AY Honors/Business/Answer Key
Template:AY patch unavailable
Template:Honor desc
1. Define the following terms:
- a. Break Even
- the point where the business is not making or losing money
- b. Business
- c. Business Plan
- a detailed, hopefully written, plan of how the business will be organized, what will be produced and sold, and at what cost. Usually includes a budget
- d. Capital
- the money used to finance the business. Can include investment by the owners, borrowed money, and retained earnings.
- e. Distribution
- several meanings including 1. The amount of money paid on the owners shares from profits. 2. The system or method of getting goods or services to market
- f. Interest
- 1. the rent on borrowed money.
- g. Micro business
- h. Price
- the amount charged to the buyer for the product or service offered by the business
- i. Product
- the good or service the business sells
- j. Production
- k. Profit
- the positive amount left after the business pays all expenses.
- l. Promotion
- activity that is designed to increase sales or general awareness of the business, its products and/or services.
- m. Service
- a product that is not a physical item.
- n. Target market
- the group of potential buyers the business is attempting to attract. A given target market is very product and business specific can be defined by some combination of geography, income level, and often other demographic characteristics like gender, age, marital status, faith, buying habits, interests, amd more. Most businesses will attract the occasional buyer from outside the target market as well, but if too many buyers are from outside the target market it is time to refine the target market.
2. Describe three ways in which a business may be conceived
The best business ideas are found at the intersection of 6 considerations, which we can remember as the 6 C's.
1. Customers
Your business will need customers and you must determine who the customers are and discover what the customers really want. The bankruptcy rolls are filled with former businesses which were based on what the business person THINKS the potential customers want. Do not assume that other people want what you want. You must do market research with real potential customers. Do not assume that your friends and family will tell you the truth about your idea because few people are willing to give honest negative feedback to someone close to them.
Also, a business with only one customer is more like a subcontractor or type of employee. If you rely on only one customer that customer controls you and can easily put you out of business. Figure out how you will diversify your customer base.
2. Compelling
A great business idea has to be something you care about. You will be spending a lot of time on your business, selling others on your business and its products and investing your money in the business. If you don't have a passion for the business your chance of failure is very high, even if all the other C's are covered. Equally important, your product must be compelling to the potential customers. Unless you offer something they absolutely have to buy (basic utilities for example) customers who think the product is just interesting are useless - you need people who will make the purchase.
3. Competency
If the business does not fit your skills and abilities you should not do the business until you acquire the appropriate skills. There might be a great potential business for a dentist in your town but if you have not graduated dental school it is not the business for you. Other cases might not be so obvious. Think about the technical, legal, sales, and other aspects of the business. If you can't do everything, and most of us can't, you will need to hire other people. Can you afford and competently supervise these specialists?
4. Capital
The business must be financially feasible. Every business has setup costs, equipment costs, cost of space. You will need enough capital to get your business set up, and to expand it over time.
5. Cashflow
Beyond the required capital, most business lose money during start up. You will need working capital (money to cover short term differences between cash inflows and outflows). Many businesses fail by running out of money because the management misjudged the cashflow situation. This problem plagues businesses that grow slower than anticipated and those that grow faster than planned for. Fast growth requires investment in people, equipment, receivables, inventory etc and this can run even an otherwise highly successful business out of money.
6. Competition
Every business has direct and indirect competition. You must evaluate your competition carefully to understand if and how you can differentiate your business from the competition successfully.
A Pathfinder Club as a Business Idea
Discuss with your Pathfinders a business they are familiar with - which could be large or small, then consider stretching their minds by analysing their Pathfinder Club as a business.
In many ways, your Pathfinder Club is a (non-profit) business. The club needs customers (children between the ages of 10-15). The most obvious potential customers are children and teens within your local church, but children in the wider community are also welcome to participate, as are children from nearby churches. If the Pathfinder Club is the business, the Pathfinders are the customers.
We know that many kids like Pathfinders, but do they really want it? There would be no demand for Pathfinders at 9 AM Tuesday morning because the kids are in school. We also need to craft the Pathfinder program to be exciting and appealing to potential customers. Too much book work without enough hands on activities will not make happy customers.
If you were thinking about leading a Pathfinder Club you'd better find it compelling because you are signing up for a big job. You also need to be able to make it compelling to your customers and their parents.
Obviously a potential leader needs to have leadership skills, and be willing and able to acquire lots of skills, just like in a business.
A new Pathfinder Club needs capital for uniforms, flags, tents, gear, and so on. It also needs cashflow from the sponsoring church, dues, fundraising etc. Without capital and cashflow your club will not have the things it needs to run, or deliver the product (club experience and fun) to the customers.
Just like any business, a Pathfinder Club has direct and indirect competition. Nearby Pathfinder Clubs (within driving distance) are direct competition because a Pathfinder might move over to a bigger/most successful/better lead/more fun Pathfinder Club. Scouts/Girl Guides are also direct competitors offering similar (though not spiritual) programs. Indirect competitors include competitive sports teams, non-competitive recreational activities, or anything else that can use up a Pathfinder's free time, even video games.
There are far more ways you should NOT come up with a business idea. Lots of businesses are started because the 'businessperson' if you can call them that, wants to do something interesting but refuses to figure out a good plan or do the market research.
3. Explain the benefits of having a management team in a business (note that one person might adopt all these roles in a small/micro business)
Each business, no matter how small needs people to perform the important functions. Someone needs to take care of the finances, production, sales, purchasing, personal management, and general management. In a very small business the proprietor might cover all these areas, while perhaps contracting out functions like accounting. In a large company there maybe departments of people to do each function. Unless the key business functions are covered, the business will not be able to function for long.
4. List ways that a business’ product/service may be promoted
Promotion, sales, marketing and advertising (all parts of promotion) is the most important function in a business. Without sales, and the promotional efforts that drive sales, the business quickly fails. The correct type of promotion depends on the type, location, size, and development stage of the business. There is no fool proof answer to successful promotion. Successful businesses carefully measure the return on their promotional efforts. They regularly try new methods of promotion and discard unsuccessful ones. They split test promotions to discover which advertisements and other promotions work better than others.
If you pursue a business degree in University you can expect to take entire courses that just introduce fields like Advertising, Marketing, and Sales Management. You might even specialize an entire 4 year degrees in one of these closely related fields, so we can only give a very light overview here.
Promotion includes:
Advertising - usually paid efforts to get a specific message out
- TV and Radio (mass media)
- Magazine and Newspaper (print media)
- Web and New Media (online, social media) including Google Adwords, Facebook Ads, YouTube ads etc
- Direct mail and flyer services
- Billboards, bus benches, on transit vehicles (outdoor)
- Signs on the outside of the business
Sponsorships - paid efforts to get the business or brand name more famous, but not with a specific call to action
- Sporting events, cultural events etc
- Buying naming rights to buildings (parks, sports stadiums, cultural centers etc)
- Promotion of charities (banks in Canada like to raise money for charities)
Online Strategy
- Websites
- Facebook, Twitter etc profiles and pages
- YouTube channels
- Putting out content like videos and images that the business hopes will be shared and go viral
- email campaigns
- Online contests (almost all contests have an online component today)
Direct Sales
- Door to door sales strategy
- Telephone sales or lead generation
- Multi-level marketing (Amway etc)
- Promotion through schools and other groups where the group becomes the sales force to raise money
- Booth at a craft market, community event etc that does direct sales
Coupons and Special Offers
- Offering money off via a coupon
- Point of Purchase (POP) displays or in-store signage
- Attaching a rider product as a bonus on another product (product bundling)
- Service bundling (get a discount for buying your TV, phone and internet together)
- Loyalty programs and point or sticker collection programs
- Affiliate marketing (Amazon uses this in a big way, as does the insurance industry)
Can you think of more promotional strategies within these categories, or even other categories?
5. Show how you determine
a. Price of the product
b. Break-even point
The break-even point (BEP) in economics, business, and specifically cost accounting, is the point at which total cost and total revenue are equal: there is no net loss or gain, and one has "broken even." A profit or a loss has not been made, although opportunity costs have been "paid", and capital has received the risk-adjusted, expected return. In short, all costs that needs to be paid are paid by the firm but the profit is equal to 0.
For planning, you will need to figure out three numbers and then graph or spreadsheet them. These are:
- Expected average revenue per unit
- Fixed costs - those costs that stay the same regardless of how many or few units you sell. Rent, basic staff, and utilities are usually fixed costs.
- Variable costs, expressed per unit at various sales levels.
There are actually two break even points. The first is a theoretical calculation of what level of sales in an accounting period (like a month or quarter) that results in the business no longer losing money. The second to occur is where the business has enough cumulative sales over time to offset all the expenses to date. It is also called getting out of the red and into the black because negative numbers in accounting reports are often printed in red ink while positive numbers are printed in black ink.
c. Profit/loss
6. Discuss ways in which the profits of a company can be used?
Profits are used in one or a combination of these ways depending on the objectives of the company:
- dividends to shareholders
- to increase the working capital (cash on hand)
- to buy assets or otherwise invest in growing the business, including increases in receivables
- to retire debt
7. Brainstorm at least 4 ideas for small business that can be conducted by Pathfinders in your club. Evaluate the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats associated with each of them.
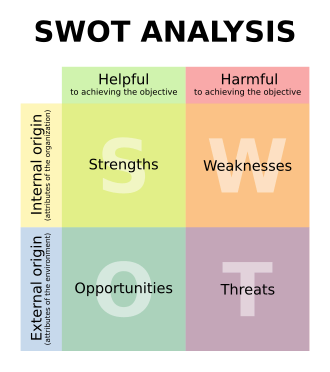
This requirement introduces the business concept of a SWOT analysis. SWOT is a popular way to evaluate business ideas and the business itself. While not a perfect tool, it is widely used in organizational decision making and can be very helpful.
When doing SWOT, you make lists of internal and external factors influencing the plan or organization. Strengths and Weaknesses are internal while Opportunities and Threats are external.
Every Pathfinder Club needs to bring in money, and every plan to bring in money is essentially a business plan. So let's run an example your own Club can expand on.
Step 1: Generate ideas for a business. Write down even seemingly crazy ideas because they may prove practical or lead to a great idea. You might also combine ideas as you move through the process.
Example ideas: flea market, car wash, making and selling quilts, building and selling bird houses.
Step 2: Take the first idea - a flea market day at your gym to make money. The Club would go into the business of renting space and tables, as well as offering ancillary services. Is this a good idea? Let's do a SWOT Analysis to find out.
Step 3: Start by everyone brainstorming points for the list of factors. Write them on a sheet of paper or a white board for all to see (which reduces duplication and encourages related ideas). Don't worry about classifying the points during the brainstorming but be thinking about Internal Strengths, and Weaknesses as well as External Opportunities and Threats. Here are some possible SWOT items.
Strengths (internal):
- The club has 10 Pathfinders and 5 adults to advertise and run the sale
- Not a lot of skill needed
- Pathfinders have time (nothing else to do on Sunday).
- Earning this honor is motivational
- Might make $1000 dollars based on rough budget
Weaknesses (internal):
- No one has any experience at this business
- Some Pathfinders are too young to help without a parent to help
- Takes up time that could be used for archery or camping or whatever
Opportunities (external):
- People like to support a good cause and Pathfinders (framed as a "youth program") is considered by everyone to be a good cause
- We can use the school gym, tables and chairs for free
- Facebook groups and walls are a good place to advertise free
- We can advertise with fliers while can collecting
- We promote the Pathfinder Club and possibly attract new members
- We introduce people to the Adventist School and adjoining church
Threats (external):
- People might leave a lot of garbage
- If it snows, few will show up
- The public school two blocks away has a similar event the week before, so people might sell their stuff there instead
- The city might require a permit and might not approve it.
Step 4: Categorize your list and weight it. While categorizing, you should see some things you missed, so add them. Don't just count up the S's and O's vs the W's and T's, you need to assign importance to them. Some threats are only remote or even not real for example. A big opportunity might be worth doing if there is limited threats and the weaknesses can be overcome. However a major weakness in an otherwise great idea can sink it.
Step 5: Can you eliminate threats and fix weaknesses? Perhaps teaming up with another group or finding a donor is the answer.
Step 6: Either make a decision (Yes or No), or compare to your SWOT on several other business ideas before making a decision.
In this example, we also did a SWOT on the car wash, quilts and birdhouses. We decided that we could earn the Woodworking honor while building the birdhouses and than sell them at our flea market event. We also decided to sell veggie tacos at the event and have a display about our Pathfinder club.
We decided that since it is January, our Canadian location (a Weakness for the carwash idea) meant cold weather (a threat in the car wash idea) and that these two factors trumped all the Strengths and Opportunities for the carwash.
8. Develop a business plan for at least one of your ideas from #7 above. Include the following in the plan:
- a. Description of business
- b. Capital needed and the source of the capital
- c. Price of the product/service
- d. Target market
- e. Promotional method
- f. Sales location
- g. Expected gains
- h. Dissemination of profit
9. Execute the plan
a. Build the management team
b. Create the product
c. Advertise the product/service
d. Sell the product or perform the service
e. Report on profit/loss
f. Report on use of profits
g. Suggestions for improvements
10. Discuss ethical issues and Christian values involved in conducting a business
a. To God
b. To the government
c. To the customer
d. To the employee
11. Recount the story of Joseph as a shrewd manager and businessman (Genesis 41:39-57), the parable of the talents (Luke 19:11-26) or other similar bible passage. Identify three lessons from the story that can be applied to your business
Genesis 41:39-57 Luke 19:11-26
Other stories to look at:
Jacob's success while working for Labon. He used some kind of business plan for his farm that is hard to understand, but it worked Genesis 30.
Jesus called no synagogue preachers to be his closest disciples. Instead Jesus called at least 6 fishermen who owned boats and sold fish. He called Matthew, a businessman contracted to the Romans as a local tax collector. and there is no indication the others were trained as preachers.
Jesus himself was a businessperson, part of a family business of craftspersons (though in English we read Jesus was a carpenter, the Greek word “tekton” actually describes a craftsman, one who constructs; a versatile builder and stone worker. Perhaps this is why Jesus ministry demonstrated such a broad knowledge of business and why about 34 of his approximately 50 recorded parables dealt with a business, finance or workplace content for the illustration.
Many of Jesus public ministry appearances appear to have occurred in the marketplace and workplace.
Paul, Priscilla and Aquila, operated a tent making business, so that none of them appear to have needed others to donate so they could preach. Lydia, a leader in the Philippian Church, was a textile dealer.
Early Adventist used businesses to support themselves. Hiram Edson farmed during the summer to support himself while preaching.
James White sold Bibles, Bible Commentaries and other reference books in the frontier to support his and Ellen White's ministry. The Whites also invested in real estate and in preparing their own books for sale. Some were critical of the White's relative financial success, but an investigation into the White's finances found that they legitimately had been supporting themselves plus the infant church from their business endeavors.