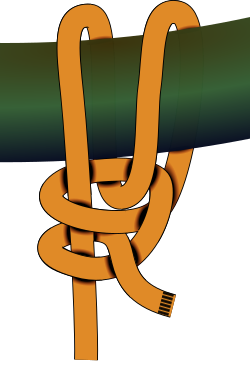
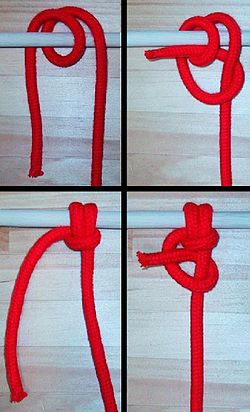
AY Honors/Knot Tying
Overview
The Challenging Part
The most challenging requirement of this honor is probably this:
9. Make a knot board showing 25 or more knots.
[[AY Honors/Knot Tying/Requirements|Tab Name/Printable Version]]
1. Define the following terms:
- a. Bight
- b. Running end
- c. Standing part
- d. Underhand loop
- e. Overhand loop
- f. Turn
- g. Bend
- h. Hitch
- i. Splice
- j. Whipping
2. Know how to care for rope.
3. Describe the difference between laid rope and braided rope and list three uses of each.
4. Identify the following types of rope:
- a. Manila
- b. Sisal
- c. Nylon
- d. Polypropylene
5. What are some advantages and disadvantages of synthetic rope?
6. Do the following to rope:
- a. Splice
- b. Eye splice
- c. Back splice
- d. Finish the end of a rope with a double crown, whipping, or a Matthew Walker's knot.
7. Make a six-foot piece of three-strand twisted rope from native materials or twine.
8. From memory tie at least 20 of the following knots and know their common uses and limitations. Demonstrate how they are used.
- a. Anchor bend
- b. Bowline
- c. Bowline on a bight
- d. Butterfly loop knot or Alpine butterfly knot
- e. Carrick bend
- f. Cat's paw
- g. Clove hitch
- h. Constrictor knot
- i. Crown knot
- j. Double bow
- k. Double sheetbend
- l. Figure eight
- m. Fisherman's bend
- n. Fisherman's loop
- o. Halter hitch
- p. Hunter's bend
- q. Lariat or Bowstring knot
- r. Lark's head
- s. Man harness knot
- t. Miller's knot
- u. Packer's knot
- v. Pipe hitch
- w. Prusik knot
- x. Sheepshank
- y. Sheet bend
- z. Slip knot
- aa. Slipped half hitch
- bb. Slipped sheet bend
- cc. Square knot
- dd. Stevedore's knot
- ee. Strangle knot
- ff. Surgeon's knot
- gg. Taut-line hitch
- hh. Timber hitch
- ii. Two half hitches
9. Make a knot board showing 25 or more knots.
Printable Answer Key Tab Name/Edit Answer Key
Investiture Achievement Tie Ins and Teaching Tips
Knot tying is an important part of Pathfindering with tie ins to Investiture Achievement and many other honors such as the various Camping Honors, Rock Climbing, Pioneering and others.
- Friends are required to tie and know the practical use of 10 knots
- Companions are required to tie and know the practical use of 20 knots
- Explorers must earn the Knot Tying Honor
- Guides must, under the guidance of an adult staff member, teach the Knot Tying Honor
- Master Guides are required to earn or hold the Knot Tying Honor.
An effective way to teach knots in a club setting is to have the staff and the older Pathfinders (the ones who already have the Knot Tying Honor) each teach a single knot at a knot tying station. The Pathfinders who are learning the knots will rotate through the stations. After a set time, ring a bell to signal that it's time to rotate, and do not allow the students to rotate until the bell rings (otherwise, they will all gravitate to the same table).
Using this approach, each of the teachers need only learn a single knot well enough to teach it, and the students will have a chance to receive one-on-one instruction for every knot. Allow at least seven or eight minutes per station. You can do this over more than one meeting if necessary, and you can involve the entire club at once rather than only a single unit.
Prior to the meeting, the rope may be cut to the proper length. Some instructors consider cutting rope during a meeting a waste of valuable teaching time, while others use it as an opportunity to teach proper binding of the rope. To prevent the cut rope from unravelling, wrap a small piece of duct tape around it before you make the cut - then cut the tape in half. This will save time, as it binds both ends of the cut in one shot.
The length of each rope should be suited to the knot it will be used for. Note that a figure eight knot does not require as much rope as a timber hitch, and that it is impossible to tie a knot on a rope that it too short to hold it. Conversely, using too much rope for small knots is a waste of good rope (and money!). Remember that the amount of rope wasted on each knot will be multiplied by the number of students.
A good way to determine proper rope length is to tie the desired knot using a long piece of rope, cut it, and then untie it. That's how long it needs to be. Cut as many of that length as you will have students, put them in a plastic baggie, and label the bag. You may have the knot instructors cut their own ropes, or you may have a squad of TLT's do this. Or you could do it yourself (but that would be depriving your TLT's and/or instructors of a valuable experience).
Two knot tying stations can easily share an eight foot table and a hot-melt glue gun - assuming the students will be mounting the knots on a board as they tie them. If you are organized and have the space, you can store their knot boards from year to year and let them add to it each year. By the time they are in the Ranger class, they will appreciate not having to tie 25 knots all at once.
A good knot board can be made from a length of lumber - 24"x12"x3/4" makes a good sized board if you are using quarter-inch diameter rope. A stick can be fastened along the edge of the board to make a convenient place to tie the hitches.
For a professional-looking knot board, prepare labels for the knots using a label maker. Again, this is something that should be done prior to the meeting, as making labels and distributing them is not an effective use of instruction time. You should also make labels with each student's name (or have students label their boards neatly) so that they will be able to find their knot boards in the future and to prevent disputes over knot board ownership. You might also consider labeling the knot boards before they are given to the students (and before the knots are tied), as this makes it easy to figure out which knots the student still needs to learn.
1
It's a good idea to begin this honor with the definitions so your Pathfinders have a working vocabulary of the various terms involved. Telling them to "make a bight" or "take the standing part" makes little sense until these terms are understood.
1a
The term bight refers to any curved section, slack part, or loop between the two ends of a rope,
1b
The free end of the rope, usually shorter. This is the end of the rope in which a knot is being tied.
1c
The part of the rope between the Running end and the Standing end (the end that doesn't move, think of it as if you are standing on that end.)
1d
A loop formed by passing the running end of a line under the standing part.
1e
A loop formed by passing the running end of a line over the standing part.
1f
1g
A bend is used to tie two ropes together, as in the Sheetbend. Technically, even the Reef knot is a bend.
1h
A hitch is used to tie a rope to a spar, ring or post, such as the Clove hitch. Hitches can also be used to tie one rope ONTO another rope, as in the Rolling hitch.
1i
A knot formed by interweaving strands of rope rather than whole lines. More time consuming but usually stronger than simple knots.
1j
A binding knot used to prevent another line from fraying.
2
- a. Keep the rope clean.
- b. Always coil a rope before storing it.
- c. Make sure wet rope is dry before coiling it.
- d. Return rope to its proper place after using it.
3
In laid rope, three bundles of fiber or twine are twisted in the same direction, placed close to each other, and allowed to twist together. In braided rope, the fibers are woven together, often around some core material.
Uses of Laid Rope
- Repels water.
- Able to withstand immense strain.
- Can be spliced with standard techniques.
Uses of Braided Rope
- Works well with pulleys and rigging.
- Spinning (lariats and lassos).
- Decorative knots.
4
4a
Manila is a type of fiber obtained from the leaves of the abacá (Musa textilis), a relative of the banana. It is mostly used to make ropes and it is one of the most durable of the natural fibers, besides true hemp. Manila is a coarse, brown fiber, about the same color and feel as a coconut shell.
4b
Sisal is valued for cordage use because of its strength, durability, ability to stretch, affinity for certain dyestuffs, and resistance to deterioration in saltwater. Sisal ropes and twines are widely employed for marine, agricultural (bailing twine), and general industrial use. Sisal fibers are smooth, straight and yellow and can be long or short.
4c
Nylon rope is often white, but any color is possible. It has a smooth, silky feeling to it, and it coils easily. Nylon rope does not float in water. It is a synthetic-fiber rope.
4d
Polypropylene rope is most often yellow, though any color is possible. It is often used in marine applications because it floats in water. The rope is sometimes difficult to tie as it is somewhat stiff and brittle. It is a synthetic-fiber rope.
The easiest way to make an initial identification of a rope is to visit a hardware store where rope is sold. The packaging will tell you what the rope is made of. If you want to be sure, buy some of each type (with the labeling) or examine it closely in the store.
5
Advantages
- Improved abrasion-resistance
- Better UV-resistance
- Lighter
- Length does not vary as much when wet
- Rot-resistant
Disadvantages
- Some synthetics do not hold knots well
- More slippery
- Melts when heated
- Stretches more than natural ropes.
6
6a
A splice (short splice or long splice) is used to join the ends of two ropes and results in the spliced part being about twice as thick as the non spliced part. The short splice retains more of the rope strength than any knots that join rope ends. It is tied using the same techniques as the eye splice (see below).
6b
| Eye splice |
|---|
|
Use: The eye splice is the best method of creating a permanent loop in the end of multi stranded rope by means of rope splicing. The ends of the rope are tucked (plaited) back into the standing end to form the loop. Originally this splice was described with each end being tucked only about three times. When the splice was made in tarred hemp or cotton this was reasonably safe. With modern synthetic ropes, five complete tucks is a minimum and additional tucks are recommended for critical loads.
How to tie:
|
6c
A back splice (also called an end splice) is a splice where the strands of the end of the rope are spliced directly back into the end without forming a loop. It is used to finish off the end of the rope to keep it from fraying. The end of the rope with the splice is about twice the thickness of the rest of the rope. Begin by unraveling the strands, and tie a crown knot. Then begin splicing the rope onto itself as with the short splice.
6d
| Double crown knot |
|---|
|
Use: A double crown knot is a decorative knot tied on the end of a laid rope to prevent it from unraveling.
How to tie:
|
| Common whipping |
|---|
|
Use: The common whipping is the simplest type of whipping knot, a series of knots intended to stop a rope from unraveling. As it can slip off of the rope easily, the common whipping should not be used for rope ends that will be handled. This whipping knot is also called 'wolf' whipping in some parts of the world.
The benefit of a common whipping is that no tools are necessary and the rope does not need to be unlayered. The problem is that it will slide off the end of the rope with little provocation. Other whippings avoid this by interweaving the whipping with the strands of the rope and creating friction with the strands to avoid slipping. Normally a natural fiber rope is whipped with twine. The size of the rope dictates the size of the twine. Any twine can be used, but tarred two strand hemp (marline) is preferred. Artificial-fiber ropes should have their ends fused by heat rather than whipped to prevent unraveling.How to tie:
|
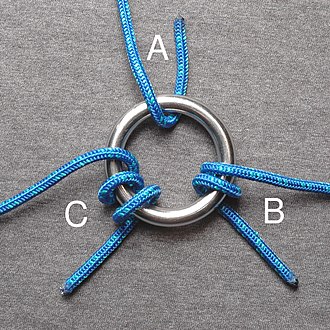
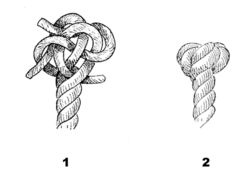
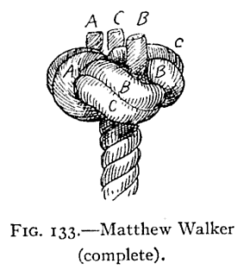
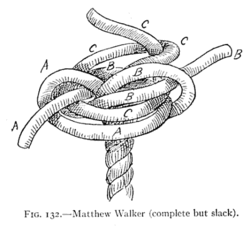
| Matthew Walker knot |
|---|
|
Use: A Matthew Walker knot is a decorative knot that is used to keep the end of a rope from fraying. It is tied by unraveling the strands of a twisted rope, knotting the strands together, then laying up the strands together again. It may also be tied using several separate cords, in which case it keeps the cords together in a bundle.
How to tie:
|
7
Making rope requires some simple apparatus which you can make yourself easily enough. The first apparatus (we'll call it the twister) is used for twisting three strands of twine (or smaller rope). When making the twister, clamp the two boards that form the handles together tightly and drill three holes through both at the same time. This will ensure that they line up. The hook/crank portion of the twister can be made from coat hanger wire. First make the two 90° bends in the center, then pass them through the holes in the handles. Finally, form the hooks on one end and the other 90° bend on the other. (This final bend prevents the crank from slipping out of the holes in the handle).
As the strands are twisted, they will tend to grab one another and twist together. To make rope, this tendency has to be controlled. This is done with a second apparatus (we'll call it the separator). It consists of a board with three holes drilled in it, forming the points of an equilateral triangle. These points should be at least six inches away from one another, and should be large enough to pass the strands of twine through.
To make rope, cut three pieces of twine about 33% longer than the desired rope. Pass each strand through a hole in the separator, then tie a non-slip loop in the end of each (a figure-eight on a bight works well for this). We will call this end of the strands the free end. Slip these loops over a hook of some sort, and pull the strands straight. Bunch the ends opposite the loops together, and tie them off, again in a loop (and again, a figure-eight on a bight works well for this). We will call this end the bound end. Make sure that the three strands are the same length from one loop to the other. Hand the bound end to a helper, then attach the loops on the free end to the hooks on the twister. Pull the twister away from the bound end (still affixed firmly to another hook) until the strands are straight and tight. Then slide the separator towards the common end. Start cranking the twister so that the hooks rotate. As you crank, your helper will allow the three strands on his side of the separator to twist together. As they do this, the helper will slide the separator towards you, going only as fast as the strands bind to one another. Be careful to keep the strands tight as you do this so that they do not bind to one another on your end of the separator. Continue twisting until the separator reaches the twister. Then tie a knot in the free end of the rope, unhook it from the twister, and slide the separator off. Tie a stopper knot, or bind the end with tape. Then cut off the few inches of untwisted strand that remain (or make a back splice). Finish the opposite end in the same manner. Voilá! You now have a rope!
Guide to making rope from natural materials and no tools. Another technique.
8
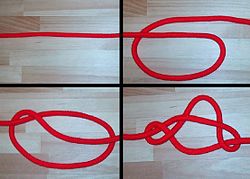
8a
| Anchor bend |
|---|
|
Use: The Anchor Bend is a knot used for attaching a rope to a ring or similar termination. The round turn and tight application help keep the rope from chafing.
How to tie:
|
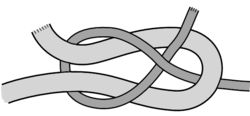
8b
| Bowline |
|---|
|
Use: This knot doesn't jam or slip when tied properly. It can be tied around a person's waist and used to lift him, because the loop will not tighten under load. In sailing, the bowline is used to tie a halyard to a sail head.
How to tie:
|
8c
| Bowline on a bight |
|---|
|
Use: This makes a secure loop in the middle of a rope which does not slip.
How to tie:
|
8d
| Alpine butterfly |
|---|
|
Use: The Butterfly Loop has a high breaking strength and is regarded by mountaineers as one of the strongest knots to attach climbers to the middle of a rope, such that they have room to move around even when the main rope goes tight, and they can be supported in either direction from the main rope. The loop is typically attached to a climbing harness by carabiner.
It can also be used to isolate a worn section of rope, where the knot is tied such that the worn section is used for the center of the loop.
|
8e
| Carrick bend |
|---|
|
Use: The Carrick bend is used for joining two lines. It is particularly appropriate for very heavy rope or cable that is too large and stiff to easily be formed into other common bends. It will not jam even after carrying a significant load or being soaked with water. The Carrick bend's aesthetically pleasing interwoven and symmetrical shape has also made it popular for decorative purposes.
In the interest of making the Carrick bend easier to untie, especially when tied in extremely large rope, the ends may be seized to prevent the knot from collapsing when load is applied. This practice also keeps the knot's profile flatter and can ease its passage over capstans or winches. The ends are traditionally seized to their standing part using a Round seizing. For expediency, a series of double constrictor knots, drawn very tight, may also be used. When seizing the Carrick bend, both ends must be secured to their standing parts or the bend will slip.
WARNING: The Carrick bend is generally tied in a flat interwoven form shown above. Without additional measures it will capsize (collapse) under load into a secure and stable, although bulky, form. If the knot is allowed to capsize naturally under tension, considerable slippage of line through the knot can occur before tightening. The knot should be upset carefully into the capsized form and worked up tight before actual use.
|
8f
| Cat's paw |
|---|
|
Use: The Cat's paw is used for connecting a rope to an object.
How to tie:
Form a bight in the middle of the line, and pull it back over itself like a girth hitch. This forms two loops, turned in opposite directions. Give each loop one more full turn in the direction that will tend to tighten it (the wrong direction will undo the loop completely). Pass both loops over the hook, rail or post and pull tight, taking care to push the bight up snugly against the turns.
If working end of the line has an eye in it, and the standing end is accessible, the knot can be tied to a closed ring, another eye, or a rail with inaccessible ends, as follows. Pass the eye around the ring or rail, then pass the standing end through its own eye (this effectively forms a girth hitch). Then pass the standing end through the eye again, and pull up tight, taking care to push the bight up snugly against the turns. When using the cat's paw to join two eyes, this process may be repeated several times to give several turns - as many as five in a fine fishing monofilament. Then when tightened, instead of pulling the bight up against the turns, both eyes are pulled equally, to make neat coils of turns in both eyes, meeting halfway between them. |
8g
| Clove hitch |
|---|
|
Use: This knot is the "general utility" hitch for when you need a quick, simple method of fastening a rope around a post, spar or stake (like tying wicks to sticks in Candle Making) or another rope (as in Macramé)
How to tie:
|
8h
| Constrictor Knot |
|---|
|
Use: The Constrictor knot is one of the most effective binding knots. Simple and secure, it is a harsh knot which can be difficult or impossible to untie once tightened. It is made similarly to a clove hitch but with one end passed under the other, forming an overhand knot under a riding turn. Because this knot will not slip when tied around a stick, it is an excellent knot for making a rope ladder.
How to tie:
WARNING: The Constrictor knot's severe bite, which makes it so effective, can damage or disfigure items it is tied around.
|
8i
| Crown Knot |
|---|
|
Use: Used a component in a back splice and in the double crown knot. Can be used to temporarily prevent the ends of a laid rope from unraveling.
How to tie:
|
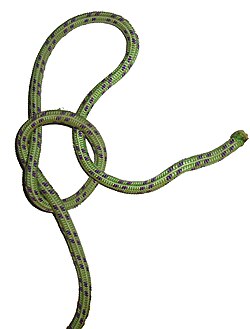
8j
| Double bowline |
|---|
|
How to tie:
|
8k
| Double sheet bend |
|---|
|
Use: The double sheet bend or double becket bend is a strong knot used to tie two ropes (usually of different thicknesses or rigidity) together. It is a doubled version of the sheet bend.
How to tie:
WARNING: As with the standard sheet bend, the two free ends should end up on the same side of the knot. If they do not, a left-handed double sheet bend results, which is much weaker.
|
8l
| Figure Eight |
|---|
|
Use: This knot is ideal for keeping the end of a rope from running out of tackle or pulley.
How to tie:
|
8m
| Fisherman's knot |
|---|
|
Use: The Fisherman's knot is a specialized bend. It consists of two overhand knots wrapped around each other. It works well for joining thin, stiff, or slippery lines.
It requires little dexterity to tie, so is often used in stubborn materials. When tightened, it becomes fairly compact, and the free ends can be cropped very close to the knot. These qualities make it very useful for fishing line--it is less likely to jam a fishing rod than many other bends, and is easier to tie with cold, wet hands.
How to tie:
|
8n
| Fisherman's loop |
|---|
|
Use: The fisherman's loop makes a non-slip loop at the end of a rope.
How to tie:
|
8o
| Halter hitch, Hitching tie |
|---|
|
Use: The halter hitch, sometimes called a hitching tie is used to tie the lead rope, which is attached to a horse's halter (or to a boat), to a post or hitching rail. The benefit of the halter hitch is that it can be released by pulling on one end of the rope. Even if there is tension on the horse-side of the rope it can still be release with ease.
How to tie:
|
8p
| Hunter's bend |
|---|
|
Use: The Hunter's bend (aka Rigger's bend) is used to join two lines. It consists of interlocking overhand knots, and can jam under moderate strain.
Hunter's bend is one of the most recent knots to be discovered. It appeared on the front page of The Times in 1978 and was credited to Dr. Edward Hunter. Dr. Hunter used it for years to tie broken shoelaces before discovering its originality through a friend in the 1970s. When it appeared on the front page, it led to much publicity for the knot and also to the foundation of the International Guild of Knot Tyers. However, the knot was presented in Knots for Mountaineering by Phil Smith ca. 1956.
|
8q
| Lariat |
|---|
|
Use: A lariat knot is the loop knot commonly used in a lasso. Its round shape, especially when tied in stiff rope, helps it slide freely along the rope it is tied around.
How to tie:
|
8r
| Lark's head |
|---|
|
Use: The lark's head is a knot (specifically, a hitch). Also called a cow hitch, it comprises two half-hitches tied in opposing directions. The cow hitch is often used to connect loop-ended lanyards to handheld electronic equipment, since it can be tied without access to the ends of the fastening loop.
How to tie:
|
8s
| Man harness knot |
|---|
|
Use: The Man harness is a knot with a loop on the bight for non-critical purposes. This knot is used when multiple people are to pull a load. Typically one end of the rope is tied to a load, and one man harness knot per puller will be tied along its length. Each loop is then pulled by a different person.
How to tie:
WARNING: The Man harness knot must have the loop loaded or it will slip and contract easily.
|
8t
| Miller's knot |
|---|
|
Use: A Miller's knot (also Sack knot or Bag knot) is a binding knot used to secure the opening of a sack or bag. Historically, large sacks often contained grains; thus the association of these knots with the miller's trade. Several knots are known interchangably by these three names. Several variations are shown here.
|
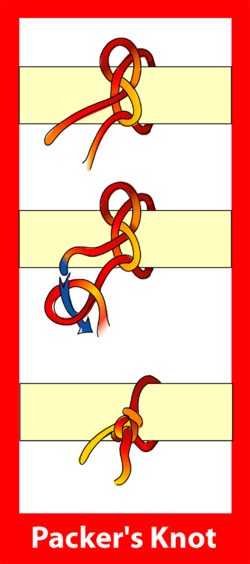
8u
| Packer's knot |
|---|
|
Use: The Packer's Knot is a binding knot usually used in smaller line.
This knot is sometimes used in baling and in parcel tying.
How to tie:
|
8v
| Pipe hitch |
|---|
|
Use: The pipe hitch is used for hoisting tubular objects (such as pipes).
How to tie:
|
8w
8x
| Sheepshank |
|---|
|
Use: The sheepshank knot is used to shorten a length of rope. It comes undone easily unless it is under tension.
WARNING: Keep this knot under tension or it will come untied.
|
8y
| Sheetbend |
|---|
|
Use: The sheet bend knot is excellent for joining two ropes together, especially if the two ropes are not the same size. When tied properly, it will not come undone, and it is easy to untie. It is very similar to the bowline.
How to tie:
|
8z
| Slip knot |
|---|
|
Use: A slip knot is one that will tighten under load, and which can be easily untied by pulling on the running end. This knot is typically a component of more complicated knots, and is generally not used by itself.
How to tie:
WARNING: If tied as shown in the illustration, the running end (on the right) will pull through the loop if even the slightest load is applied to the standing end (on the left). If one reverses the standing end and running ends in the illustration, the knot is far more stable. As shown, the knot will hold a load on the running end, but not on the standing end.
|
8aa
| Slipped half-hitch |
|---|
|
Use: A slipped half-hitch is a knot used to attach a line to a rod or bar. It does not provide great strength compared to some other knots, but it can be tied relatively quickly and released very easily. These characteristics mean that it is used on square-rigged ships for securing the gaskets that bind stowed sails to the yards.
How to tie:
WARNING: Never use this knot in a critical situation. It comes untied at the slightest provocation.
|
8bb
| Slipped sheet bend |
|---|
|
Use: The slipped sheet bend is used in non-critical situations for temporarily joining two ropes.
How to tie:
WARNING: The slightest tug on the running end will untie this knot instantly - even if the knot is under load.
|
8cc
| Square Knot |
|---|
|
Use: Also known as a Reef knot, the Square Knot is easily learned and useful for many situations. It is most commonly used to tie two lines together at the ends. This knot is used at sea in reefing and furling sails. It is used in first aid to tie off a bandage or a sling because the knot lies flat.
How to tie:
WARNING: Do not rely on this knot to hold weight in a life or death situation. It has been known to fail.
|
8dd
| Stevedore knot |
|---|
|
Use: The Stevedore knot is a stopper knot, often tied near the end of a rope. It is more bulky and less prone to jamming than the closely related figure-eight knot. This knot is excellent for anchoring a tarp. Pass the end of the rope through a tarp's grommet, tie a stevedore, and anchor the other end with a taut-line hitch. Its added bulk prevents it from pulling through the grommet.
How to tie:
|
8ee
| Strangle knot |
|---|
|
Use: The Strangle knot is a simple binding knot. Similar to the constrictor knot, it also features an overhand knot under a riding turn. The difference is that the ends emerge at the outside edges, rather than between the turns as for a constrictor. This knot is actually a rearranged double overhand knot and makes up each half of the double fisherman's knot.
When tightened, it is very slip-resistant. It is ideal for constructing a pilot ladder (like a rope ladder, but with wooden rungs).
|
8ff
| Surgeon's knot |
|---|
|
Use: The surgeon's knot is similar to a square knot, except that the first stage is doubled. This helps the knot stay tight while it is being tied.
|
8gg
| Taut-line hitch |
|---|
|
Use: The Taut-Line Hitch is an adjustable loop knot for use on lines under tension. It is useful when the length of a line will need to be periodically adjusted in order to maintain tension. It is made by tying a Rolling hitch around the standing part after passing around an anchor object. Tension is maintained by sliding the hitch to adjust size of the loop, thus changing the effective length of the standing part without retying the knot. When under tension, however, the knot will grip the cord and will be difficult to cause to slip.
It is typically used for securing tent lines in outdoor activities involving camping, by arborists when climbing trees, for creating adjustable moorings in tidal areas, and to secure loads on vehicles. A versatile knot, the Taut-line hitch was even used by astronauts during STS-82, the second Space Shuttle mission to repair the Hubble Space Telescope. How to tie:
|
8hh
| Timber hitch |
|---|
|
Use: The timber hitch is a knot used to attach a single length of rope to a piece of wood. This knot is easily undone after use.
How to tie:
|
8ii
| Two half hitches |
|---|
|
Use: This reliable knot is quickly tied and is the hitch most often used in mooring.
How to tie:
|
9
References
- List of Knots on Wikipedia
- "Why Knot? an introduction to knots, splices & rope" DVD and rope available through AdventSource.org. Every requirement is completely covered by this resource.
- http://www.animatedknots.com/ is a very good free resource. You can download the knots to your computer as well.
Content on this wiki is generated by people like you, and no one has created a lesson plan for this honor yet. You could do that and make the world a better place.
See AY Honors/Model Lesson Plan if you need ideas for creating one.