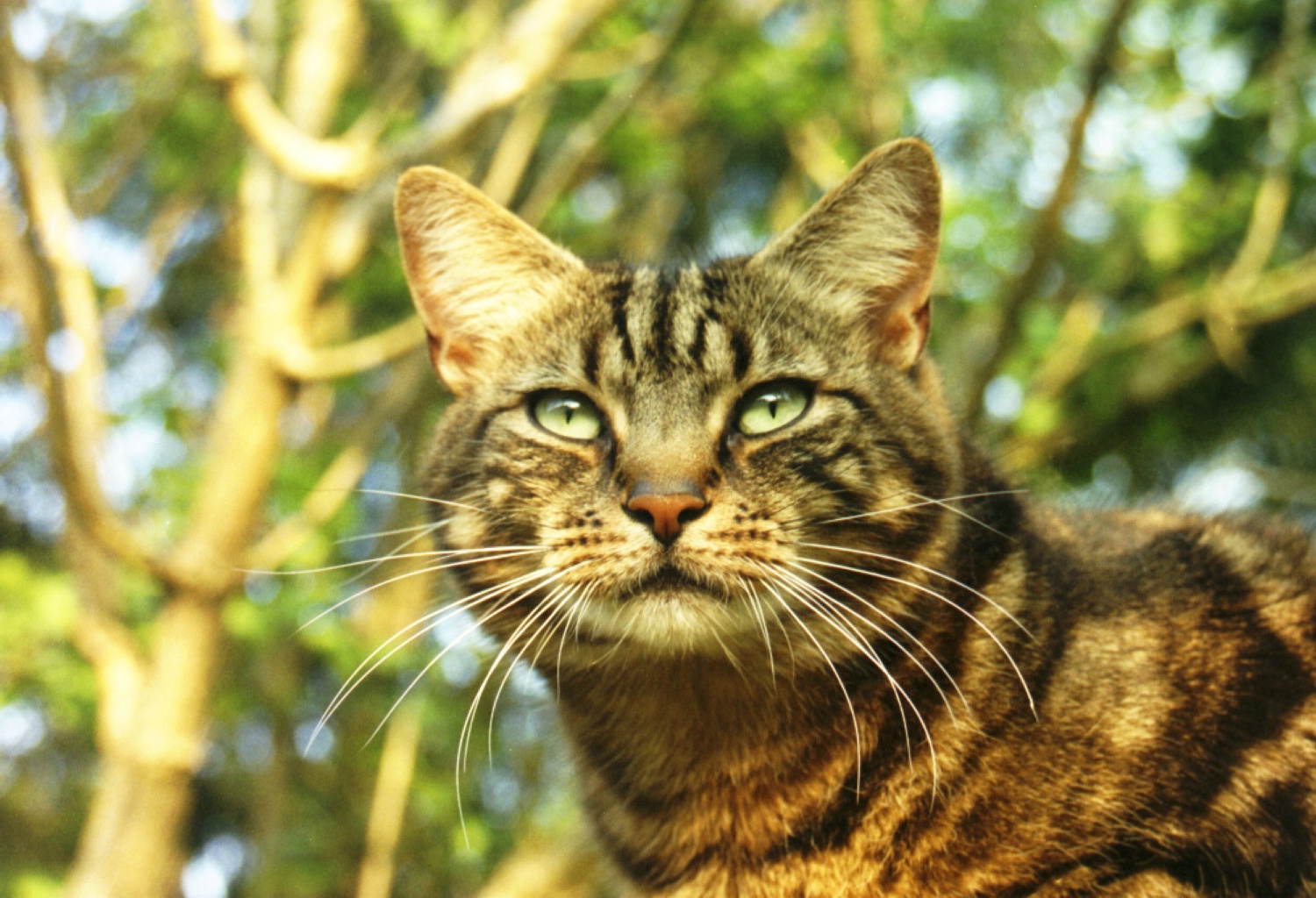
Cat
Cat (Felis silvestris)
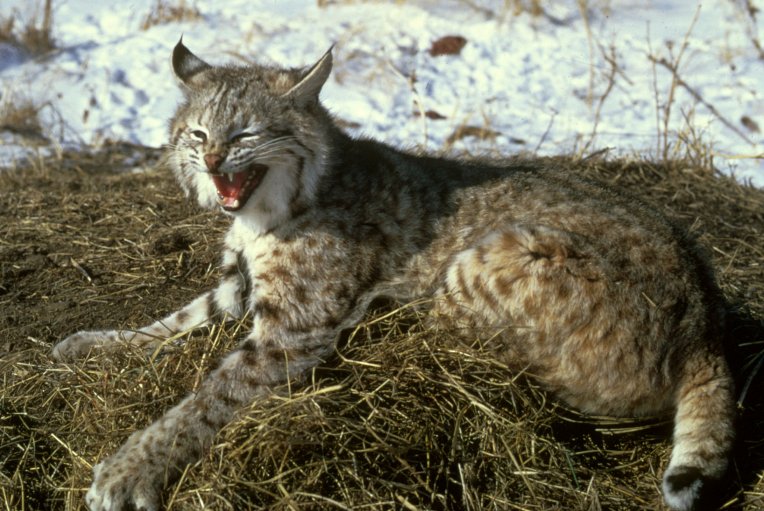
Lynx
Bobcat/Lynx (Lynx spp.)
Mouse
Mouse (Mus musculus)
Horse
Horse (Equus caballus)
Cattle
Pig
Pig (Sus domestica)
Squirrel
Puma
Mountain Lion, Puma (Puma concolor)
Oposum
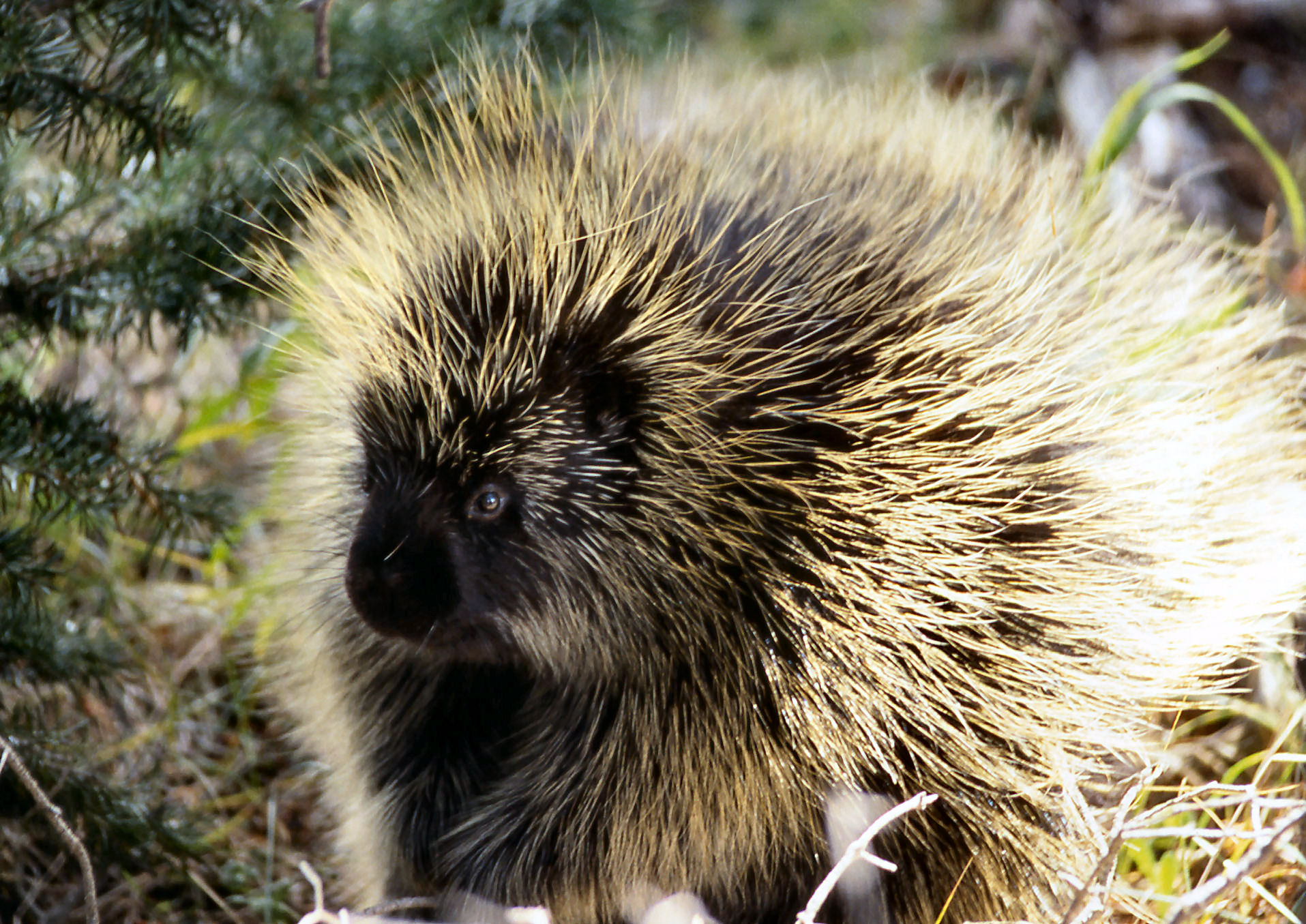
Porcupine
Porcupine (Erethizon dorsatum)
Skunk
Skunk (Mephitis mephitis)
Weasels, minks, fishers, and otters

Mink (Mustela vison) Weasels, minks, fishers, and otters

Pine Martin (Martes martes) tracks in snow

Otter scat
Weasels, minks, fishers, and otters (Mustelidae)
- Otter
- Otters have a dense layer (1,000 hairs/mm², 650,000 hairs per sq. in) of very soft underfur which, protected by their outer layer of long guard hairs, keeps them dry under water and traps a layer of air to keep them warm.
- All otters have long, slim, streamlined bodies of extraordinary grace and flexibility, and short limbs; in most cases they have webbed paws. Most have sharp claws to grasp prey, but the short-clawed otter of southern Asia has only vestigial claws, and two closely-related species of African otter have no claws at all: these species live in the often muddy rivers of Africa and Asia and locate their prey by touch.
- Weasels
- Weasels vary in length from 15 to 35 centimeters (6 to 14 inches), and usually have a light brown upper coat, white belly and black fur at the tip of the tail; in many species, populations living at high latitudes moult to a white coat with black fur at the tip of the tail in winter. They have long slender bodies, which enable them to follow their prey into burrows. Their tails are typically almost as long as the rest of their bodies. As is typical of small carnivores, weasels have a reputation for cleverness and guile. They also have tails that can be any where from 22-33cm long and they use these to defend the food they get and to claim territory from other weasels.
Reptiles and Amphibians
Snakes
Snake (')
Frogs
Frogs and Toads (Anura)
Turtles
Turtle (Testudines)
Birds
Crow (')
Robin (')
Pigeon (')
Sparrow (')
Heron (')
Herring Gull (')
Sand Piper (')
Canada Goose (Branta canadensis)
Duck (')
Grouse (')
Turkey (')
2. Name at least three things that tracks tell us.
Animal tracks can tell us many things about the animal that made them, including:
- The species
- Its direction of travel
- How fast it was going
- How large it was
- How long ago the animal made the tracks.
- Sometimes tracks can tell the gender of the animal
- Sometimes tracks can tell us the animal's age.
3. Trail some animal tracks, identify the animal if possible, and tell whether it was running or walking. Measure between the tracks of one animal when running and walking.
Trailing and Identifying
This is a perfect activity for an afternoon hike during a campout. Bring a tape measure, some powdered plaster of Paris, and a mixing bowl so that you can measure the tracks and make casts. You can also bring water, though it is better to keep that for drinking rather than mixing with plaster. You can probably find some water along the way, but just to make sure, you should bring some water for the plaster. You can refill a bottle for plaster making without treating it as long as you make it obvious that it is not fit for drinking (mud is a good indicator).
Instruct your Pathfinders that they are to look for animal tracks along the way. When they find some (or when you do), try to figure out the species by comparing the track to those in a field guide or those depicted in the answers to requirement one. See if you can find more tracks nearby. Which way was the animal moving? How far can you track it?
Walking vs Running
If the tracks are far apart relative to the size of the animal, it was most likely running. Another indicator of running is that the tracks are deeper than those made by a walking creature (running makes the feet strike the ground with greater force).
Measuring Tracks
There is nothing in this requirement to suggest that the tracks of one animal made while running and walking has to be a wild animal, or even that you have to find a set of tracks like these pre-made. If you or a person in your group, or a person you know has a dog, take it to a sandy area and have it walk and run. Then get a tape measure and determine the distance between the tracks.
4. Maintain a tracking station for at least three days by doing the following:
a. Select a flat open space in some quiet place near your camp or home.
Do not select a space too close to your campsite, because you do not want to attract them into your camp. Animals need water, so a really good place to select is around a source of fresh water. River banks, stream banks, near ponds, and the shores of lakes are all good places to find animal tracks. However, the place you select must be quiet. Avoid places that are frequented by people.
b. Smooth out ground, mud, sand, etc.
There may already be some tracks in the area, but you are interested in fresh tracks. Smoothing the ground erases them and allows for fresh prints.
c. Place food out for wildlife.
Another option is to use a salt or mineral block. The type of food you place will affect the type of animals you attract, as will the season. If there is plenty of food available without your "bait," the animals will be suspicious and stay away. However, if they are hungry (as in winter) or if the food you select is irresistable, they will be more likely to come. Sliced apples out of season will attract many types of animals.
d. Check each day for tracks and replenish food when necessary.
When camping, remember to store your food in a place where the animals cannot get to it. Seal it tightly and place it out of the reach of raccoons and bears (both of which are very clever at getting food). Under no circumstances should you store food in a tent - especially in one that people will be sleeping in. A tent poses no barrier to a hungry skunk.
The morning is the best time to check for tracks. Most forest creatures are nocturnal, so in the morning the tracks will be freshest. Also, human visitors are less likely to trample the tracks before you get a chance to observe and if necessary, cast them.
5. Name two animals for each tracking group.
- a. Flatfoots
- Flatfoots include bears, raccoons, porcupines, and skunks.
- b. Toe walkers
- Toe walkers include dogs, cats, lynxes, wolves, and coyotes.
- c. Toenail walkers
- Toenail walkers include deer, antelope, moose, pigs, cattle, and horses. Basically, any hoofed animal is a toe walker.
- d. Bounders or long hindleggers
- These include rabbits, squirrels, mice, and rats.
6. Name four signs of the presence of mammals.
Animals leave many indications that they were present. These are collectively called sign. Sign includes:
- Tracks
- Not only footprints, but marks left on the ground by the tail or by other body parts. Beavers and rats both leave tail marks on the ground.
- Scat
- Scat is another word for animal droppings or manure.
- Fur and antlers
- Animals may leave bits of fur behind if it gets caught in a tree's bark, or in thorns. In the fall deer drop antlers.
- Cuttings
- Cuttings are things such as acorn shells which have been nibbled on. Deer and squirrel often leave them behind.
- Scratches on trees
- Bears, members of the cat family, and other predators will sharpen their claws on tree trunks. Sometimes they will do this to mark their territory.
- Scent Posts
- Many animals mark their territory by urinating on trees or other prominent items. If you are walking through the woods and smell a strong musky odor, look around — you may find other sign.
- Carcasses
- Once a predator has had its fill of a kill, it will leave the carcass. Some animals will guard their carcasses though so they can feed on them again after they've digested some of the previous meal, so be careful if you find one.
7. Distinguish between rabbit and squirrel tracks, and between dog and cat family tracks.
Rabbit vs Squirrel Tracks
Rabbits leave a distinctive pattern when the bound along. The front feet are thrown between the hind feet, but one of them is almost invariably thrown farther back, and the two forefeet often print one behind the other (though sometimes they print side-by-side). A rabbit's hind feet leave larger oval-shaped prints about the size of a man's thumbprint. Since they use the hind feet rather than their forefeet to leap forward, they will push out some material behind them. It may be difficult to make out individual toes in a rabbit print.
Squirrels are also bounders, and like the rabbit, they throw both forefeet between their hind feet. But unlike the rabbit, the squirrel's forefeet generally print side-by-side. The hind feet should print five toes (four finger-like and one thumb-like) and no claws. The forefeet should print only four toes.
In general, a rabbit's pads are shaped like an oval while a squirrel's pads are shaped like a human hand.
Dog vs Cat Tracks
Unlike dogs, cats can retract their claws, and they do so when walking. Therefore, you should expect to find claw marks present in dog tracks, but absent in cat tracks. In general dogs tracks are larger than cat tracks, but you cannot rely on this alone, as there are some very small dogs and some very large cats.
8. Name two groups of animals (mammals, birds, insects, etc.) that leave tracks or scent trails that another of their kind can follow.
Some species of mammal and some species of insect leave scent trails to communicate with others of their species. Canines, cats, deer, moose, and others will mark their territory with urine.
Ants lay down pheromone trails that lead to food sources. If you have ever seen a column of ants scurrying about in single file, you can be sure they are following a scent trail.
9. Name two birds for each of the following type of tracks:
a. Hopping
Most perching bird (passerines) hop, though many can both hop and walk (such as ravens, blackbirds, and robins). Jays, sparrows, cardinals, titmice, nuthatches, finches, and many others hop.
b. Walking
Walking birds include crows, most waterfowl and shore birds (sandpipers, egrets, herons, etc), and most game birds (wild turkeys, geese, ducks, grouse, doves, pigeons, etc).
10. Besides tracks, give two other signs of the presence of birds.
- Feathers
- Droppings
- Nests
- Birdsongs (if you can hear them, they must be present!)
- Eggs or eggshells
- Pellets: Birds of prey regurgitate the indigestible portions of their meals. Birds have no teeth so they rip their prey apart with their beaks and swallow large chunks at a time. Then they digest the soft portions (such as meat) leaving the hair and bones behind to collect into pellets. They cough up these pellets which can be found by the astute observer.
11. Name two birds identified by their flying patterns.
12. In your area, observe tracks or trail of one or more of the following:
a. Toad or frog
b. Snake
c. Turtle
d. Mollusk
e. Earthworm
f. Mole
References
- The Complete Tracker by Len McDougall, 1997. ISBN 156731-326-4