AY Honors/Digestion/Answer Key
Digestion
1. Have the Nutrition Honor.
The answers for the Nutrition honor can be found in the Household Arts chapter of this book.
2. Keep a record of what and how much food you eat for two weeks. Compare your diet to that of the food pyramid.
If you have access to the Internet, you can visit the USDA's MyPyramidTracker.gov web site, the official home of the Food Pyramid. Once you register, you can enter all the foods you eat in a day, and it will analyze your nutrient intake (among other things) based on this information. MyPyramidTracker can retain the information you enter for up to a year, so tracking it for a week will be easy.
If your Pathfinders do not have access to the Internet, have them record their diets on paper. You can then use the website to extract the necessary data by entering each food individually, or you can find a cookbook that has nutrient values of various foods in an appendix. Another option would be to meet in a place that has public Internet access, such as a library or Internet cafe. Then your Pathfinders can enter the data they have collected for a week and analyze it there.
The values in the table below are for children who are physically active for 60 minutes or more per day. Use the USDA website for adults and less active children.
| Food Group | Grains | Vegetables | Fruits | Milk | Meat & Beans |
| 10 year-old Male | 7 oz | 3 cups | 2 cups | 3 cups | 6 ounces |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 year-old Female | 6 oz | 2.5 cups | 2 cups | 3 cups | 5.5 ounces |
| 11 year-old Male | 7 oz | 3 cups | 2 cups | 3 cups | 6 ounces |
| 11 year-old Female | 6 oz | 2.5 cups | 2 cups | 3 cups | 5.5 ounces |
| 12 year-old Male | 8 oz | 3 cups | 2 cups | 3 cups | 6.5 ounces |
| 12 year-old Female | 7 oz | 3 cups | 2 cups | 3 cups | 6 ounces |
| 13 year-old Male | 9 oz | 3.5 cups | 2 cups | 3 cups | 6.5 ounces |
| 13 year-old Female | 7 oz | 3 cups | 2 cups | 3 cups | 6 ounces |
| 14 year-old Male | 10 oz | 3.5 cups | 2.5 cups | 3 cups | 7 ounces |
| 14 year-old Female | 8 oz | 3 cups | 2 cups | 3 cups | 6.5 ounces |
| 15 year-old Male | 10 oz | 5 cups | 2.5 cups | 3 cups | 7 ounces |
| 15 year-old Female | 8 oz | 3 cups | 2 cups | 3 cups | 6.5 ounces |
3. What is digestion? What is another name for the human digestive system?
Digestion is the conversion of food into substances that can be absorbed by the body. Another name for the human digestive system is the gastrointestinal tract, or just the GI tract for short.
4. Where does saliva come from? What are the three functions of saliva?
Saliva, often informally known as spit, is the moist, clear, and usually somewhat frothy substance produced in the mouth. Saliva is produced in and secreted from the salivary glands.
- Saliva moistens food so it can be swallowed easily.
- Saliva contains an enzyme that breaks some starches down into maltose and dextrin.
- Saliva protects teeth from decay by plaque. Saliva is used to neutralize acids made from sugars in the mouth, therefore helping to prevent demineralization. Remineralization is when saliva helps repair the damaged crystals of the tooth enamel.
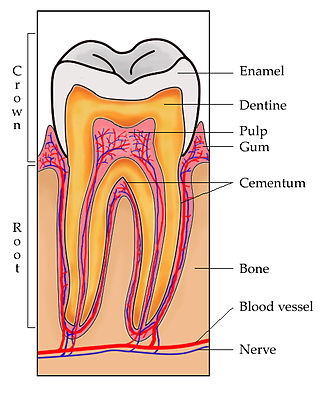
5. Be able to identify the following parts of the tooth. What role do the teeth play in digestion?
The primary function of teeth is to tear and chew food, reducing it into smaller pieces. This is the first step in the digestive process.
Enamel
Enamel is the outside covering of the exposed portion of a tooth. It is the hardest substance that is part of the human body.
Dentin
Dentin (also called Dentine) is the substance between the enamel (substance in the crown) or cementum (substance in the root) of a tooth and the pulp chamber.
Pulp
The dental pulp is the part in the center of a tooth made up of living soft tissue.
Gum
The gums consist of the tissue surrounding the roots of the teeth and covering the jawbone.
Cementum
Cementum is a specialized bony substance covering the root of a tooth.
Periodontal membrane
The periodontal membrane is the tissue between the tooth and the tooth socket. It holds the tooth in place.
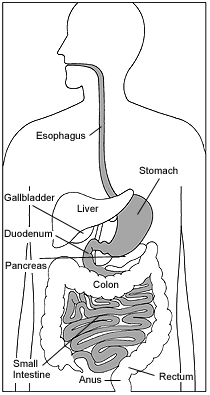
6. Be able to label a diagram or model of all the organs that help with digestion, starting from where the food goes into the mouth to where it is expelled from the anus.
Food enters the body through the mouth where it is manipulated by the tongue and chewed with the teeth. Salivary glands secrete saliva which is used to soften and lubricate the food. The tongue then pushes the food down the esophagus and it enters the stomach. The main job of the stomach is to break down large fat molecules into smaller ones, so that they can be absorbed into the intestines more easily. Food remains in the stomach for a few hours before it is passed into the upper part of the small initestine - the duodenum. The small intestine is the site where most of the nutrients from ingested food are absorbed. There are microscopic finger-like projections called villi covering the small intestinal walls which increase surface area for absorption.
The large intestine comes after the small intestine in the digestive tract. The large intestine is mainly responsible for storing waste, reclaiming water, maintaining the water balance, and absorbing some vitamins, such as vitamin K.
By the time the chyme has reached this tube, almost all nutrients and 90% of the water have been absorbed by the body. The rectum comes after the large intestine and acts as a temporary storage facility for feces. Feces are expelled from the body through the anus during the act of defecation, which is the primary function of the anus.
Related Organs
The liver secretes bile into the small intestine, employing the gallbladder as a reservoir. The pancreas secretes a fluid containing several enzymes into the small intestine. Both these secretory organs aid in digestion.
7. Know the difference between food bolus and chyme.
Bolus is any fairly large quantity of matter, usually food, making its way through the digestive tract.
Chyme is the liquid substance found in the stomach before entering the duodenum. It is made of partially digested food, water, hydrochloric acid, and various digestive enzymes.
8. Where does bile come from? Where is it stored? What does it do in the duodenum?
Bile (or gall) is a bitter, greenish-yellow fluid secreted by the liver. It is stored in the gallbladder between meals and upon eating is discharged into the duodenum where it aids the process of digestion.
9. What are villi? What makes them absorb the nutrients so quickly? At what point are all the nutrients removed from the food/chyme? Compare the amount of water absorbed by plain paper compared to a similar sized paper towel using an 1/8 cup (17.2 ml) of water.
10. What happens if too much water is present in the large intestine? What happens if not enough water is present?
11. How does fiber in your diet aid in digestion? How long should food remain in the digestive tract? What happens if food stays in the digestive system too long?
12. Demonstrate the digestion of starch into simple sugar using the iodine test.
13. What are the six basic nutrients that are essential for life and where does the bulk of their digestion/absorption take place?
14. Know the difference between monosaccharide, disaccharide, and polysaccharide. What is the most important carbohydrate?
15. What are amino acids? How many are needed to make all the proteins in the body? What is meant by essential amino acids? How many of them are essential? Where can you get all the essential amino acids?
Definition of Essential Amino acids: the nine a-amino acids required for protein synthesis that cannot be synthesized by humans and must be obtained in the diet: histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan, and valine. Note: http://www.google.com enter definition essential amino acids to get this and other related definitions! [1]
Only some foods contain all the essential amino acids. These are: milk and dairy products, eggs, fish, meat and poultry. If you don't eat animal products, the only way you can get all the essential amino acids is by combining plant foods. For example: corn plus peas or beans, rice plus beans, lentils plus bread. [2] Google results:[3]
16. What is ATP? What is it used for? What does your body make ATP from? What three sets of chemical reactions make ATP in your body? Why do we need to breathe oxygen?
17. Know the difference between water and fat soluble vitamins. What are two common vitamins that are fat soluble? What are two vitamins that are water soluble?
Fat-soluble vitamins may be stored in the body and can cause toxicity when taken in excess. Water-soluble vitamins are not stored in the body, with the exception of Vitamin B12, which is stored in the liver.
Fat-soluble vitamins include A, D, E, and K.
Water-soluble vitamins include the eight B's and C.
18. List four (4) Bible texts that refer to digestion.
Ezekiel 2:3 - Then he said to me, "Son of man, eat this scroll I am giving you and fill your stomach with it." So I ate it, and it tasted sweet as honey in my mouth.
Matthew 15:17 - "Don't you see that whatever enters the mouth goes into the stomach the then out of the body?"
1 Corinthians 6:13 - "Food for the stomach and the stomach for the food" - but God will destroy them both. The body is not meant for sexual immorality; but for the Lord and the Lord for the body.
Proverbs 18:20 - From the fruit of his mouth a man's stomach is filled; with the harvest from his lips he is satisfied.
19. List five (5) E.G. White references that promote proper digestion. Choose a variety of topics.
- Counsels on Diet and Foods, page 175, paragraph 2
- Selected Messages Book 2, page 415, paragraph 3
- Testimony Studies on Diet and Foods, page 91, paragraph 7
- Child Guidance, page 390, paragraph 3
- A Call to Medical Evangelism and Health Education, page 36, paragraph 1